
How to Use INA226: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
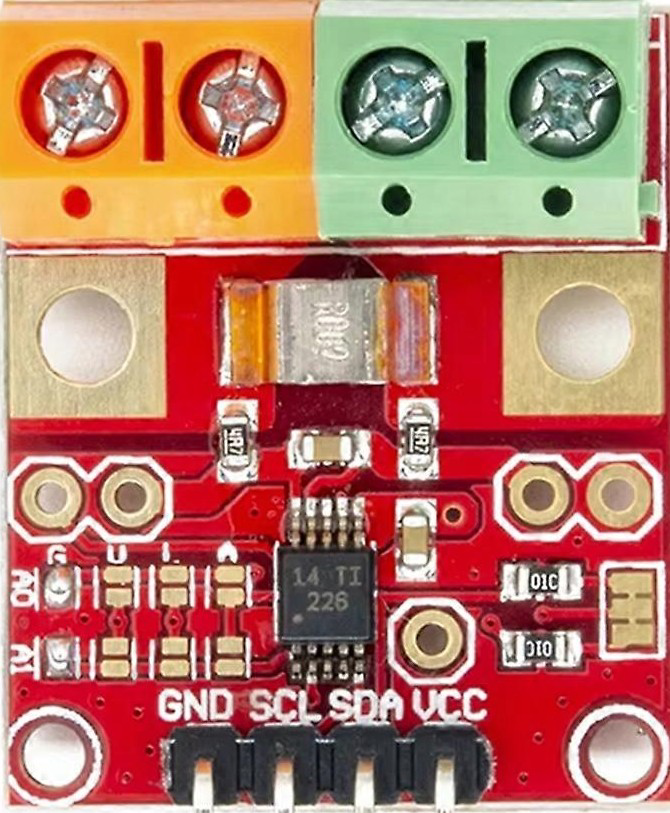
 Design with INA226 in Cirkit Designer
Design with INA226 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The INA226 is a high-side current shunt monitor with an integrated I2C interface. It is designed to measure the voltage across a shunt resistor, enabling precise current flow measurements. Additionally, the INA226 can calculate power consumption by combining current and voltage measurements, making it a versatile tool for power monitoring applications.
Explore Projects Built with INA226
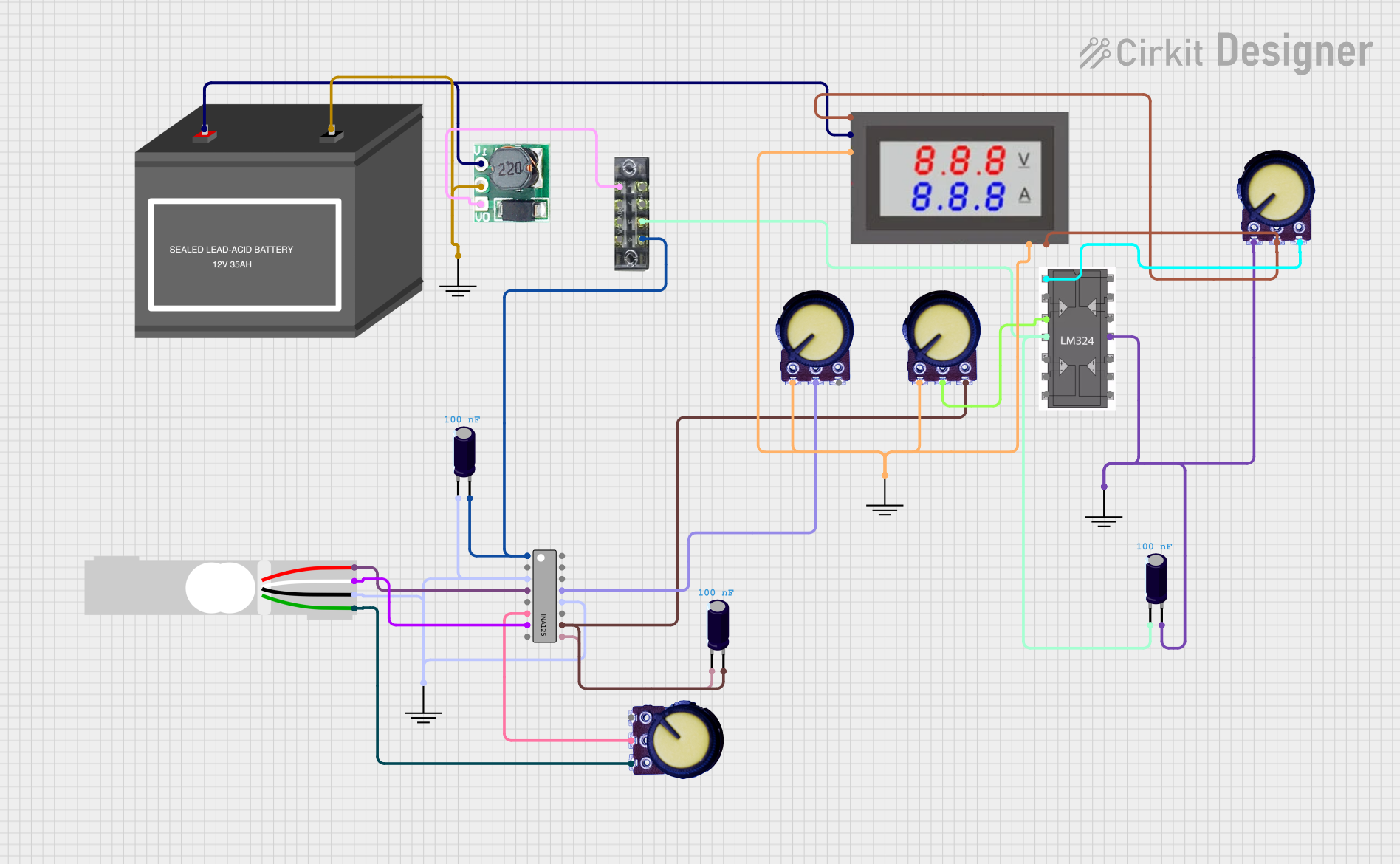
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer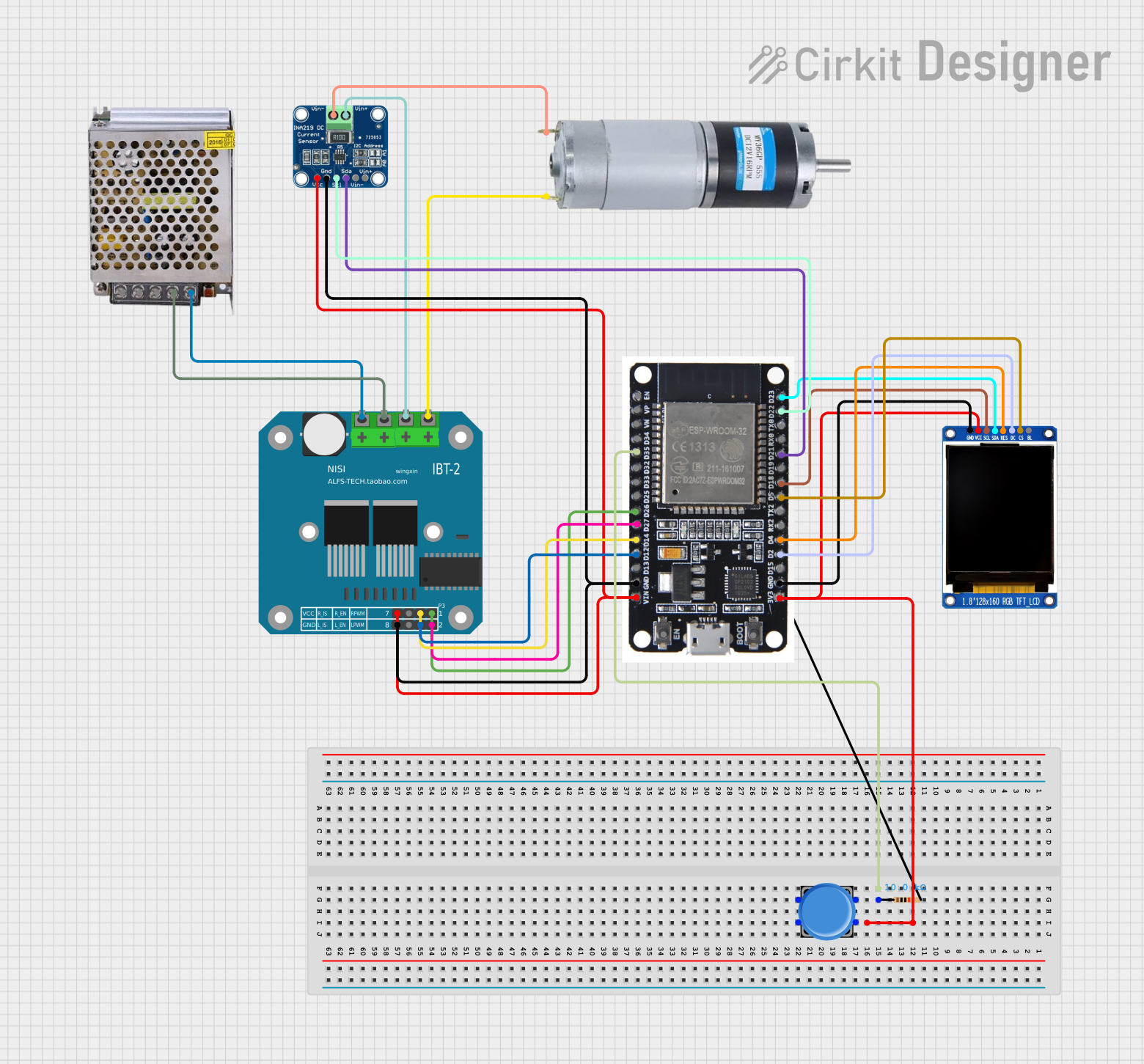
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer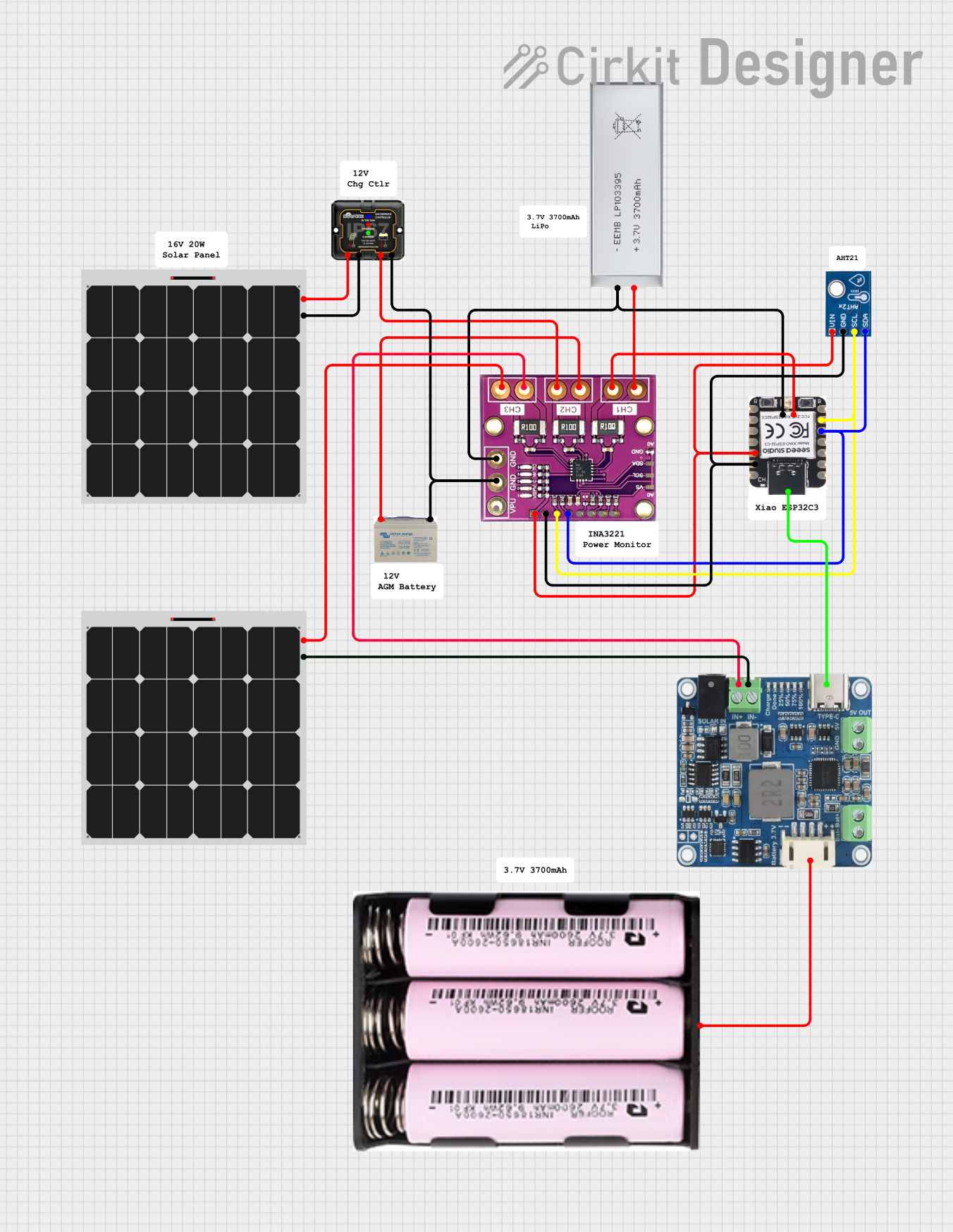
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with INA226

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Battery management systems
- Power supply monitoring
- Energy metering in industrial and consumer electronics
- Solar power systems
- Server and data center power monitoring
Technical Specifications
The INA226 offers a range of features and specifications that make it suitable for a variety of applications. Below are the key technical details:
Key Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Supply Voltage (VCC) | 2.7V to 5.5V |
| Input Voltage Range | 0V to 36V |
| Shunt Voltage Range | ±81.92mV |
| Current Measurement Range | Configurable (depends on shunt resistor) |
| Communication Interface | I2C (up to 1 MHz) |
| Resolution | 16-bit |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +125°C |
| Power Consumption | 330 µA (typical) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The INA226 is available in a small 10-pin VSSOP package. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VIN+ | Positive input for shunt voltage measurement |
| 2 | VIN- | Negative input for shunt voltage measurement |
| 3 | GND | Ground |
| 4 | SCL | I2C clock line |
| 5 | SDA | I2C data line |
| 6 | ALERT | Alert output (programmable threshold) |
| 7 | ADDR | I2C address selection |
| 8 | VCC | Power supply input (2.7V to 5.5V) |
| 9, 10 | NC | No connection |
Usage Instructions
The INA226 is straightforward to use in a circuit. Below are the steps and considerations for integrating it into your design.
Connecting the INA226
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a 2.7V to 5.5V power source and the GND pin to ground.
- Shunt Resistor: Place a shunt resistor between the high-side power source and the load. Connect the VIN+ and VIN- pins across the shunt resistor.
- I2C Interface: Connect the SCL and SDA pins to the corresponding I2C lines of your microcontroller. Use pull-up resistors (typically 4.7kΩ) on these lines.
- I2C Address: Configure the I2C address using the ADDR pin. This allows multiple INA226 devices to share the same I2C bus.
- Alert Pin (Optional): Use the ALERT pin to monitor programmable thresholds for current, voltage, or power.
Important Considerations
- Shunt Resistor Selection: Choose a shunt resistor with a low resistance value to minimize power loss, but ensure it provides a measurable voltage drop within the INA226's input range (±81.92mV).
- I2C Pull-Up Resistors: Ensure proper pull-up resistors are used on the I2C lines to maintain signal integrity.
- Bypass Capacitor: Place a 0.1µF ceramic capacitor close to the VCC pin for power supply decoupling.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the INA226 with an Arduino UNO to measure current and voltage:
#include <Wire.h>
// INA226 I2C address (default is 0x40, adjust if ADDR pin is configured)
#define INA226_ADDRESS 0x40
// INA226 register addresses
#define REG_CONFIG 0x00
#define REG_SHUNT_VOLTAGE 0x01
#define REG_BUS_VOLTAGE 0x02
void setup() {
Wire.begin(); // Initialize I2C communication
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication for debugging
// Configure the INA226 (default configuration)
Wire.beginTransmission(INA226_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(REG_CONFIG); // Point to the configuration register
Wire.write(0x45); // MSB: Set averaging, bus voltage conversion time, etc.
Wire.write(0x27); // LSB: Set shunt voltage conversion time
Wire.endTransmission();
}
void loop() {
float shuntVoltage = readShuntVoltage();
float busVoltage = readBusVoltage();
// Calculate current (I = V / R, where R is the shunt resistor value)
float shuntResistor = 0.1; // Example: 0.1 ohm
float current = shuntVoltage / shuntResistor;
// Print the results
Serial.print("Shunt Voltage (mV): ");
Serial.println(shuntVoltage * 1000); // Convert to mV
Serial.print("Bus Voltage (V): ");
Serial.println(busVoltage);
Serial.print("Current (A): ");
Serial.println(current);
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before the next reading
}
float readShuntVoltage() {
return readRegister(REG_SHUNT_VOLTAGE) * 2.5e-6; // Convert to volts
}
float readBusVoltage() {
return readRegister(REG_BUS_VOLTAGE) * 1.25e-3; // Convert to volts
}
int16_t readRegister(uint8_t reg) {
Wire.beginTransmission(INA226_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(reg); // Point to the desired register
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(INA226_ADDRESS, 2); // Request 2 bytes
int16_t value = (Wire.read() << 8) | Wire.read(); // Combine MSB and LSB
return value;
}
Notes on the Code
- Replace the
shuntResistorvalue with the actual resistance of your shunt resistor. - Ensure the I2C address matches your INA226 configuration.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
No I2C Communication:
- Ensure the correct I2C address is used.
- Verify pull-up resistors are present on the SDA and SCL lines.
- Check for proper wiring and connections.
Incorrect Current or Voltage Readings:
- Verify the shunt resistor value and ensure it is within the INA226's input range.
- Check for noise or instability in the power supply.
Alert Pin Not Functioning:
- Ensure the ALERT pin is properly configured in the INA226 registers.
- Verify the threshold values are set correctly.
Tips for Troubleshooting
- Use an I2C scanner sketch to confirm the INA226 is detected on the I2C bus.
- Double-check all connections, especially the shunt resistor and I2C lines.
- Use an oscilloscope or logic analyzer to debug I2C communication if needed.
By following this documentation, you should be able to successfully integrate and use the INA226 in your projects.