
How to Use Exhaust Fan: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Exhaust Fan in Cirkit Designer
Design with Exhaust Fan in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
An exhaust fan is a device designed to expel air from an enclosed space, typically to remove heat, moisture, or odors. By improving ventilation and air quality, exhaust fans are essential in maintaining a comfortable and safe environment. These fans are commonly used in residential, commercial, and industrial settings, such as bathrooms, kitchens, workshops, and factories.
Explore Projects Built with Exhaust Fan
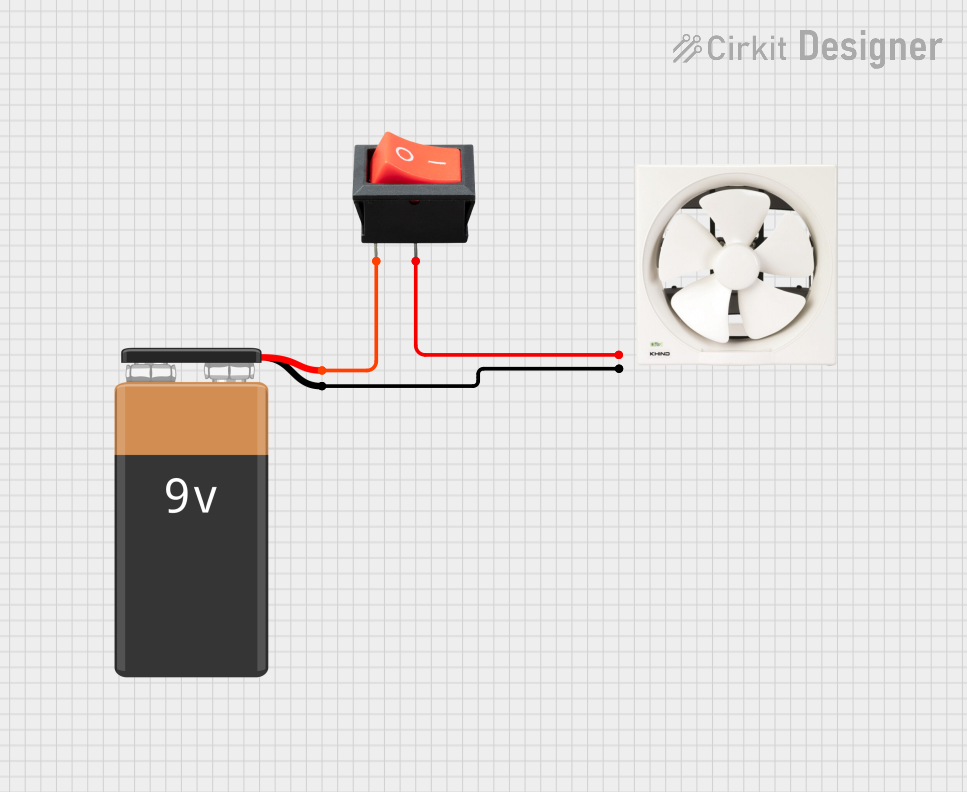
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer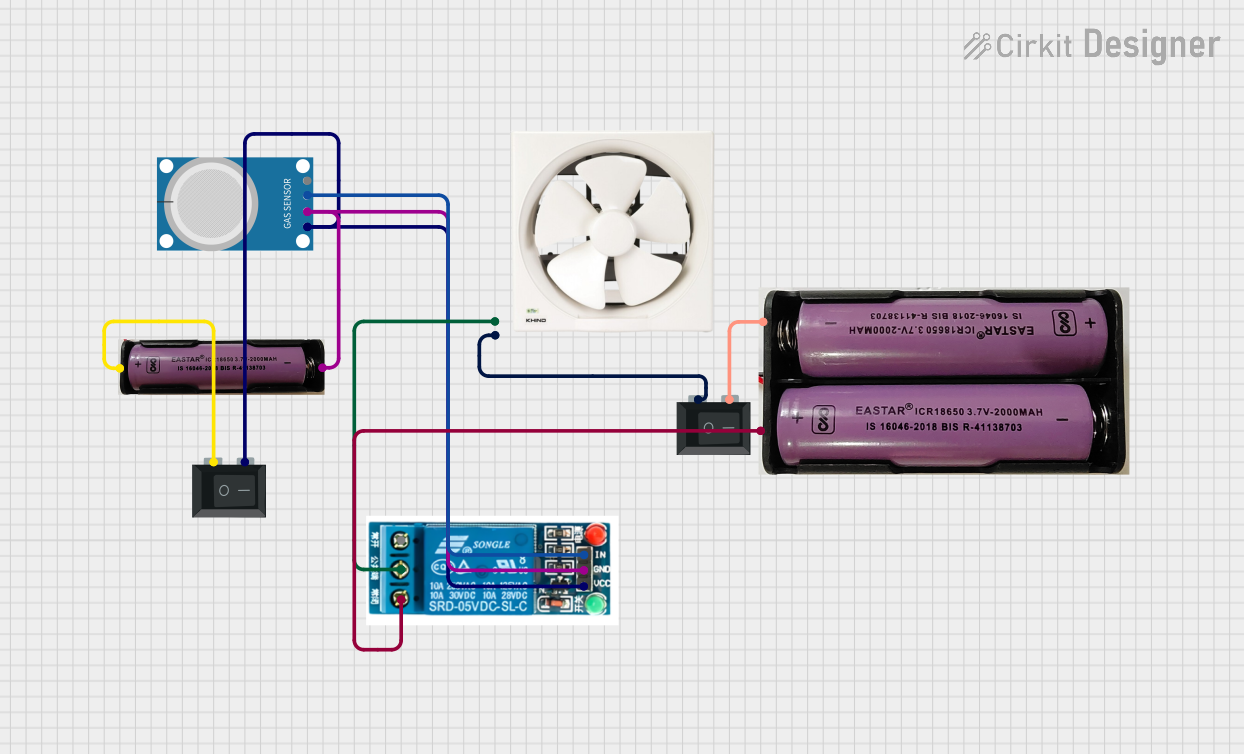
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer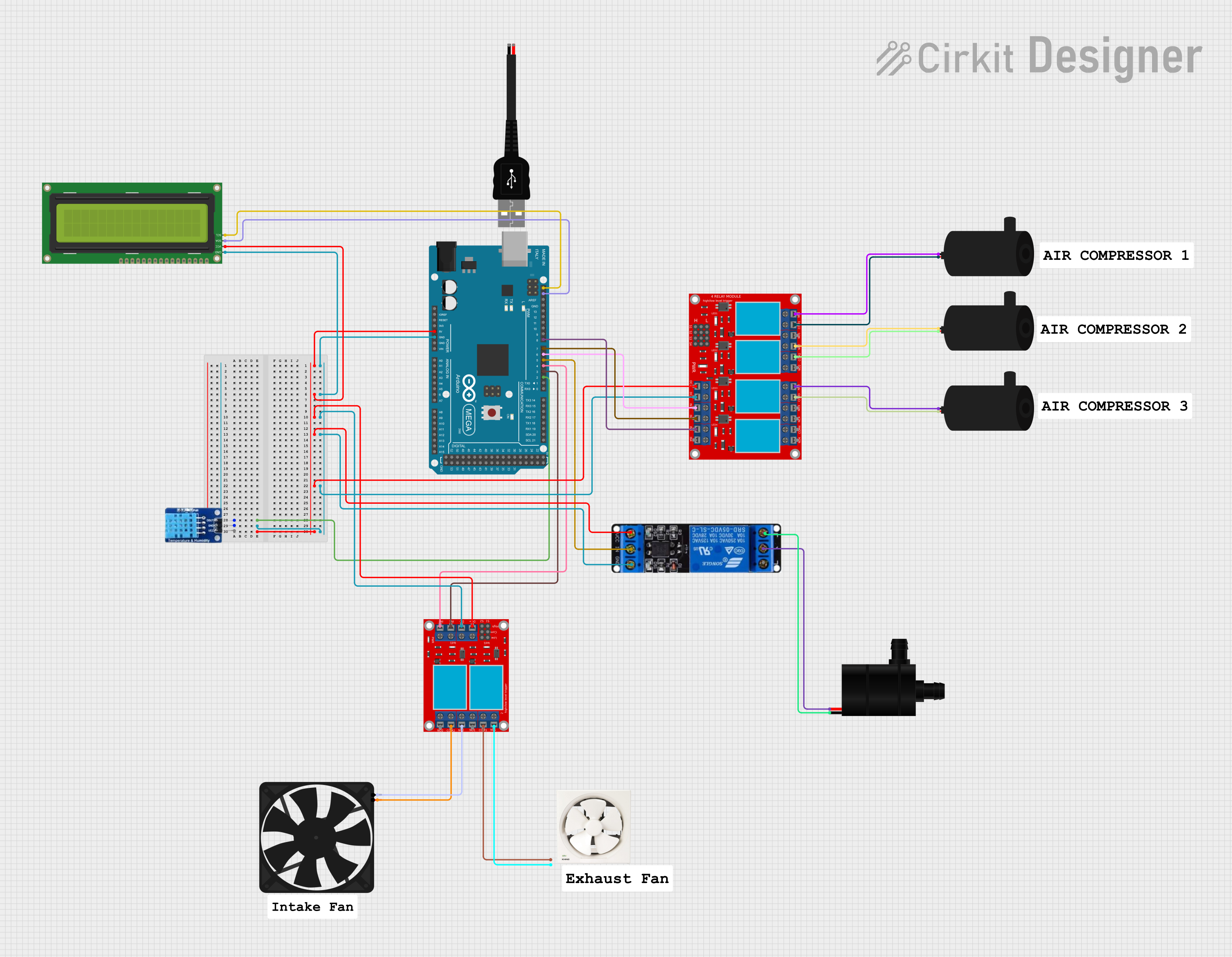
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer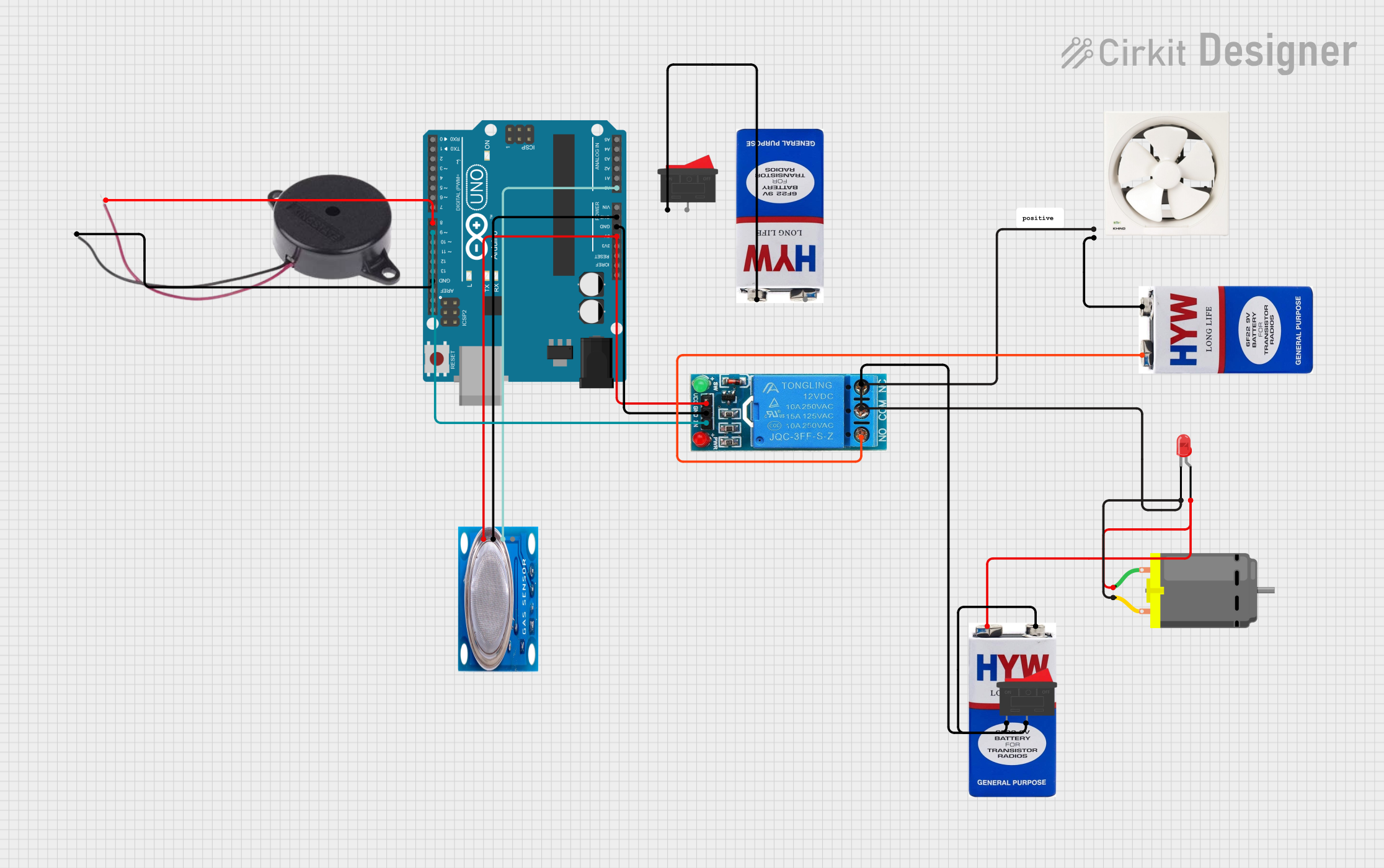
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Exhaust Fan

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Bathrooms: To remove moisture and prevent mold growth.
- Kitchens: To expel cooking fumes, smoke, and odors.
- Workshops: To ventilate fumes from chemicals or machinery.
- Factories: To maintain air quality and regulate temperature.
- Server Rooms: To dissipate heat generated by electronic equipment.
Technical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a standard exhaust fan. Specifications may vary depending on the model and manufacturer.
Key Technical Details
- Operating Voltage: 110V AC or 220V AC (varies by region)
- Power Consumption: 20W to 100W (depending on size and capacity)
- Airflow Capacity: 50 CFM to 500 CFM (Cubic Feet per Minute)
- Noise Level: 30 dB to 60 dB
- Material: Plastic or metal housing with aluminum or plastic blades
- Mounting Type: Wall-mounted or ceiling-mounted
- Speed Control: Single-speed or variable-speed options
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
For exhaust fans with an electrical connection, the wiring typically involves three main terminals or wires. Below is a table describing the connections:
| Pin/Wire | Description | Color Code (Typical) |
|---|---|---|
| Live (L) | Connects to the live AC supply line | Brown or Red |
| Neutral (N) | Connects to the neutral AC line | Blue |
| Ground (G) | Connects to the ground for safety | Green or Yellow-Green |
Note: Always refer to the manufacturer's wiring diagram for specific models.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Determine the Voltage: Verify the operating voltage of the exhaust fan (e.g., 110V or 220V AC) and ensure compatibility with your power supply.
- Wiring:
- Connect the Live (L) wire of the fan to the live terminal of the AC power source.
- Connect the Neutral (N) wire to the neutral terminal of the AC power source.
- Connect the Ground (G) wire to the ground terminal for safety.
- Switch Control: Optionally, connect a wall switch or relay to control the fan's operation.
- Secure Mounting: Install the fan securely on a wall or ceiling, ensuring proper alignment for optimal airflow.
- Test the Fan: Turn on the power and test the fan to ensure it operates correctly.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Safety First: Always disconnect the power supply before wiring or servicing the fan.
- Proper Ventilation: Ensure the exhaust fan is installed in a location where it can effectively expel air to the outside.
- Avoid Obstructions: Keep the fan blades and vents free from obstructions to maintain efficiency.
- Use a Speed Controller: For variable-speed fans, use a compatible speed controller to adjust airflow as needed.
- Regular Maintenance: Clean the fan blades and housing periodically to prevent dust buildup and maintain performance.
Example: Connecting an Exhaust Fan to an Arduino UNO
For exhaust fans with DC motors, you can control the fan using an Arduino UNO and a relay module. Below is an example code snippet:
// Example: Controlling an exhaust fan with Arduino UNO and a relay module
// Connect the relay module's IN pin to Arduino pin 7
// Ensure the relay is rated for the fan's voltage and current
const int relayPin = 7; // Pin connected to the relay module
void setup() {
pinMode(relayPin, OUTPUT); // Set relay pin as output
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW); // Ensure the relay is off initially
}
void loop() {
// Turn the fan ON
digitalWrite(relayPin, HIGH); // Activate the relay
delay(10000); // Keep the fan on for 10 seconds
// Turn the fan OFF
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW); // Deactivate the relay
delay(10000); // Keep the fan off for 10 seconds
}
Note: This example assumes the exhaust fan operates on DC voltage and is compatible with the relay module. For AC fans, additional safety precautions and components (e.g., optoisolators) are required.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Fan Does Not Turn On:
- Cause: Loose or incorrect wiring.
- Solution: Double-check all connections and ensure the power supply is active.
Fan Makes Excessive Noise:
- Cause: Dust buildup or loose mounting.
- Solution: Clean the fan blades and housing. Tighten all mounting screws.
Fan Operates Intermittently:
- Cause: Faulty switch or relay.
- Solution: Inspect and replace the switch or relay if necessary.
Low Airflow:
- Cause: Obstructed vents or clogged blades.
- Solution: Remove any obstructions and clean the fan thoroughly.
FAQs
Q: Can I use an exhaust fan in a high-humidity environment?
A: Yes, but ensure the fan is rated for high-humidity use and has proper insulation.Q: How do I calculate the required CFM for my space?
A: Multiply the room's volume (length × width × height) by the desired air changes per hour (ACH), then divide by 60.Q: Can I control the fan speed?
A: Yes, if the fan supports variable speed control. Use a compatible speed controller or dimmer switch.Q: Is it safe to install an exhaust fan myself?
A: If you are experienced with electrical work, you can install it. Otherwise, hire a licensed electrician for safety.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use and maintain an exhaust fan for various applications.