
How to Use Led 5mm White: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Led 5mm White in Cirkit Designer
Design with Led 5mm White in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A 5mm white light-emitting diode (LED) is a compact and efficient electronic component that emits bright white light when an electric current flows through it. It is widely used in various applications due to its low power consumption, long lifespan, and high brightness. This LED is commonly employed in indicator lights, displays, backlighting, and decorative lighting.
Explore Projects Built with Led 5mm White

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer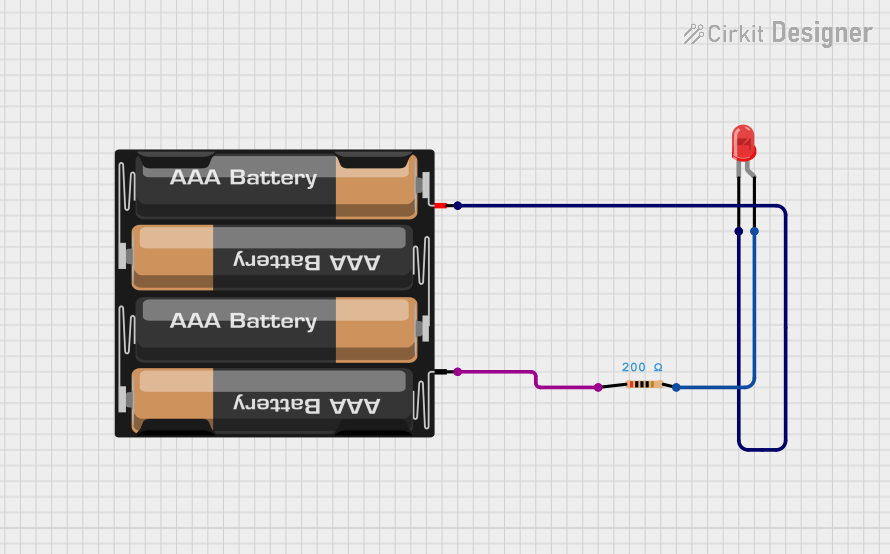
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer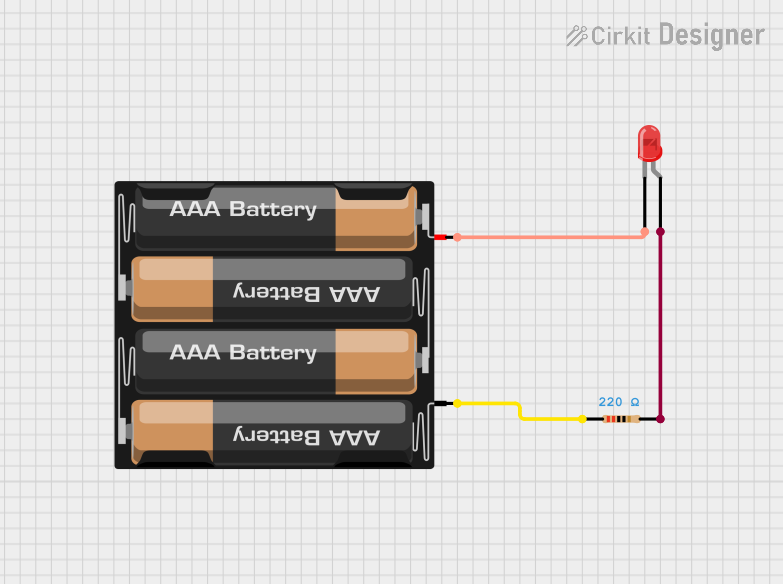
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer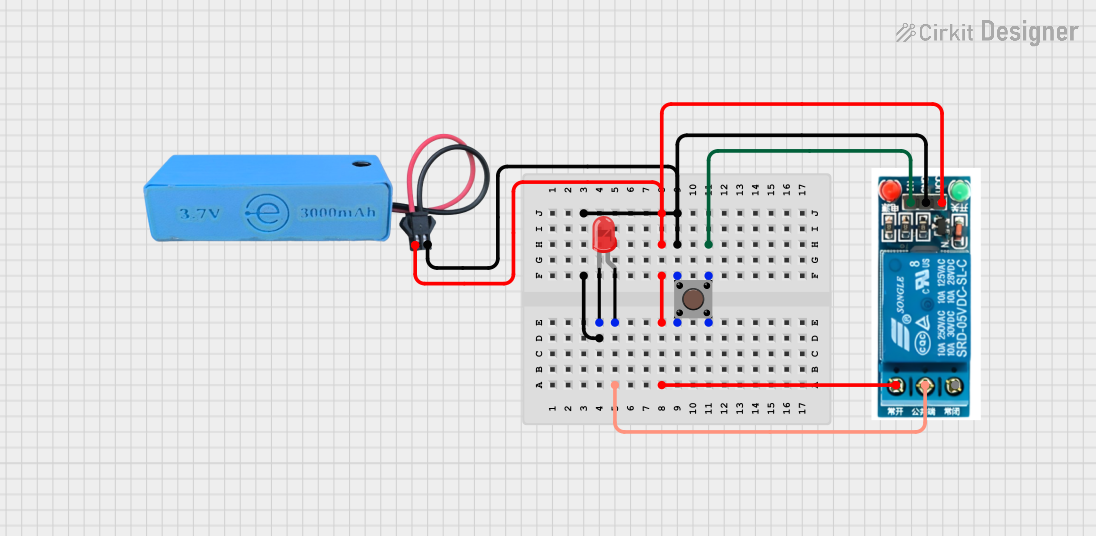
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Led 5mm White

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
- Type: 5mm White LED
- Forward Voltage (Vf): 3.0V to 3.4V
- Forward Current (If): 20mA (typical)
- Maximum Current (Imax): 30mA
- Luminous Intensity: 8,000 to 12,000 mcd (millicandela)
- Viewing Angle: 20° to 30°
- Wavelength: 450nm to 460nm (white light spectrum)
- Polarity: Anode (+) and Cathode (-)
- Operating Temperature: -40°C to +85°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Name | Description | Identification |
|---|---|---|
| Anode | Positive terminal, connects to V+ | Longer leg of the LED |
| Cathode | Negative terminal, connects to GND | Shorter leg of the LED, flat edge |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the LED in a Circuit
Determine the Resistor Value: To prevent damage to the LED, always use a current-limiting resistor in series. The resistor value can be calculated using Ohm's Law: [ R = \frac{V_{supply} - V_f}{I_f} ]
- (V_{supply}): Supply voltage
- (V_f): Forward voltage of the LED (3.0V to 3.4V)
- (I_f): Desired forward current (typically 20mA)
For example, if (V_{supply} = 5V) and (V_f = 3.2V): [ R = \frac{5V - 3.2V}{0.02A} = 90\Omega ] Use the nearest standard resistor value (e.g., 100Ω).
Connect the LED:
- Connect the anode (longer leg) to the positive terminal of the power supply through the resistor.
- Connect the cathode (shorter leg) to the ground (GND).
Power the Circuit: Apply the appropriate voltage to the circuit. The LED will emit bright white light.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Polarity: Ensure correct polarity when connecting the LED. Reversing the polarity may damage the component.
- Current Limiting: Always use a resistor to limit the current. Exceeding the maximum current rating can permanently damage the LED.
- Heat Dissipation: While LEDs generate minimal heat, ensure proper ventilation in high-power applications.
- Series and Parallel Configurations: For multiple LEDs, calculate resistor values for each configuration to ensure uniform brightness.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
The 5mm white LED can be easily interfaced with an Arduino UNO for various projects. Below is an example of how to blink the LED using Arduino:
// Define the pin connected to the LED
const int ledPin = 13; // Pin 13 is the built-in LED pin on Arduino UNO
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set the LED pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
- Note: If using an external LED, connect the anode to the Arduino pin (e.g., pin 13) through a 220Ω resistor, and connect the cathode to GND.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
LED Does Not Light Up:
Cause: Incorrect polarity.
Solution: Verify that the anode is connected to the positive terminal and the cathode to GND.
Cause: No current-limiting resistor or incorrect resistor value.
Solution: Ensure a resistor is used and calculate the correct value based on the supply voltage.
LED is Dim:
- Cause: Insufficient current.
- Solution: Check the resistor value and ensure the current is within the recommended range (20mA).
LED Burns Out Quickly:
- Cause: Excessive current.
- Solution: Use a resistor to limit the current to 20mA.
Flickering LED:
- Cause: Unstable power supply or loose connections.
- Solution: Check the power source and ensure all connections are secure.
FAQs
Q: Can I connect the LED directly to a 5V power supply?
A: No, you must use a current-limiting resistor to prevent damage to the LED.Q: What happens if I reverse the polarity?
A: The LED will not light up, and prolonged reverse connection may damage the component.Q: Can I use this LED with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, but ensure the forward voltage of the LED is within the range of the supply voltage, and use an appropriate resistor.Q: How do I connect multiple LEDs?
A: For series connections, sum the forward voltages and calculate the resistor value accordingly. For parallel connections, use individual resistors for each LED to ensure uniform brightness.