
How to Use Qwiic Cable - Breadboard Jumper (4-pin): Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
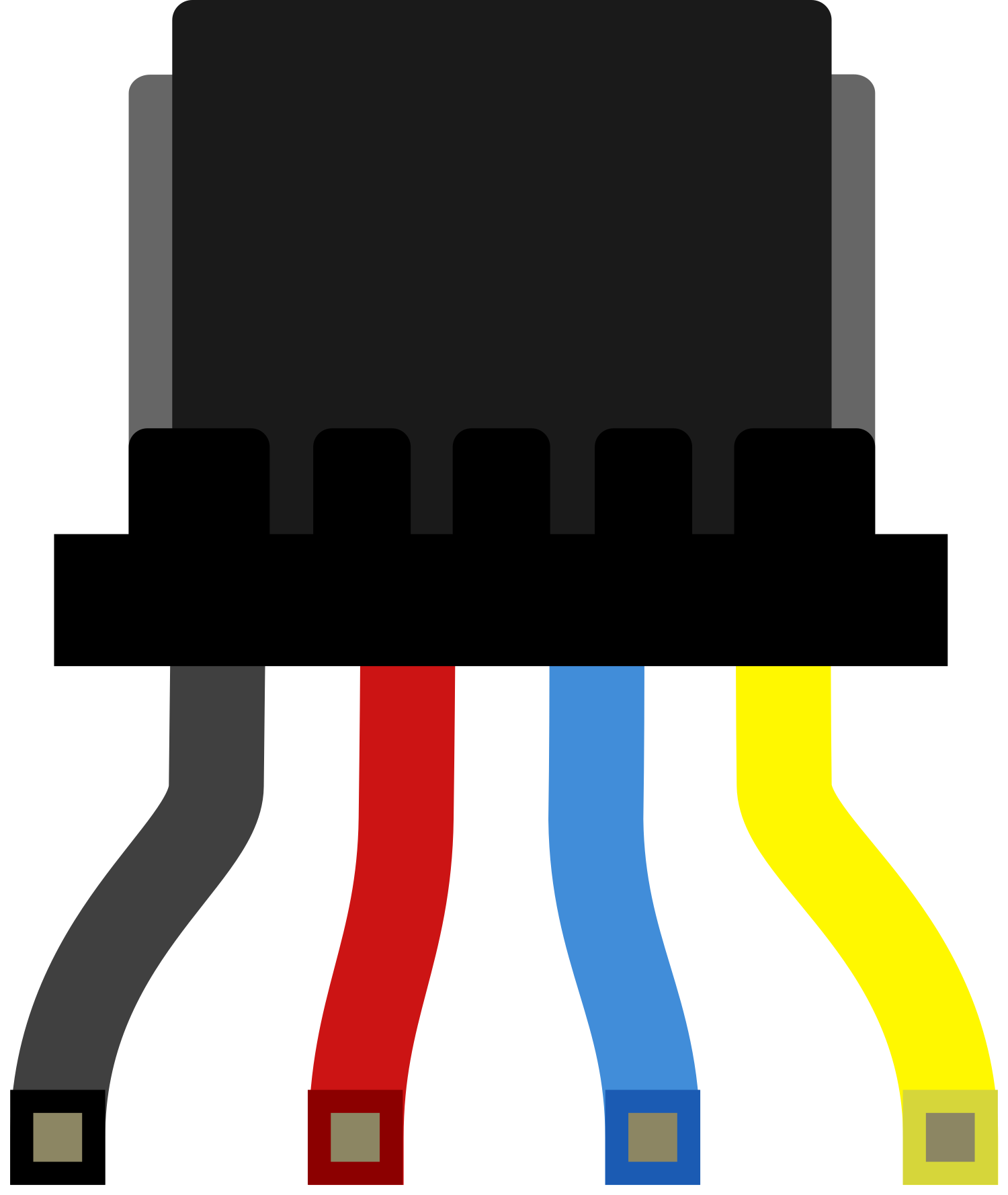
 Design with Qwiic Cable - Breadboard Jumper (4-pin) in Cirkit Designer
Design with Qwiic Cable - Breadboard Jumper (4-pin) in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Qwiic Cable - Breadboard Jumper (4-pin) is an essential component designed to facilitate seamless and solderless connections between Qwiic-enabled devices and a standard breadboard. This cable is particularly useful for rapid prototyping, educational purposes, and hobbyist projects where ease of use and flexibility are paramount. Common applications include interfacing sensors, actuators, and modules with microcontrollers such as the Arduino UNO in a plug-and-play fashion.
Explore Projects Built with Qwiic Cable - Breadboard Jumper (4-pin)
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Qwiic Cable - Breadboard Jumper (4-pin)

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
The Qwiic Cable - Breadboard Jumper is characterized by the following technical specifications:
- Connector Type: 1mm pitch, 4-pin JST connector on one end, and male breadboard jumper leads on the other.
- Cable Length: Typically ranges from 100mm to 200mm, but may vary by manufacturer.
- Wire Gauge: 28 AWG.
- Voltage Rating: Typically 3.3V to 5V, conforming to standard Qwiic system requirements.
- Current Rating: Up to 1A, but this may vary based on wire gauge and insulation material.
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Qwiic Connector | Breadboard Jumper Color | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SDA | Blue | Serial Data Line |
| 2 | SCL | Yellow | Serial Clock Line |
| 3 | VCC | Red | Power Supply Voltage |
| 4 | GND | Black | Ground |
Usage Instructions
Connecting to a Breadboard
- Identify the Pins: Refer to the pin configuration table above to identify the SDA, SCL, VCC, and GND leads.
- Insert into Breadboard: Insert the male jumper leads into the breadboard, ensuring that each pin is connected to the correct breadboard row.
- Connect to Qwiic Device: Attach the Qwiic connector to your Qwiic-enabled device, ensuring a firm connection.
Best Practices
- Power Considerations: Ensure that the power supply voltage (VCC) matches the requirements of your Qwiic-enabled device.
- Signal Integrity: Keep the cable length as short as possible to maintain signal integrity, especially for I2C high-speed communication.
- Avoid Force: Do not apply excessive force when connecting or disconnecting the Qwiic connector to prevent damage.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Loose Connections: If the device is not functioning, check that all connections are secure and correctly inserted into the breadboard and Qwiic device.
- Incorrect Wiring: Double-check that the SDA and SCL lines are not swapped and that VCC and GND are correctly connected.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the Qwiic Cable with a 5V system? A: Yes, the Qwiic system is typically 3.3V, but the cables are usually 5V tolerant. However, always check the specifications of your specific Qwiic-enabled device.
Q: How do I extend the length of my Qwiic connection? A: You can use multiple Qwiic cables connected in series, but be aware that extending the length too much may affect I2C communication quality.
Q: Is it possible to connect multiple Qwiic devices using one cable? A: No, the Qwiic Cable - Breadboard Jumper is designed for a one-to-one connection. For multiple devices, use a Qwiic hub or daisy-chain compatible devices.
Example Arduino Code
Below is an example of how to initialize an I2C communication with a Qwiic-enabled device using an Arduino UNO. This is a generic setup and may vary depending on the specific device.
#include <Wire.h>
void setup() {
Wire.begin(); // Join the I2C bus as a master
Serial.begin(9600); // Start serial communication at 9600 baud rate
}
void loop() {
// Your device-specific communication code here
}
Remember to consult the datasheet of your specific Qwiic-enabled device for the correct I2C addresses and commands.