
How to Use Sigcom Pull: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Sigcom Pull in Cirkit Designer
Design with Sigcom Pull in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Sigcom Pull (SG-42SK), manufactured by SIGCOM, is a versatile electronic component designed for use in signal communication systems. It primarily functions as a pull-up or pull-down resistor, ensuring stable signal levels in digital circuits. By maintaining a defined logic state when no active signal is present, the Sigcom Pull prevents floating inputs and improves the reliability of digital systems.
Explore Projects Built with Sigcom Pull
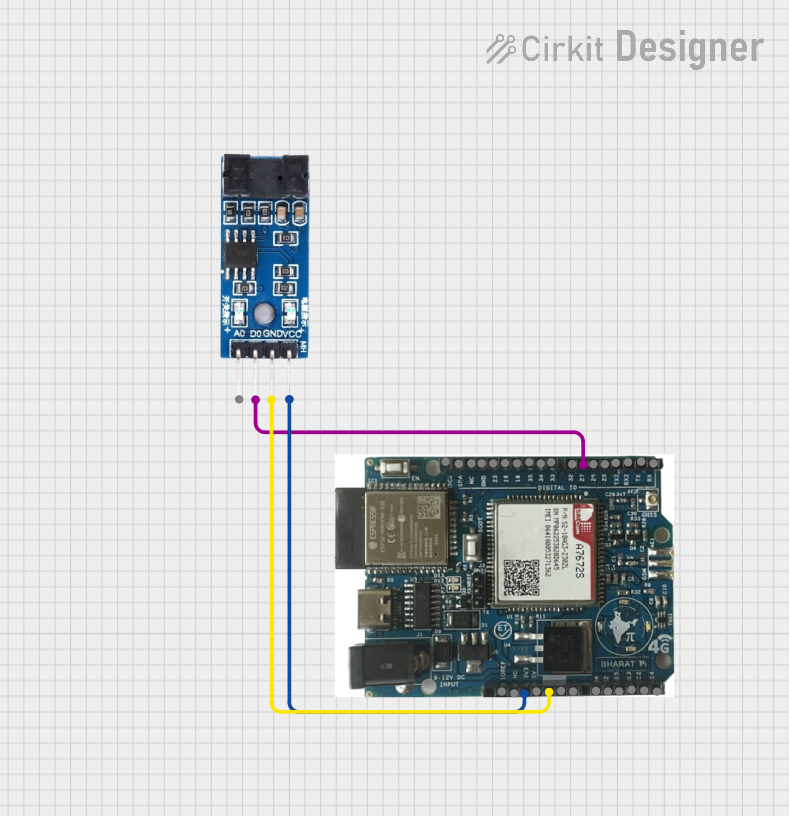
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer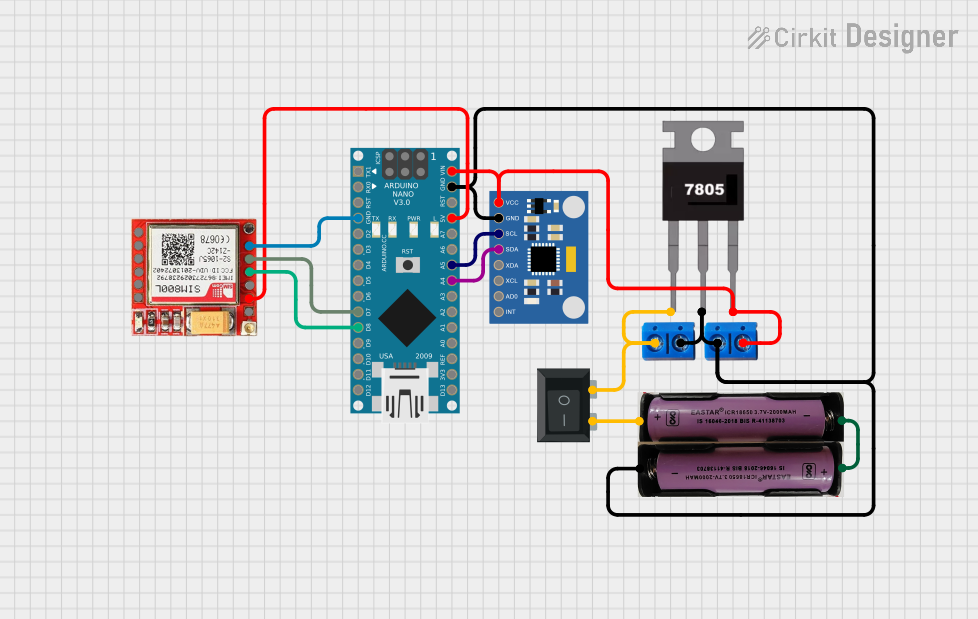
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer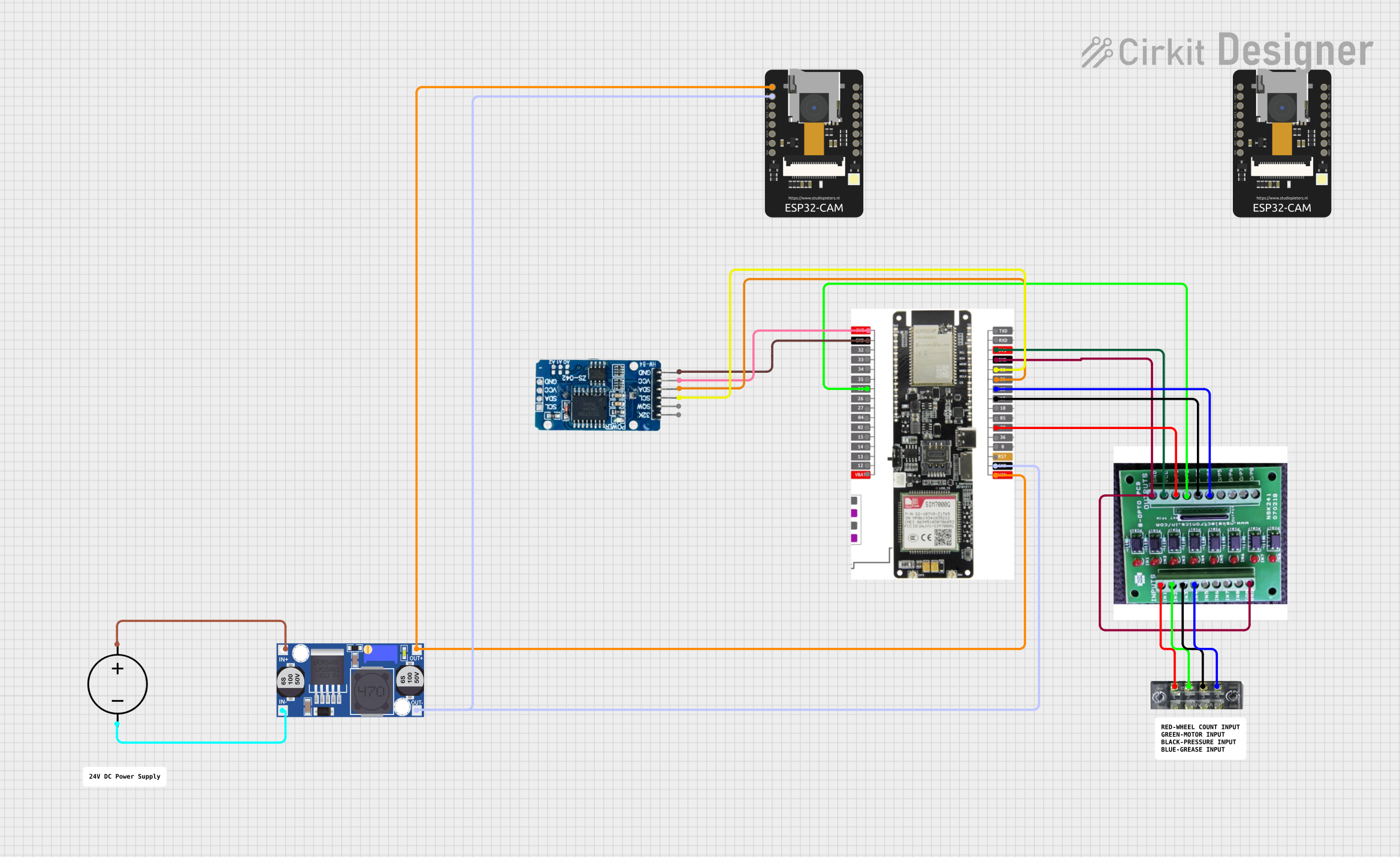
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer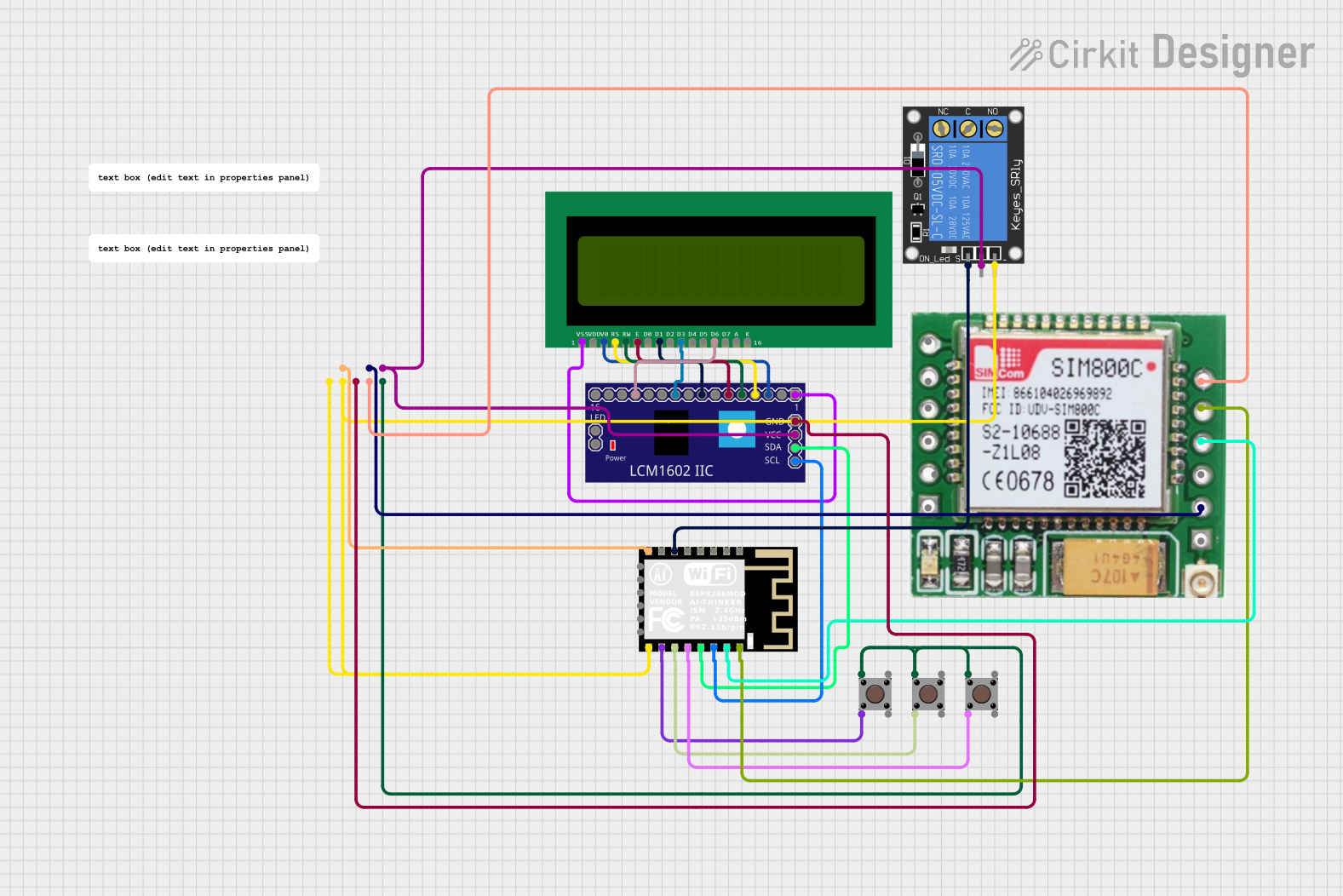
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Sigcom Pull

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Digital signal stabilization in microcontroller circuits
- Pull-up or pull-down resistor for GPIO pins
- Noise reduction in high-speed communication lines
- Ensuring proper logic levels in I2C, SPI, and UART interfaces
- Used in debounce circuits for mechanical switches
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | SIGCOM |
| Part Number | SG-42SK |
| Resistance Range | 1 kΩ to 100 kΩ |
| Tolerance | ±1% |
| Maximum Voltage Rating | 50 V |
| Maximum Power Rating | 0.25 W (1/4 W) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +125°C |
| Package Type | Through-hole or SMD |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Sigcom Pull (SG-42SK) is a two-terminal component. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Terminal 1 | Connect to the signal line or VCC/GND |
| 2 | Terminal 2 | Connect to the signal line or VCC/GND |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Determine the Required Configuration:
- For a pull-up resistor, connect one terminal of the Sigcom Pull to the signal line and the other terminal to the positive voltage supply (VCC).
- For a pull-down resistor, connect one terminal to the signal line and the other terminal to ground (GND).
Select the Appropriate Resistance Value:
- Choose a resistance value that balances power consumption and signal stability. Common values are 4.7 kΩ or 10 kΩ for digital circuits.
Connect the Component:
- Solder the Sigcom Pull to the circuit board, ensuring proper orientation and secure connections.
Test the Circuit:
- Verify that the signal line maintains the desired logic level when no active signal is present.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid Excessive Current: Ensure the resistance value is high enough to limit current flow and prevent damage to the circuit.
- Check Voltage Ratings: Do not exceed the maximum voltage rating of 50 V.
- Minimize Noise: Use decoupling capacitors in conjunction with the Sigcom Pull for high-speed circuits to reduce noise.
- Arduino Compatibility: The Sigcom Pull can be used with Arduino boards to stabilize GPIO pins. Below is an example of using the Sigcom Pull with an Arduino UNO.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
// Example: Using Sigcom Pull (SG-42SK) as a pull-up resistor with Arduino UNO
const int buttonPin = 2; // Pin connected to the button
const int ledPin = 13; // Pin connected to the onboard LED
void setup() {
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT); // Set button pin as input
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set LED pin as output
digitalWrite(buttonPin, HIGH); // Enable internal pull-up resistor
}
void loop() {
int buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin); // Read the button state
if (buttonState == LOW) {
// Button is pressed (logic LOW due to pull-up configuration)
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn on the LED
} else {
// Button is not pressed
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn off the LED
}
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Signal Line Still Floating:
- Cause: Incorrect resistance value or improper connection.
- Solution: Verify the resistance value and ensure the Sigcom Pull is securely connected to the signal line and VCC/GND.
Excessive Power Dissipation:
- Cause: Resistance value too low, causing high current flow.
- Solution: Use a higher resistance value to limit current.
Component Overheating:
- Cause: Voltage or power rating exceeded.
- Solution: Ensure the voltage across the Sigcom Pull does not exceed 50 V and the power dissipation stays below 0.25 W.
Noise in Signal Line:
- Cause: High-frequency noise or insufficient decoupling.
- Solution: Add decoupling capacitors near the signal line to filter out noise.
FAQs
Q1: Can the Sigcom Pull (SG-42SK) be used with 3.3 V systems?
A1: Yes, the Sigcom Pull is compatible with 3.3 V systems as long as the resistance value is chosen appropriately.
Q2: What is the recommended resistance value for I2C pull-up resistors?
A2: For I2C communication, 4.7 kΩ or 10 kΩ is commonly used, depending on the bus speed and capacitance.
Q3: Can I use the Sigcom Pull in high-frequency circuits?
A3: Yes, but it is recommended to use decoupling capacitors to minimize noise and ensure signal integrity.
Q4: Is the Sigcom Pull available in surface-mount packages?
A4: Yes, the SG-42SK is available in both through-hole and surface-mount (SMD) packages for different design requirements.