
How to Use Dual Channel Brushed ESC 20A: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
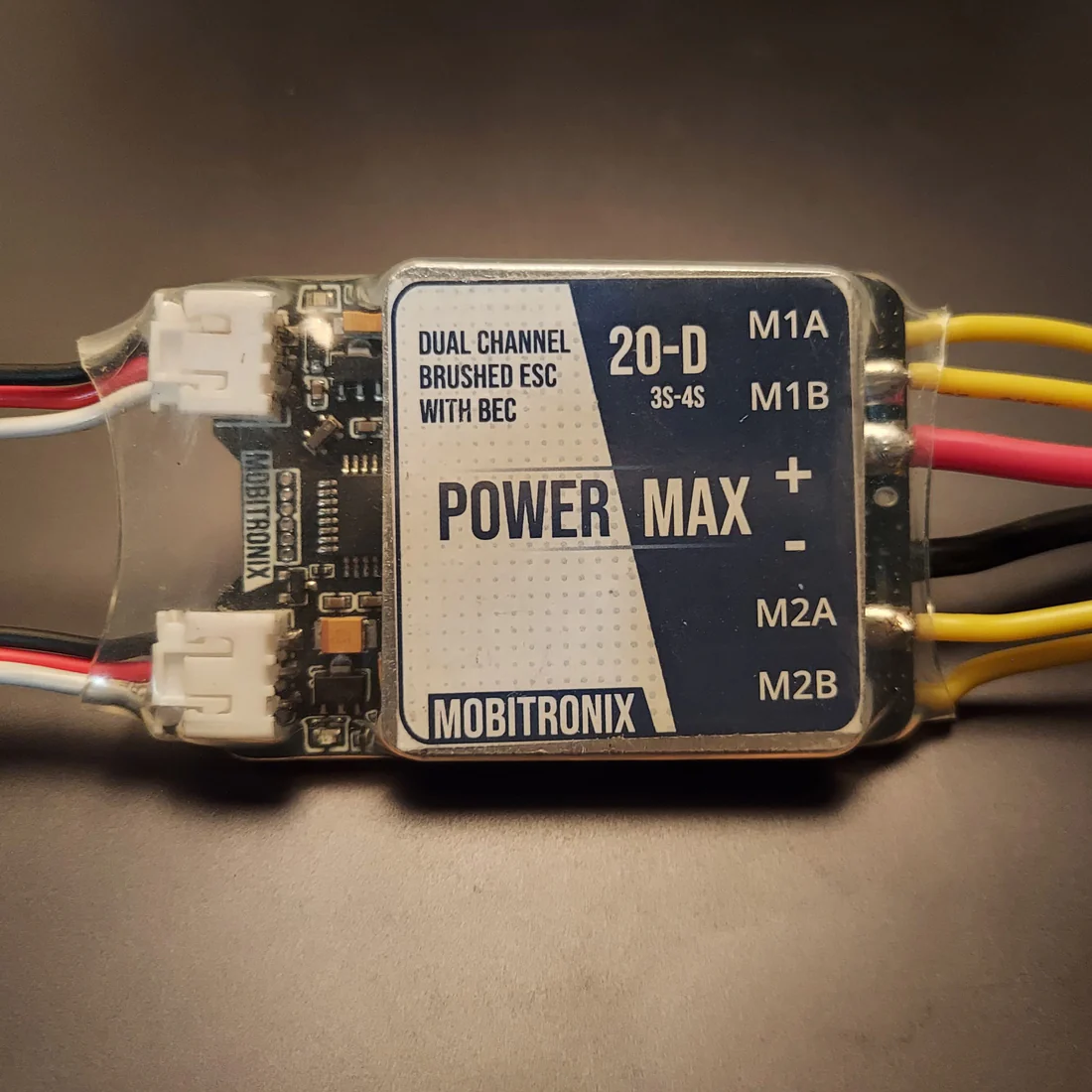
 Design with Dual Channel Brushed ESC 20A in Cirkit Designer
Design with Dual Channel Brushed ESC 20A in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Dual Channel Brushed ESC 20A (Manufacturer: Mobitronix, Part ID: PowerMax) is a high-performance electronic speed controller designed to control the speed and direction of two brushed DC motors. With a current rating of 20A per channel, this ESC is ideal for applications such as remote-controlled (RC) vehicles, drones, robotics, and other projects requiring precise motor control. Its dual-channel design allows independent control of two motors, making it a versatile choice for multi-motor systems.
Explore Projects Built with Dual Channel Brushed ESC 20A
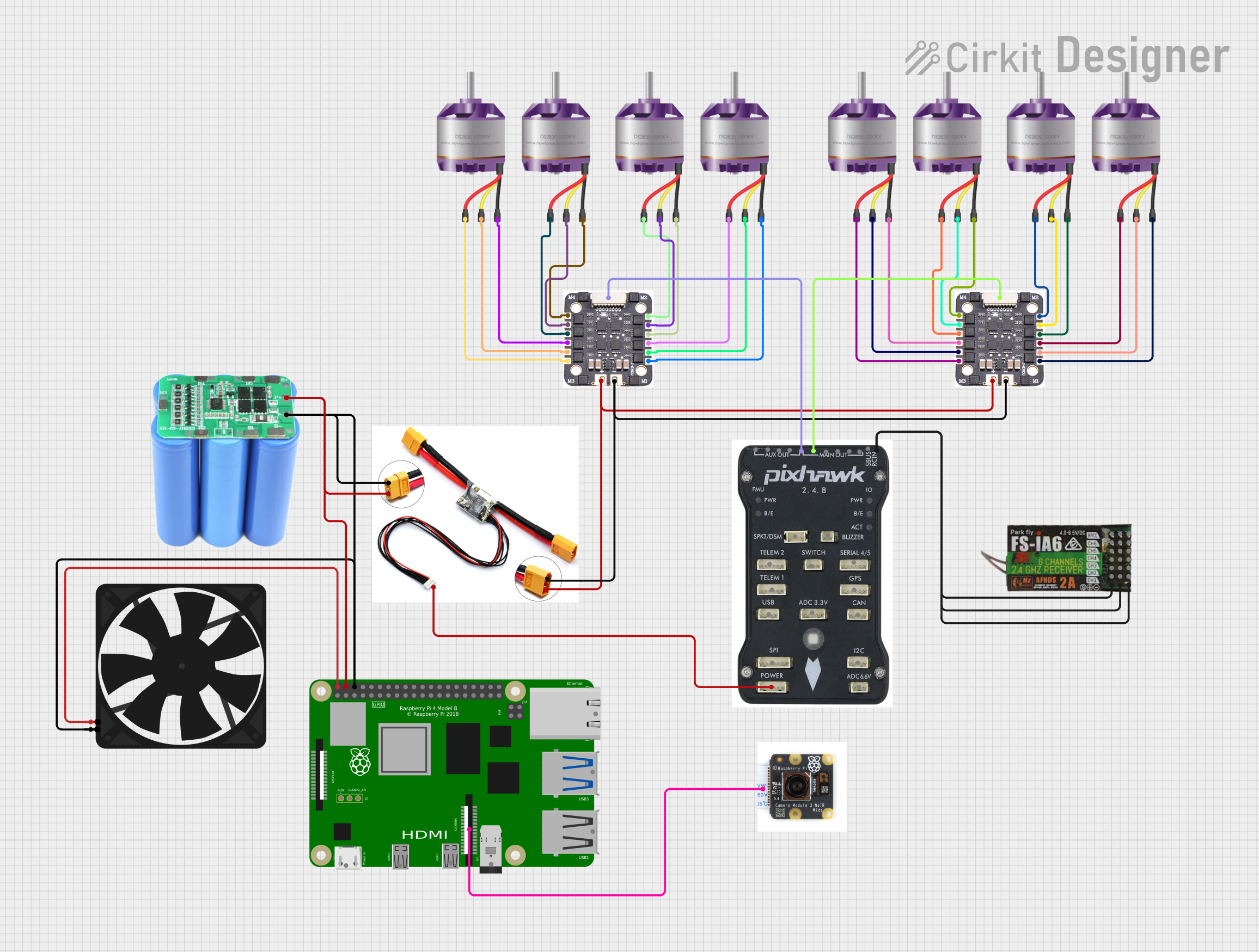
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer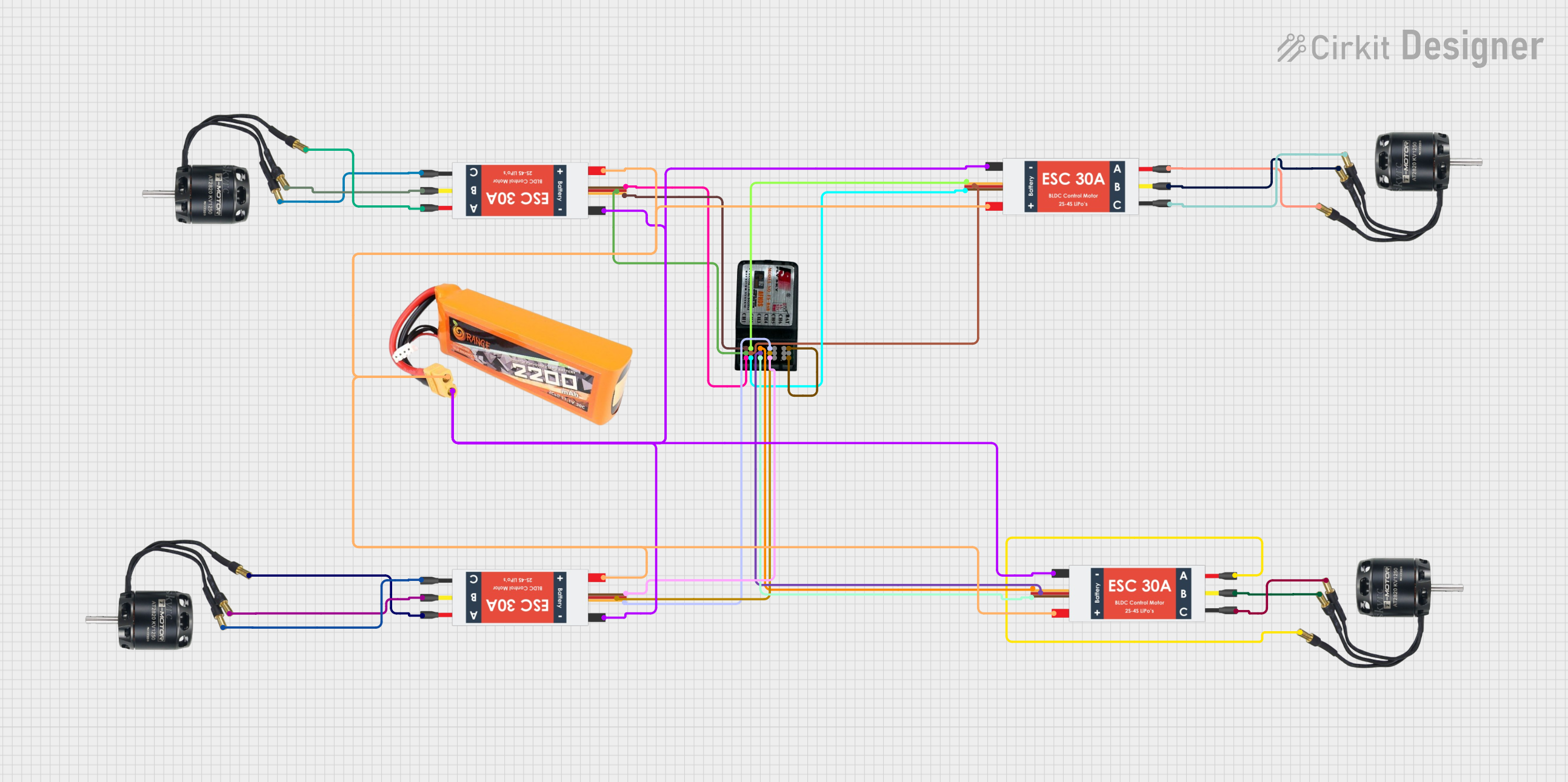
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer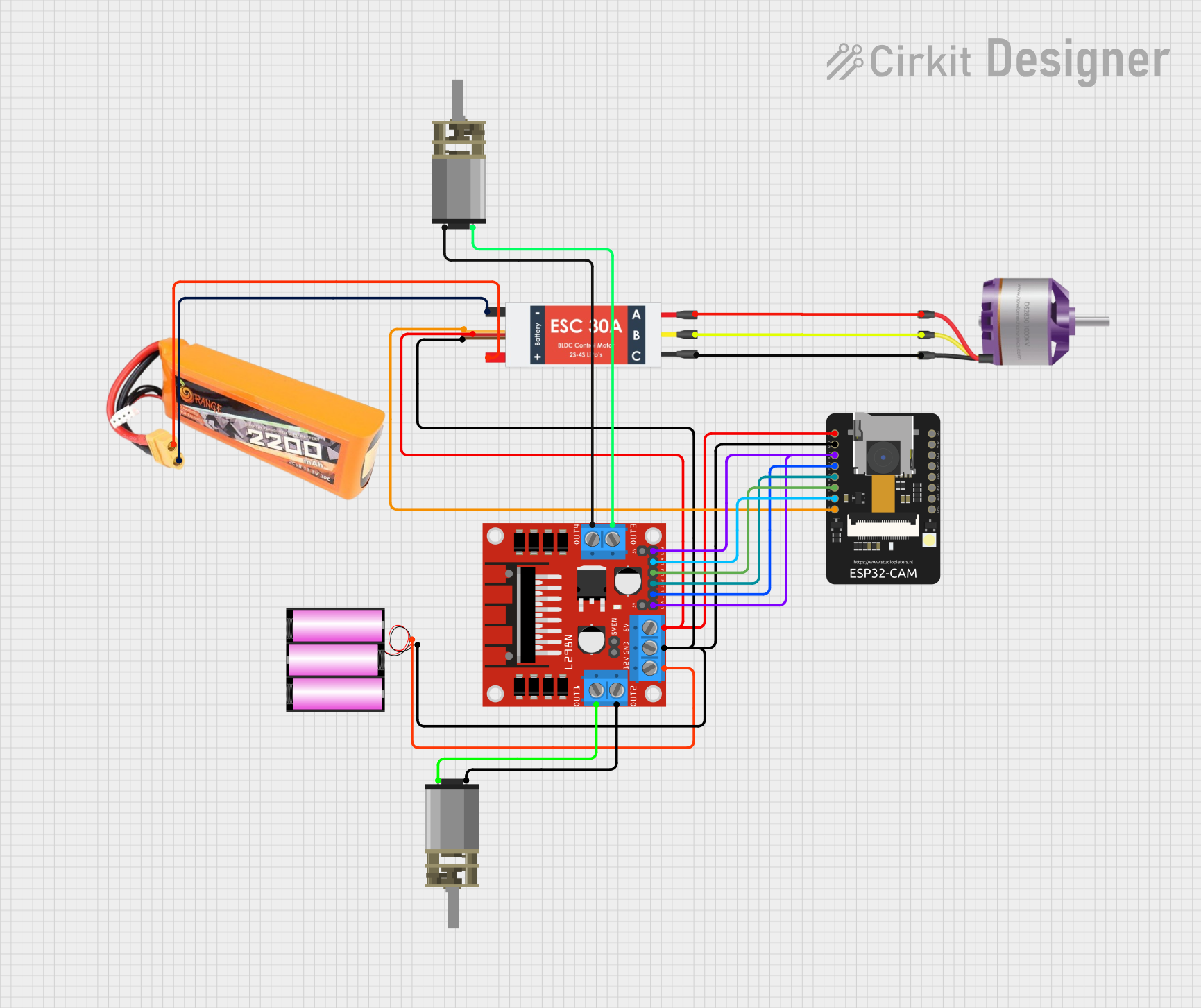
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer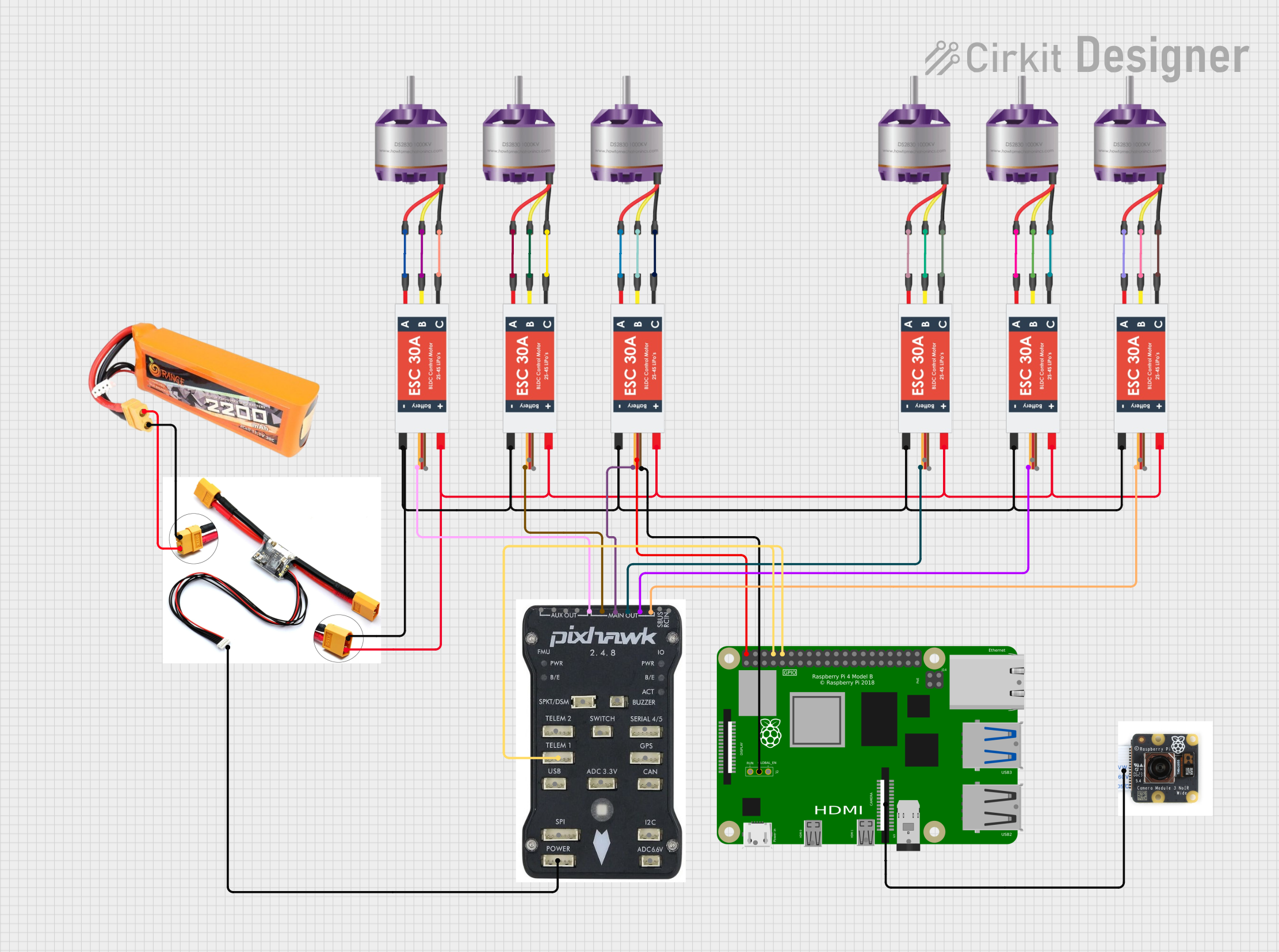
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Dual Channel Brushed ESC 20A

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- RC cars, boats, and drones
- Robotics and automation systems
- DIY motorized projects
- Educational and prototyping platforms
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the Dual Channel Brushed ESC 20A:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Mobitronix |
| Part ID | PowerMax |
| Motor Type Supported | Brushed DC Motors |
| Channels | 2 (independent control) |
| Continuous Current Rating | 20A per channel |
| Peak Current Rating | 25A per channel (for 10 seconds) |
| Input Voltage Range | 6V to 24V DC |
| PWM Input Signal Range | 1ms to 2ms (standard RC PWM signal) |
| Control Frequency | 50Hz to 500Hz |
| Operating Temperature | -10°C to 60°C |
| Dimensions | 60mm x 40mm x 15mm |
| Weight | 45g |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The ESC has the following pin configuration:
Input/Output Connections
| Pin Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VIN | Power Input | Positive input voltage (6V to 24V DC). Connect to the power source. |
| GND | Power Input | Ground connection. Connect to the negative terminal of the power source. |
| M1+ | Motor Output | Positive terminal for Motor 1. |
| M1- | Motor Output | Negative terminal for Motor 1. |
| M2+ | Motor Output | Positive terminal for Motor 2. |
| M2- | Motor Output | Negative terminal for Motor 2. |
| PWM1 | Signal Input | PWM signal input for Motor 1 control. |
| PWM2 | Signal Input | PWM signal input for Motor 2 control. |
| EN | Signal Input | Enable pin. Pull HIGH to enable the ESC, LOW to disable it. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VIN and GND pins to a DC power source within the range of 6V to 24V. Ensure the power source can supply sufficient current for the motors.
- Motor Connections: Connect the brushed DC motors to the M1+/M1- and M2+/M2- terminals. Ensure the motors are compatible with the ESC's voltage and current ratings.
- PWM Signal: Provide a PWM signal to the PWM1 and PWM2 pins to control the speed and direction of the motors. A 1ms pulse corresponds to full reverse, 1.5ms to stop, and 2ms to full forward.
- Enable Pin: Pull the EN pin HIGH to enable the ESC. Pull it LOW to disable the ESC.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Heat Dissipation: Ensure proper ventilation or use a heatsink if the ESC operates near its maximum current rating for extended periods.
- Power Supply: Use a power source with sufficient current capacity to avoid voltage drops or overheating.
- Signal Integrity: Use shielded cables for PWM signals in noisy environments to prevent interference.
- Motor Compatibility: Verify that the motors' voltage and current ratings are within the ESC's specifications.
Example: Using the ESC with an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control the Dual Channel Brushed ESC 20A using an Arduino UNO:
// Example code to control the Dual Channel Brushed ESC 20A with Arduino UNO
#include <Servo.h> // Include the Servo library to generate PWM signals
Servo motor1; // Create a Servo object for Motor 1
Servo motor2; // Create a Servo object for Motor 2
void setup() {
motor1.attach(9); // Attach Motor 1 PWM signal to pin 9
motor2.attach(10); // Attach Motor 2 PWM signal to pin 10
pinMode(8, OUTPUT); // Set pin 8 as output for the Enable pin
digitalWrite(8, HIGH); // Enable the ESC by pulling the EN pin HIGH
}
void loop() {
// Set Motor 1 to full forward
motor1.writeMicroseconds(2000); // 2ms pulse for full forward
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Set Motor 1 to stop
motor1.writeMicroseconds(1500); // 1.5ms pulse to stop
delay(2000); // Wait for 2 seconds
// Set Motor 2 to full reverse
motor2.writeMicroseconds(1000); // 1ms pulse for full reverse
delay(2000); // Run for 2 seconds
// Set Motor 2 to stop
motor2.writeMicroseconds(1500); // 1.5ms pulse to stop
delay(2000); // Wait for 2 seconds
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motors Not Spinning
- Cause: The EN pin is not pulled HIGH.
- Solution: Ensure the EN pin is connected to a HIGH signal (e.g., 5V from the Arduino).
Erratic Motor Behavior
- Cause: Noisy or unstable PWM signal.
- Solution: Use shielded cables for PWM signals and ensure the Arduino's ground is connected to the ESC's ground.
Overheating
- Cause: Operating near or above the ESC's current rating for extended periods.
- Solution: Reduce the load on the motors or improve heat dissipation with a heatsink or fan.
No Response from ESC
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient power supply.
- Solution: Double-check all connections and ensure the power supply meets the voltage and current requirements.
FAQs
Can I use this ESC with a single motor?
- Yes, you can use only one channel of the ESC if your application requires a single motor.
What happens if I exceed the 20A current rating?
- The ESC may overheat or shut down to protect itself. Prolonged overcurrent conditions can damage the ESC.
Can I use this ESC with a LiPo battery?
- Yes, as long as the battery voltage is within the 6V to 24V range.
Is this ESC compatible with other microcontrollers?
- Yes, it can be controlled by any microcontroller capable of generating a standard RC PWM signal.