
How to Use MINIBOOST 5V @ 1A : Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with MINIBOOST 5V @ 1A in Cirkit Designer
Design with MINIBOOST 5V @ 1A in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
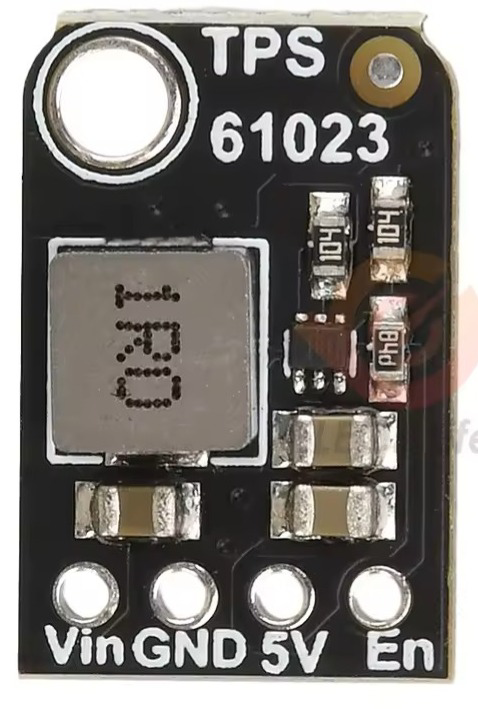
The MINIBOOST 5V @ 1A is a compact DC-DC boost converter module designed and manufactured by Adafruit. It utilizes the TPS61023 IC to efficiently step up input voltages to a stable 5V output, capable of delivering up to 1A of current. This module is ideal for powering small electronic devices, microcontrollers, and low-power peripherals from lower voltage sources such as batteries.
Explore Projects Built with MINIBOOST 5V @ 1A
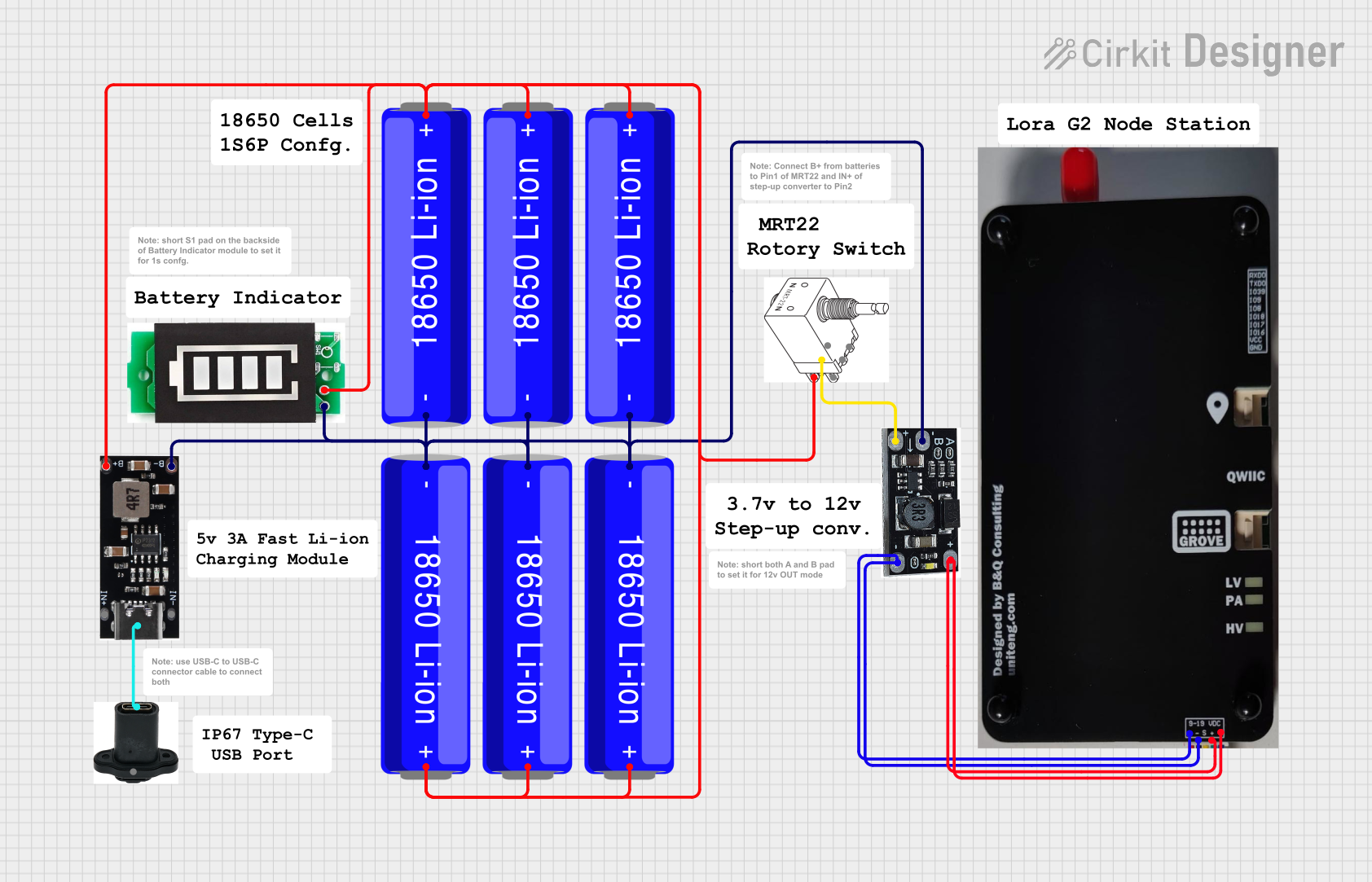
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer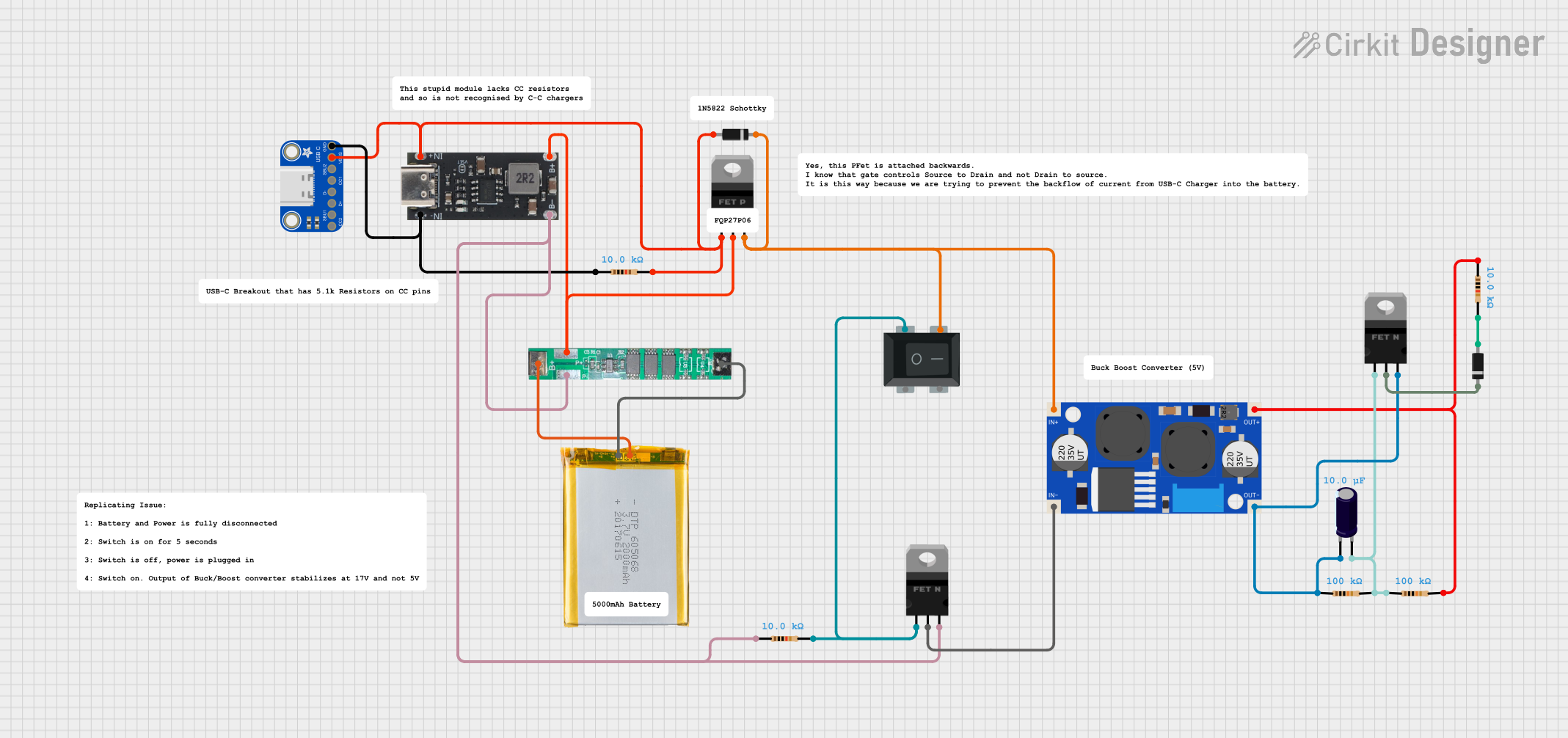
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer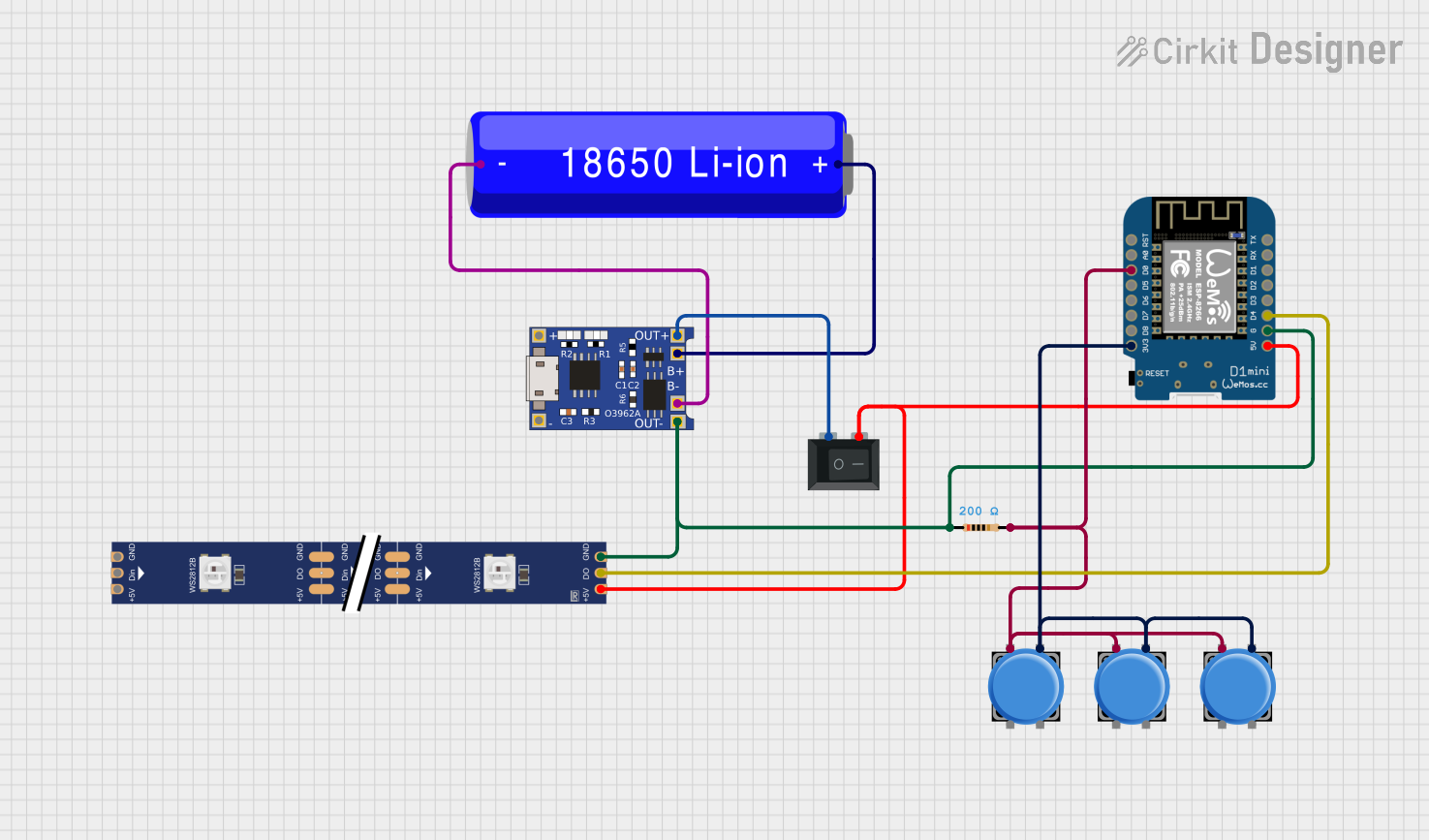
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with MINIBOOST 5V @ 1A

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Powering 5V microcontrollers (e.g., Arduino, ESP32) from 3.7V LiPo batteries
- Boosting voltage from AA/AAA battery packs
- Portable electronics and wearables
- Low-power IoT devices
- Backup power systems
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the MINIBOOST 5V @ 1A module:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 1.8V to 5.5V |
| Output Voltage | 5V (regulated) |
| Maximum Output Current | 1A |
| Efficiency | Up to 90% (depending on load) |
| Switching Frequency | 1.5 MHz |
| Dimensions | 11.5mm x 17.5mm x 4mm |
| Weight | ~1g |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The MINIBOOST module has four pins, as described in the table below:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN | Input voltage pin. Connect to a power source (e.g., battery) within 1.8V-5.5V. |
| GND | Ground pin. Connect to the ground of your circuit. |
| VOUT | Regulated 5V output pin. Connect to the load or device requiring 5V power. |
| EN | Enable pin. Pull high to enable the module, or low to disable it. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connect the Input Voltage (VIN):
- Attach a power source (e.g., a 3.7V LiPo battery or a 2xAA battery pack) to the
VINpin. - Ensure the input voltage is within the range of 1.8V to 5.5V.
- Attach a power source (e.g., a 3.7V LiPo battery or a 2xAA battery pack) to the
Connect the Ground (GND):
- Connect the
GNDpin to the ground of your circuit.
- Connect the
Connect the Output Voltage (VOUT):
- Attach the device or load requiring 5V power to the
VOUTpin. - Ensure the load does not exceed the maximum output current of 1A.
- Attach the device or load requiring 5V power to the
Enable the Module:
- Pull the
ENpin high (connect to VIN) to enable the module. - To disable the module, pull the
ENpin low (connect to GND).
- Pull the
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Input Voltage Range: Ensure the input voltage remains within the specified range (1.8V to 5.5V). Exceeding this range may damage the module.
- Output Current Limit: Do not exceed the maximum output current of 1A to prevent overheating or damage.
- Heat Dissipation: Although the module is efficient, it may generate heat under high loads. Ensure adequate ventilation or heat dissipation if operating near the maximum current.
- Decoupling Capacitors: For optimal performance, use decoupling capacitors (e.g., 10µF) close to the input and output pins to reduce noise and improve stability.
Example: Using MINIBOOST with Arduino UNO
The following example demonstrates how to power an Arduino UNO using the MINIBOOST module and a 3.7V LiPo battery.
Circuit Connections
- Connect the positive terminal of the LiPo battery to the
VINpin of the MINIBOOST. - Connect the negative terminal of the LiPo battery to the
GNDpin of the MINIBOOST. - Connect the
VOUTpin of the MINIBOOST to the 5V pin of the Arduino UNO. - Connect the
GNDpin of the MINIBOOST to the GND pin of the Arduino UNO.
Arduino Code Example
// Example code to blink an LED on pin 13 of Arduino UNO
// This demonstrates the Arduino running on power supplied by the MINIBOOST module.
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Voltage:
- Cause: The
ENpin is not pulled high. - Solution: Ensure the
ENpin is connected toVINto enable the module.
- Cause: The
Output Voltage Drops Under Load:
- Cause: The load exceeds the maximum output current of 1A.
- Solution: Reduce the load or ensure the connected device does not draw more than 1A.
Module Overheating:
- Cause: Prolonged operation at high current or insufficient ventilation.
- Solution: Reduce the load or improve heat dissipation by adding airflow or a heatsink.
Noise or Instability in Output Voltage:
- Cause: Insufficient decoupling capacitors.
- Solution: Add a 10µF capacitor close to the
VOUTpin to stabilize the output.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the MINIBOOST to power a Raspberry Pi?
A: The MINIBOOST is not recommended for powering a Raspberry Pi, as it typically requires more than 1A of current under load.
Q: What happens if the input voltage drops below 1.8V?
A: The module will stop boosting and the output voltage will drop. Ensure the input voltage remains within the specified range.
Q: Can I leave the EN pin floating?
A: No, the EN pin must be explicitly pulled high to enable the module or low to disable it. Leaving it floating may result in unpredictable behavior.