
How to Use anegena: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
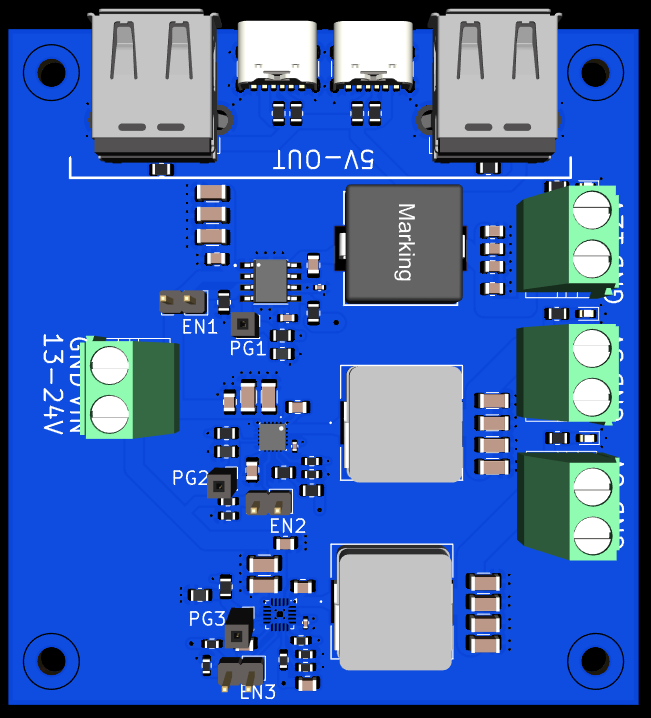
 Design with anegena in Cirkit Designer
Design with anegena in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
- The Anegena is a versatile electronic component that can function as either a signal amplifier or a specialized sensor, depending on its design and configuration. Its adaptability makes it a valuable component in a wide range of electronic circuits.
- Common applications include audio signal amplification, environmental sensing (e.g., temperature, pressure, or light), and integration into IoT devices for data acquisition and processing.
Explore Projects Built with anegena
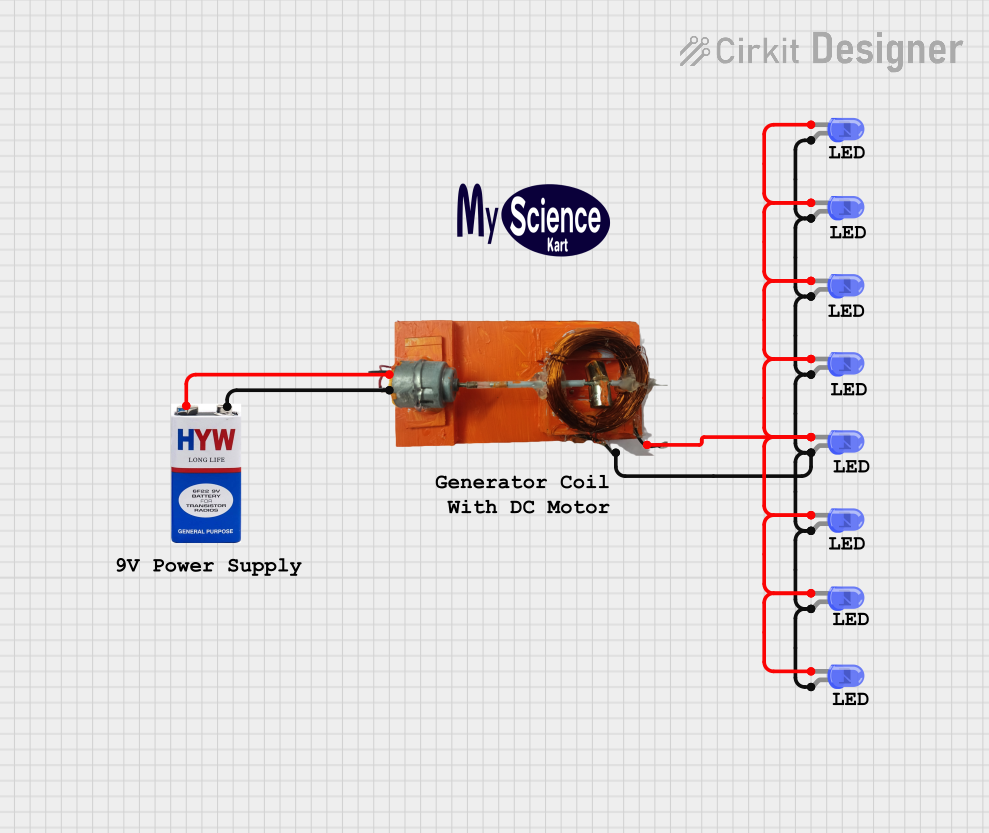
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer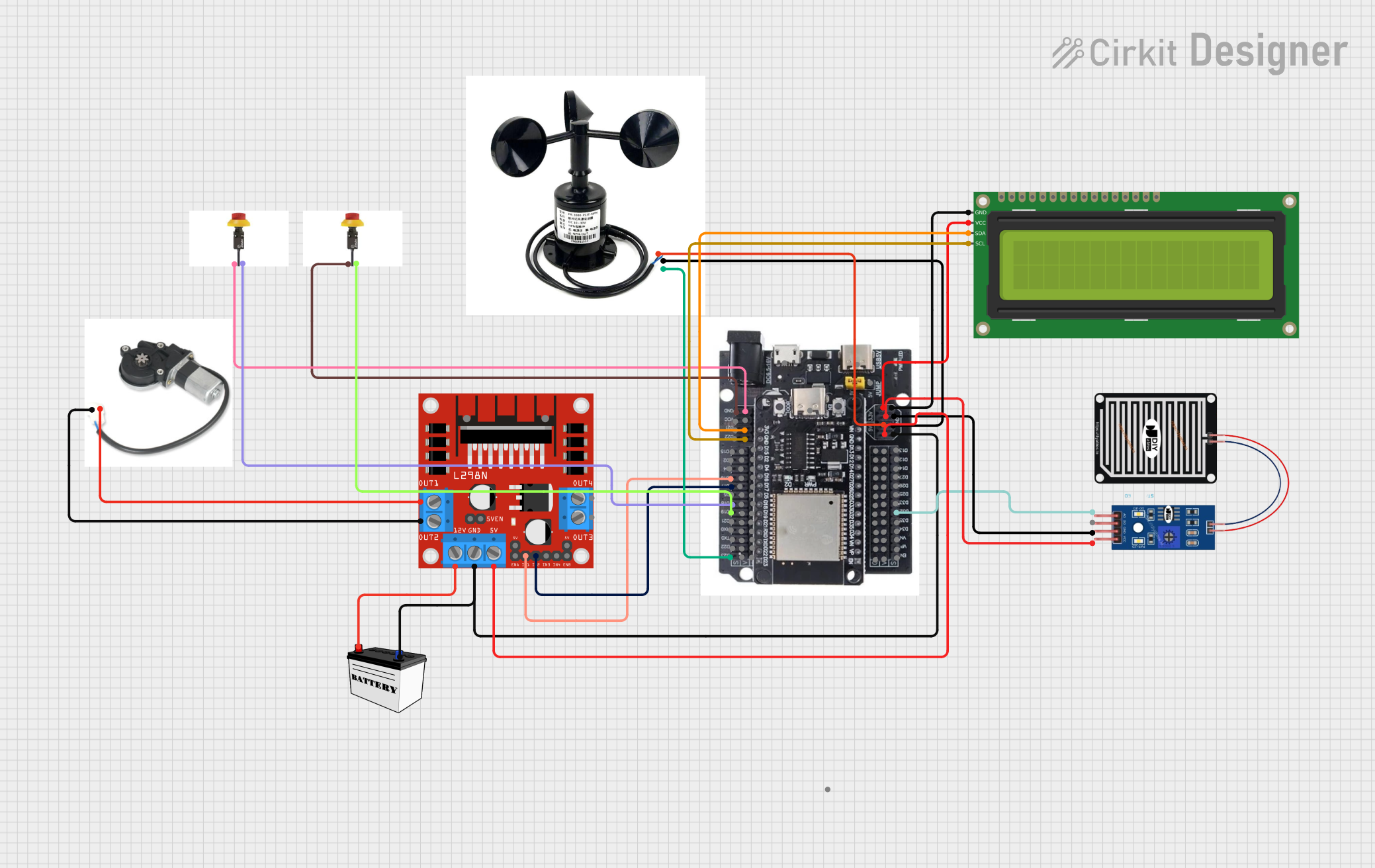
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer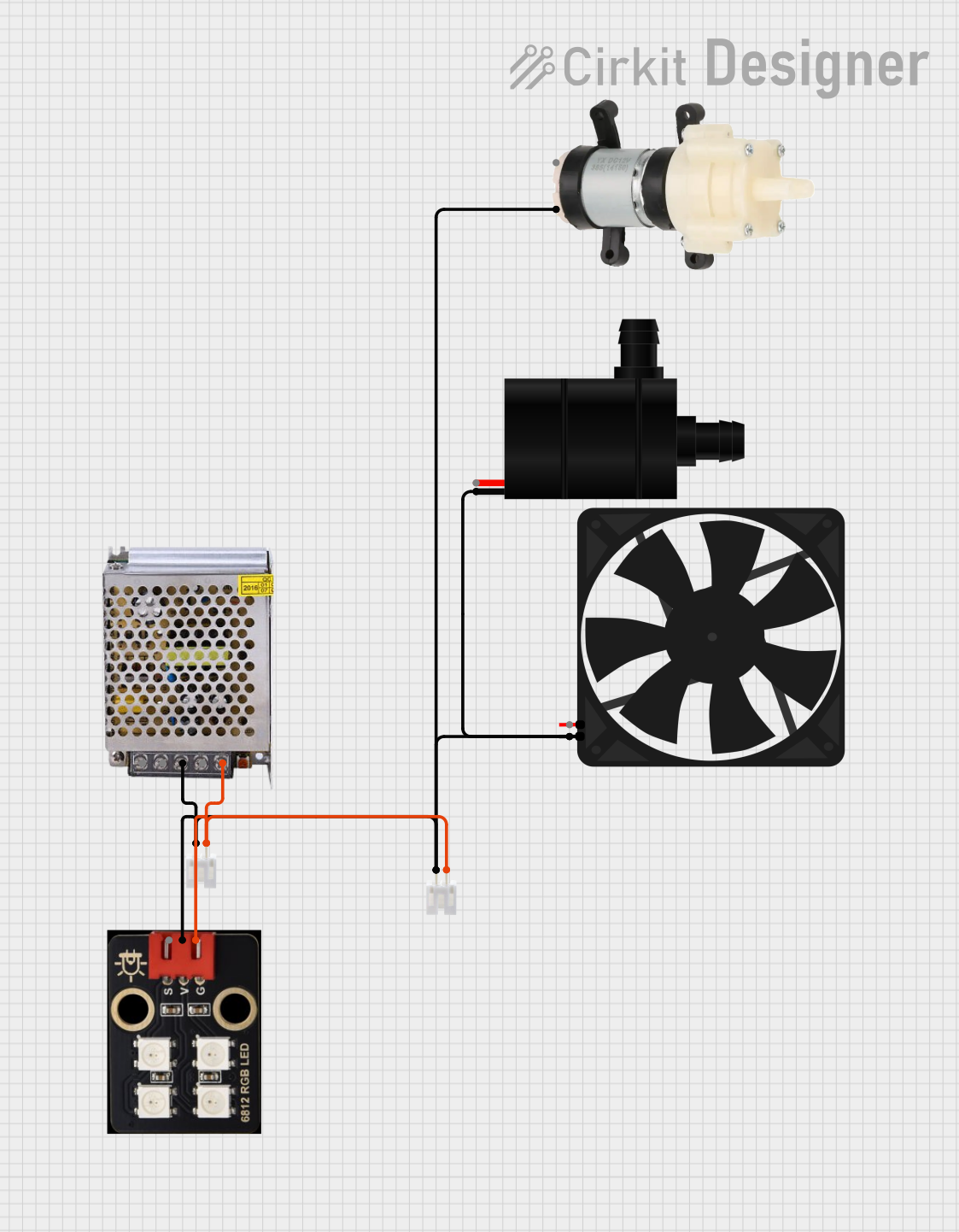
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with anegena

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
- Type: Signal amplifier or sensor (varies by model)
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V to 5V DC
- Current Consumption: 10mA (typical), 20mA (maximum)
- Output Signal: Analog or digital (depending on configuration)
- Operating Temperature Range: -40°C to 85°C
- Sensitivity: Adjustable (for sensor models)
- Dimensions: 20mm x 15mm x 5mm
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Anegena typically has a 4-pin configuration. The table below describes each pin:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply input (3.3V to 5V DC) |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | OUT | Output signal (analog or digital, depending on the model) |
| 4 | ADJ | Adjustment pin for sensitivity or gain (connect to a potentiometer or MCU) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Anegena in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a 3.3V or 5V DC power source and the GND pin to the ground of your circuit.
- Output Signal: Connect the OUT pin to the input of your microcontroller (e.g., Arduino) or another processing circuit. For analog models, ensure the microcontroller has an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) to read the signal.
- Sensitivity Adjustment: Use the ADJ pin to fine-tune the sensitivity or gain. This can be done by connecting a potentiometer or using a PWM signal from a microcontroller.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply Stability: Use a decoupling capacitor (e.g., 0.1µF) between VCC and GND to ensure stable operation.
- Signal Noise: For analog output models, minimize noise by using shielded cables or placing the Anegena away from high-frequency components.
- Calibration: If using the Anegena as a sensor, calibrate it for your specific application to ensure accurate readings.
- Arduino Integration: The Anegena can be easily interfaced with an Arduino UNO. Below is an example code snippet for reading an analog signal from the Anegena.
// Example Arduino code for reading an analog signal from the Anegena
const int anegenaPin = A0; // Connect the OUT pin of Anegena to Arduino pin A0
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
pinMode(anegenaPin, INPUT); // Set the Anegena pin as input
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(anegenaPin); // Read the analog value from Anegena
float voltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0); // Convert the value to voltage
Serial.print("Anegena Voltage: ");
Serial.println(voltage); // Print the voltage to the Serial Monitor
delay(500); // Wait for 500ms before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Signal:
- Cause: Incorrect power supply or loose connections.
- Solution: Verify that the VCC and GND pins are properly connected and the power supply is within the specified range.
Inconsistent Readings:
- Cause: Electrical noise or improper calibration.
- Solution: Add a decoupling capacitor near the Anegena and recalibrate the component.
Output Signal Too Weak or Strong:
- Cause: Sensitivity or gain not properly adjusted.
- Solution: Use the ADJ pin to fine-tune the sensitivity or gain.
Overheating:
- Cause: Exceeding the maximum voltage or current ratings.
- Solution: Ensure the power supply is within the specified range and avoid short circuits.
FAQs
Q: Can the Anegena be used with a 12V power supply?
A: No, the Anegena is designed to operate within a 3.3V to 5V range. Using a 12V supply may damage the component.Q: How do I know if my Anegena is functioning as a sensor or amplifier?
A: Check the model number or datasheet. Sensor models typically have specific sensitivity ratings, while amplifier models focus on gain.Q: Can I use the Anegena with a Raspberry Pi?
A: Yes, the Anegena can be used with a Raspberry Pi. For analog output models, you will need an external ADC since the Raspberry Pi lacks built-in analog input.Q: What is the maximum distance between the Anegena and the microcontroller?
A: For optimal performance, keep the distance under 1 meter. Use shielded cables for longer distances to reduce noise.
This concludes the documentation for the Anegena. For further assistance, refer to the manufacturer's datasheet or contact technical support.