
How to Use Outlet: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Outlet in Cirkit Designer
Design with Outlet in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
An outlet, also known as a power socket or receptacle, is a device that provides a connection point for electrical appliances and equipment to access the power supply. Outlets are essential components in residential, commercial, and industrial electrical systems, enabling the safe and convenient distribution of electricity. They are designed to accommodate various plug types and configurations, depending on regional standards and specific applications.
Explore Projects Built with Outlet
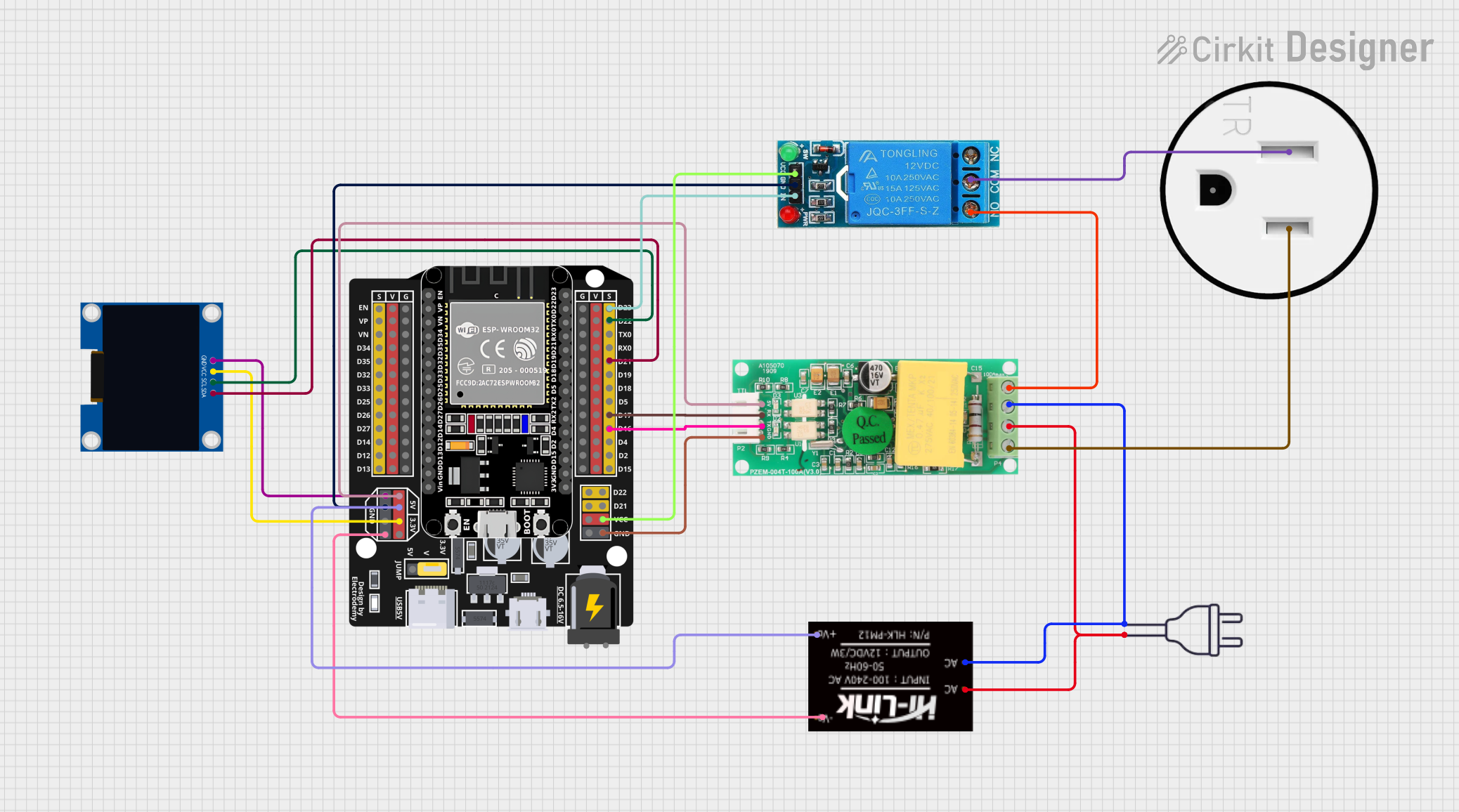
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer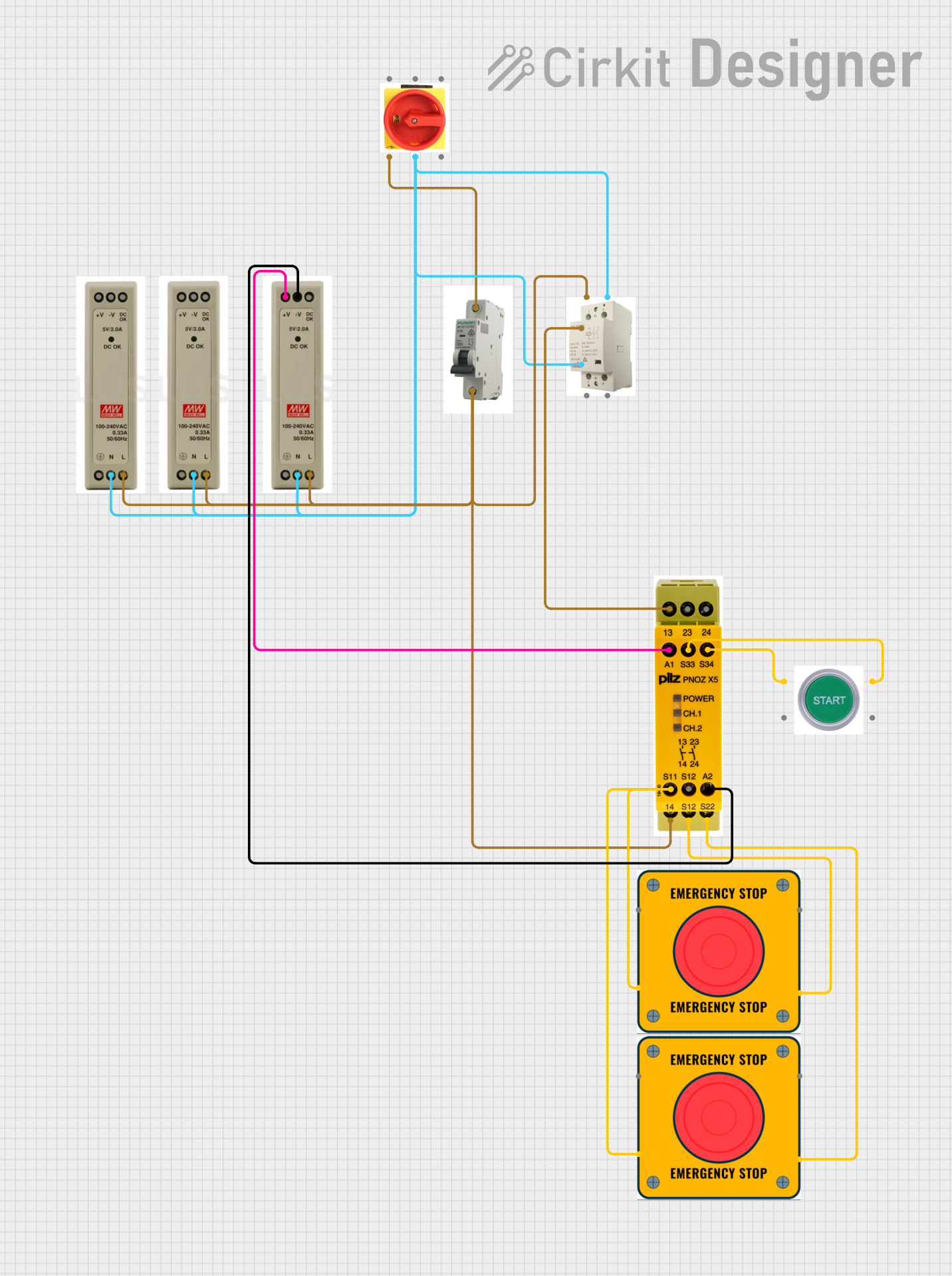
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer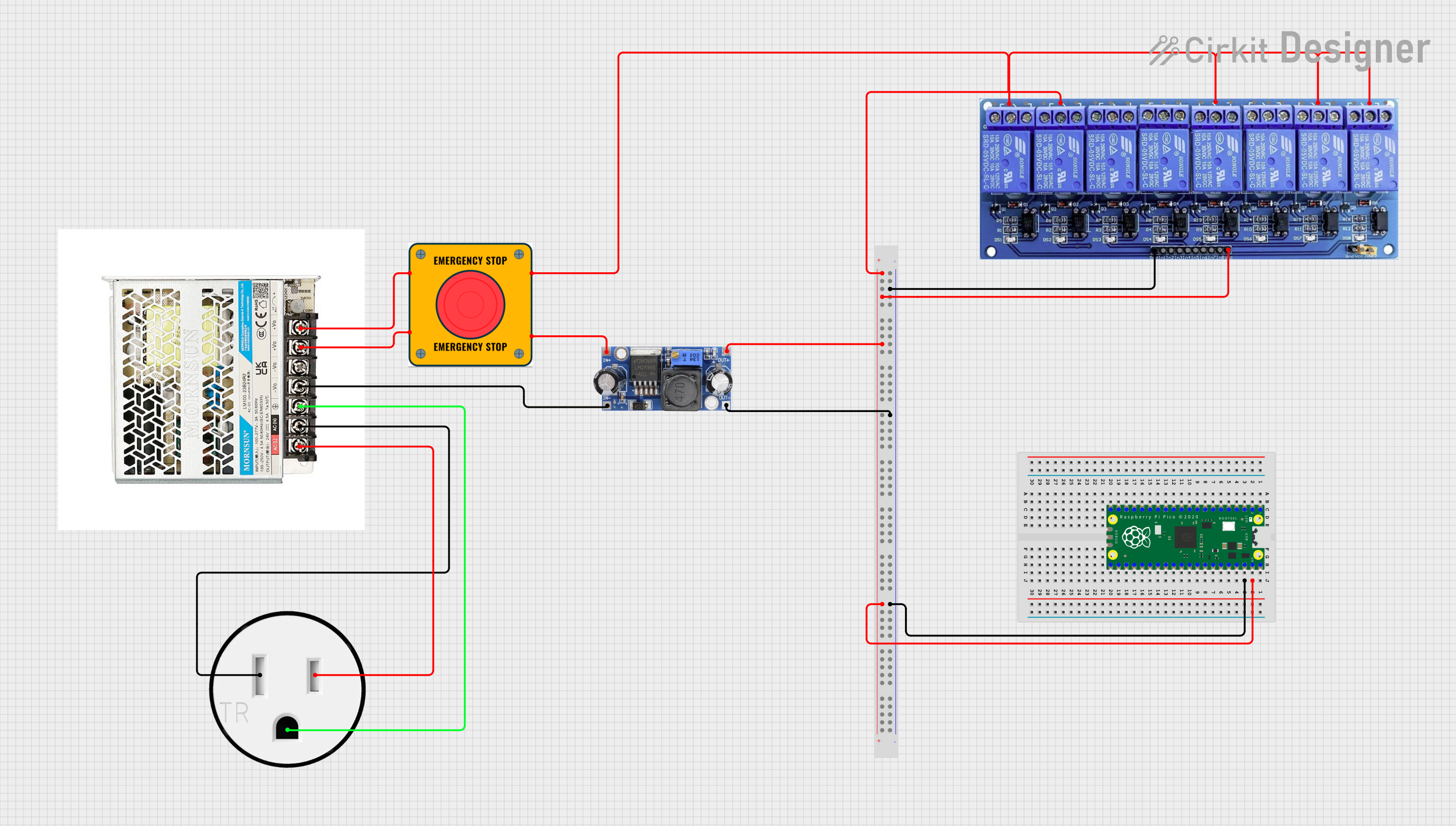
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer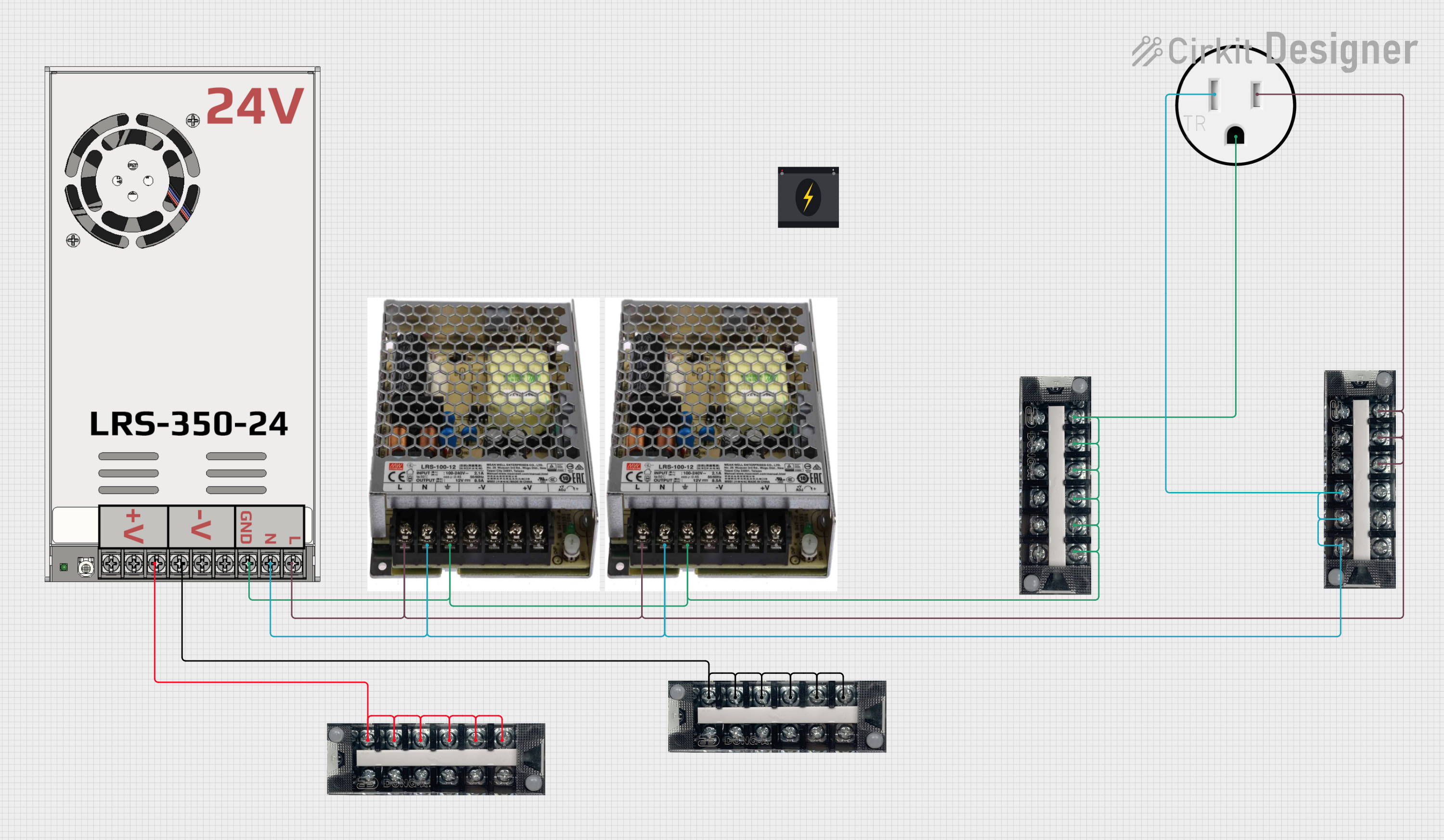
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Outlet

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Powering household appliances such as refrigerators, televisions, and lamps.
- Providing electricity to office equipment like computers, printers, and monitors.
- Supporting industrial tools and machinery in workshops and factories.
- Charging portable devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
- Integrating with smart home systems for automated control and monitoring.
Technical Specifications
Outlets come in various types and configurations, depending on the region and application. Below are the general technical specifications for a standard outlet:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Voltage Rating | 110V-120V (North America), 220V-240V (Europe, Asia, etc.) |
| Current Rating | 10A, 15A, or 20A (depending on the outlet type and application) |
| Frequency | 50Hz or 60Hz (varies by region) |
| Number of Pins | 2-pin or 3-pin configurations (live, neutral, and optional ground) |
| Material | Flame-retardant plastic housing, copper or brass internal contacts |
| Mounting Style | Wall-mounted or surface-mounted |
| Safety Features | Childproof shutters, surge protection, and ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCI) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Below is a table describing the pin configuration for a standard 3-pin outlet:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Live (L) | Supplies the active phase of the AC voltage. |
| Neutral (N) | Completes the circuit by providing a return path for the current. |
| Ground (G) | Provides a safety path to prevent electric shock in case of a fault. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Outlet in a Circuit
Installation:
- Ensure the power supply to the circuit is turned off before installation.
- Connect the live (L), neutral (N), and ground (G) wires to the corresponding terminals on the outlet.
- Secure the outlet in the wall box using screws and attach the faceplate.
Testing:
- After installation, turn the power supply back on and use a multimeter to verify the voltage at the outlet.
- Check for proper grounding to ensure safety.
Connecting Devices:
- Plug the appliance or device into the outlet, ensuring the plug matches the outlet type.
- Avoid overloading the outlet by connecting devices that exceed its current rating.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Always follow local electrical codes and standards during installation.
- Use outlets with built-in surge protection for sensitive electronic devices.
- Regularly inspect outlets for signs of wear, damage, or overheating.
- Avoid using adapters or extension cords for high-power appliances.
- For outdoor installations, use weatherproof outlets with proper enclosures.
Example: Controlling an Outlet with an Arduino UNO
If you want to control an outlet using an Arduino UNO, you can use a relay module to switch the outlet on and off. Below is an example code snippet:
/*
Example: Controlling an Outlet with Arduino UNO and Relay Module
This code demonstrates how to control an outlet using a relay module.
WARNING: Ensure proper isolation between high-voltage and low-voltage circuits.
*/
const int relayPin = 7; // Pin connected to the relay module
void setup() {
pinMode(relayPin, OUTPUT); // Set the relay pin as an output
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW); // Ensure the relay is off initially
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(relayPin, HIGH); // Turn the relay (and outlet) ON
delay(5000); // Keep the outlet ON for 5 seconds
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW); // Turn the relay (and outlet) OFF
delay(5000); // Keep the outlet OFF for 5 seconds
}
Note: When working with high-voltage outlets, always prioritize safety. Use proper insulation, and never handle live wires.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Power at the Outlet:
- Cause: Tripped circuit breaker or blown fuse.
- Solution: Check the breaker panel and reset the breaker or replace the fuse.
Loose Connection:
- Cause: Worn or improperly installed outlet.
- Solution: Turn off the power and tighten the terminal screws or replace the outlet.
Overheating:
- Cause: Overloaded outlet or poor contact.
- Solution: Reduce the load on the outlet and inspect for damage.
Sparking When Plugging In:
- Cause: Worn contacts or loose wiring.
- Solution: Replace the outlet and ensure proper wiring.
FAQs
Q: Can I install an outlet myself?
A: Yes, but only if you have basic electrical knowledge and follow local codes. Otherwise, hire a licensed electrician.Q: What is a GFCI outlet?
A: A Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) outlet is designed to protect against electric shock by cutting off power when a ground fault is detected.Q: How do I know if an outlet is grounded?
A: Use a plug-in outlet tester or a multimeter to check for proper grounding.Q: Can I use a 110V outlet in a 220V region?
A: No, outlets must match the voltage and frequency of the local power supply.
By following this documentation, you can safely and effectively use outlets in your electrical projects. Always prioritize safety and consult a professional when in doubt.