
How to Use SparkFun GNSS L1/L5 Breakout - NEO-F10N, SMA: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
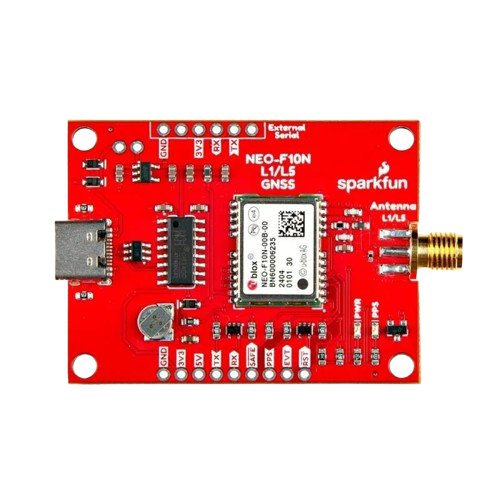
 Design with SparkFun GNSS L1/L5 Breakout - NEO-F10N, SMA in Cirkit Designer
Design with SparkFun GNSS L1/L5 Breakout - NEO-F10N, SMA in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The SparkFun GNSS L1/L5 Breakout - NEO-F10N, SMA (GPS-24114) is a high-precision Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) module designed for applications requiring accurate positioning and timing. It features the u-blox NEO-F10N module, which supports dual-band GNSS reception (L1 and L5) for enhanced accuracy and reliability. This breakout board is equipped with an SMA connector for an external antenna, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, including autonomous vehicles, drones, surveying, and IoT devices.
Explore Projects Built with SparkFun GNSS L1/L5 Breakout - NEO-F10N, SMA

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer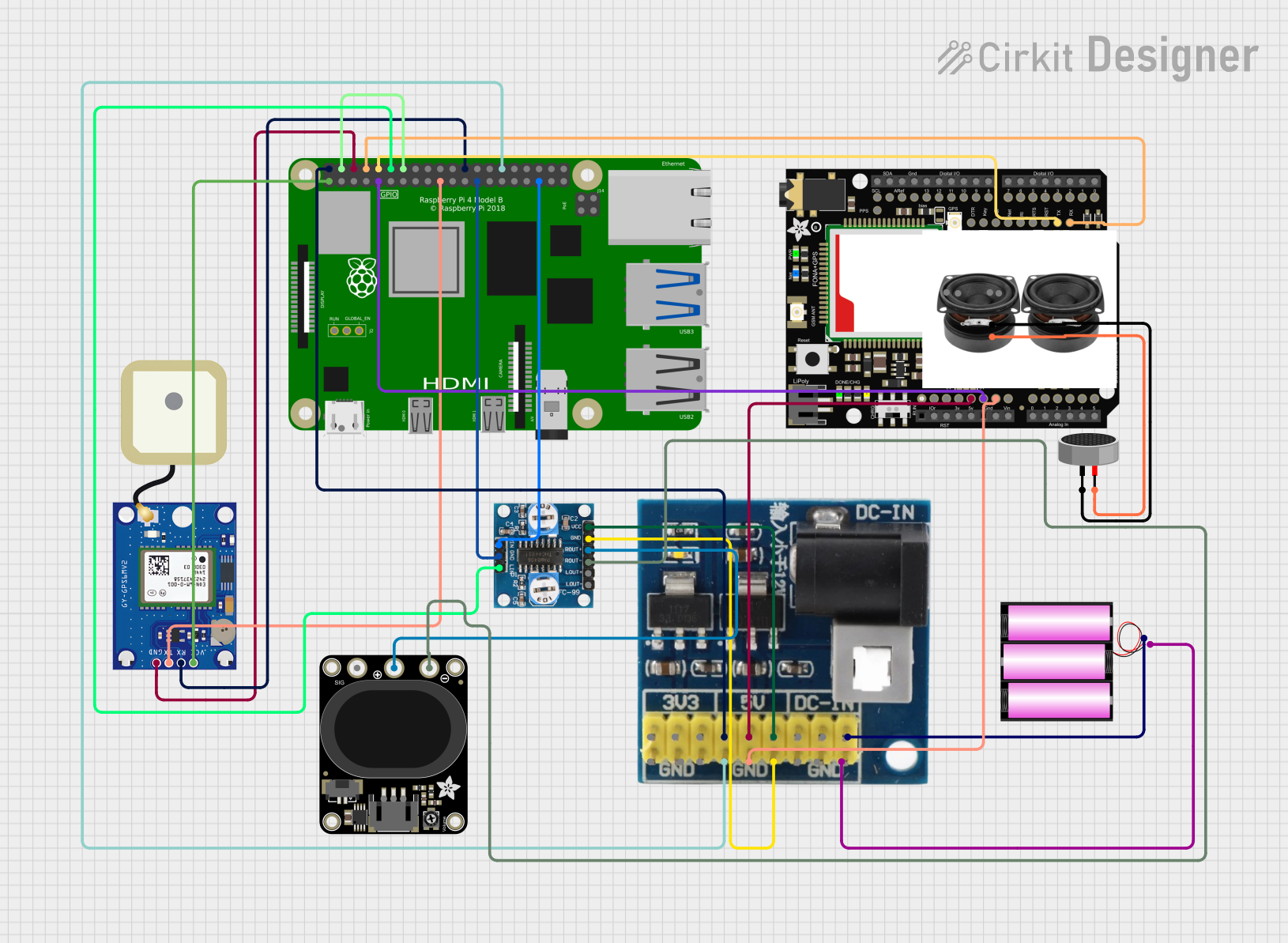
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer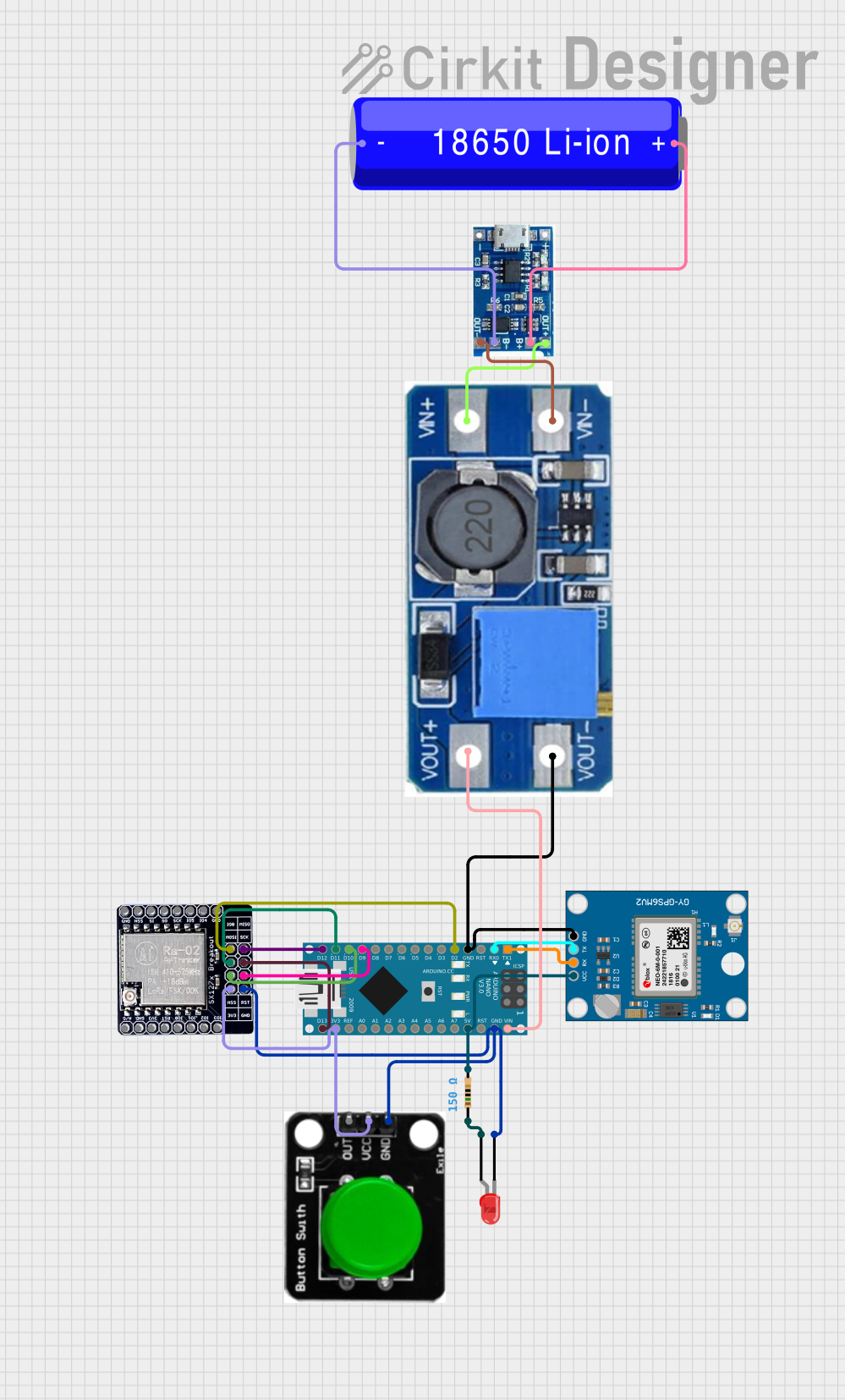
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with SparkFun GNSS L1/L5 Breakout - NEO-F10N, SMA

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- High-precision navigation for drones and autonomous vehicles
- Surveying and mapping
- Timing synchronization for communication systems
- IoT devices requiring accurate geolocation
- Research and development in GNSS technologies
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| GNSS Module | u-blox NEO-F10N |
| Frequency Bands | L1 (1575.42 MHz), L5 (1176.45 MHz) |
| Positioning Accuracy | Down to 0.3 meters (with RTK corrections) |
| Update Rate | Up to 10 Hz |
| Input Voltage | 3.3V (regulated) |
| Power Consumption | ~30 mA (typical) |
| Antenna Connector | SMA (external antenna required) |
| Communication Interfaces | UART, I2C |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Dimensions | 25.4 mm x 25.4 mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Name | Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GND | 1 | Ground connection |
| 3.3V | 2 | Power supply input (3.3V regulated) |
| TX | 3 | UART Transmit (data output from the module) |
| RX | 4 | UART Receive (data input to the module) |
| SDA | 5 | I2C Data Line |
| SCL | 6 | I2C Clock Line |
| PPS | 7 | Pulse Per Second output for timing applications |
| RST | 8 | Reset pin (active low) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the 3.3V pin to a regulated 3.3V power source and the GND pin to the ground.
- Antenna Connection: Attach an external GNSS antenna to the SMA connector for optimal signal reception.
- Communication Interface:
- For UART communication, connect the TX and RX pins to the corresponding UART pins on your microcontroller.
- For I2C communication, connect the SDA and SCL pins to the I2C bus of your microcontroller.
- Optional Connections:
- Use the PPS pin for precise timing applications.
- Connect the RST pin to a GPIO pin on your microcontroller for manual resets if needed.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Antenna Placement: Ensure the external antenna has a clear view of the sky for optimal satellite reception.
- Power Supply: Use a clean and stable 3.3V power source to avoid noise and interference.
- UART/I2C Selection: Configure your microcontroller to use the appropriate communication protocol.
- RTK Corrections: For high-precision applications, use Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) corrections with a compatible base station.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to interface the SparkFun GNSS L1/L5 Breakout with an Arduino UNO using UART communication:
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Define RX and TX pins for SoftwareSerial
SoftwareSerial mySerial(4, 3); // RX = Pin 4, TX = Pin 3
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize hardware serial for debugging
mySerial.begin(9600); // Initialize software serial for GNSS module
Serial.println("SparkFun GNSS L1/L5 Breakout Example");
}
void loop() {
// Check if data is available from the GNSS module
if (mySerial.available()) {
// Read and print GNSS data to the Serial Monitor
while (mySerial.available()) {
char c = mySerial.read();
Serial.print(c);
}
}
}
Note: Ensure the GNSS module's baud rate matches the mySerial.begin() value (default is 9600).
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No GNSS Fix:
- Ensure the external antenna is properly connected and has a clear view of the sky.
- Check the power supply for stability and correct voltage.
- Verify the module's configuration and communication settings.
No Data Output:
- Confirm the TX and RX connections between the GNSS module and the microcontroller.
- Ensure the baud rate in your code matches the module's default baud rate (9600).
Intermittent Signal Loss:
- Avoid placing the antenna near sources of interference, such as Wi-Fi routers or metal objects.
- Use a high-quality GNSS antenna for better performance.
FAQs
Q: Can I use this module indoors?
A: While the module may work indoors near windows, optimal performance requires a clear view of the sky.
Q: What type of antenna should I use?
A: Use an active GNSS antenna with an SMA connector for best results.
Q: How do I enable RTK corrections?
A: RTK corrections require additional hardware (e.g., a base station) and configuration. Refer to the u-blox NEO-F10N datasheet for detailed instructions.
Q: Can I power the module with 5V?
A: No, the module requires a regulated 3.3V power supply. Use a voltage regulator if your system operates at 5V.