
How to Use SLA BATTERY SMART CHARGER: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
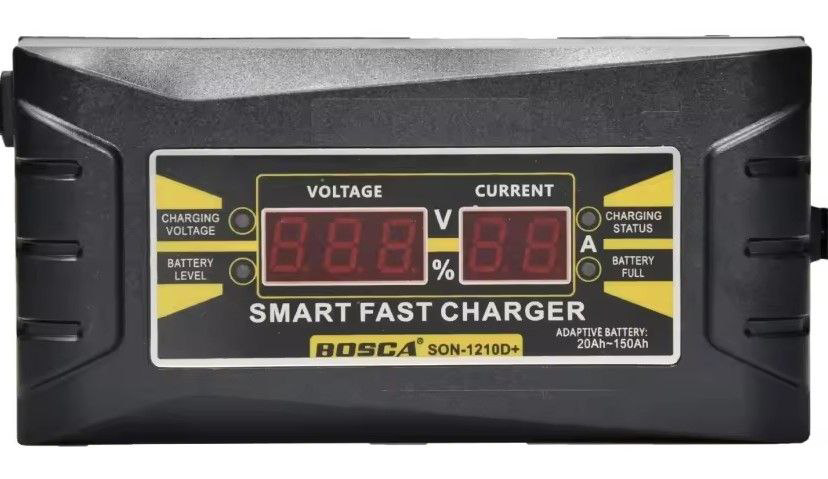

 Design with SLA BATTERY SMART CHARGER in Cirkit Designer
Design with SLA BATTERY SMART CHARGER in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The SLA Battery Smart Charger is a specialized charging device designed for sealed lead-acid (SLA) batteries. It features advanced charging algorithms, automatic charging cycles, and built-in safety mechanisms to ensure efficient and safe charging. With temperature compensation and overcharge protection, this charger helps extend the lifespan of SLA batteries while maintaining optimal performance.
Explore Projects Built with SLA BATTERY SMART CHARGER

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer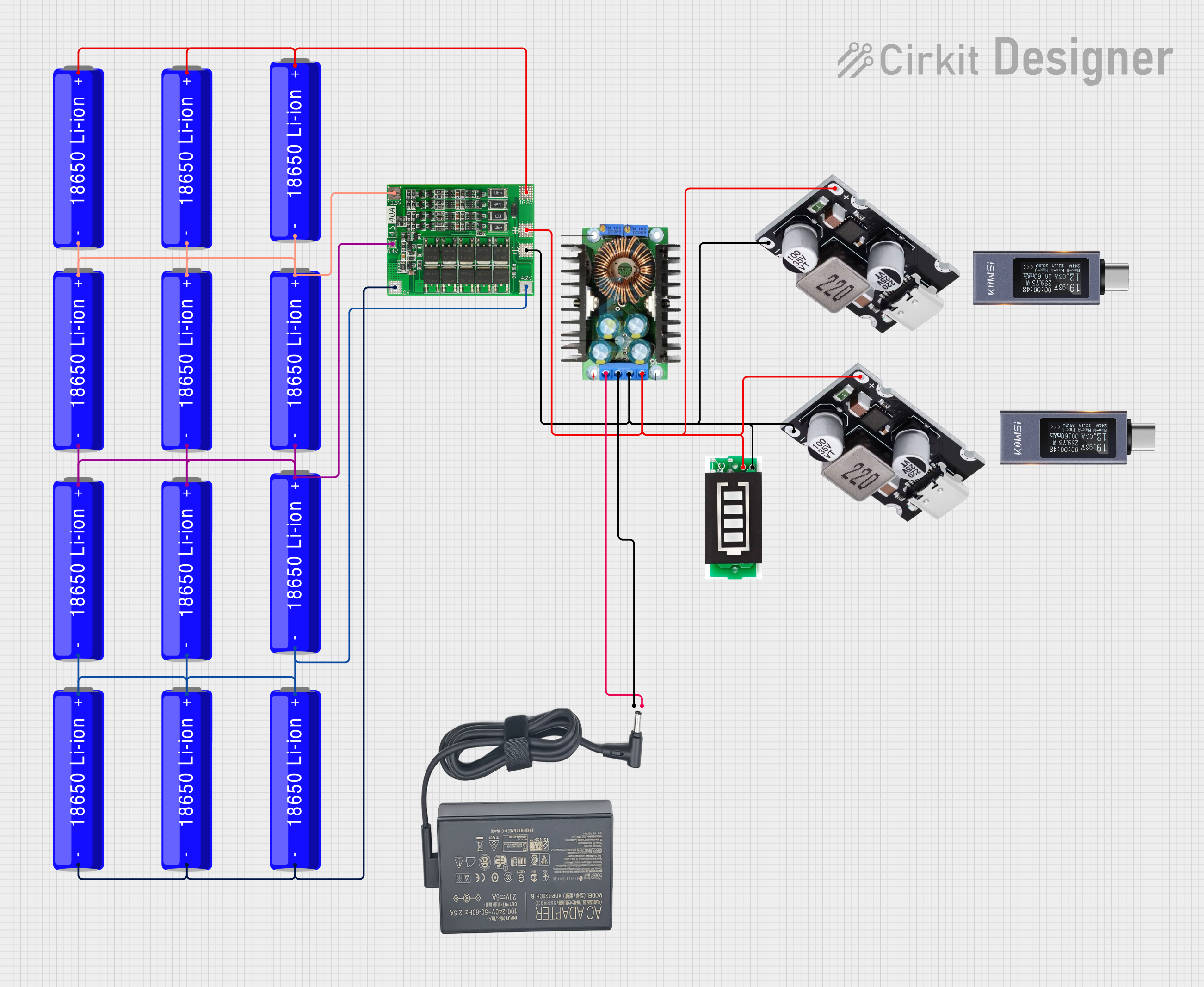
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer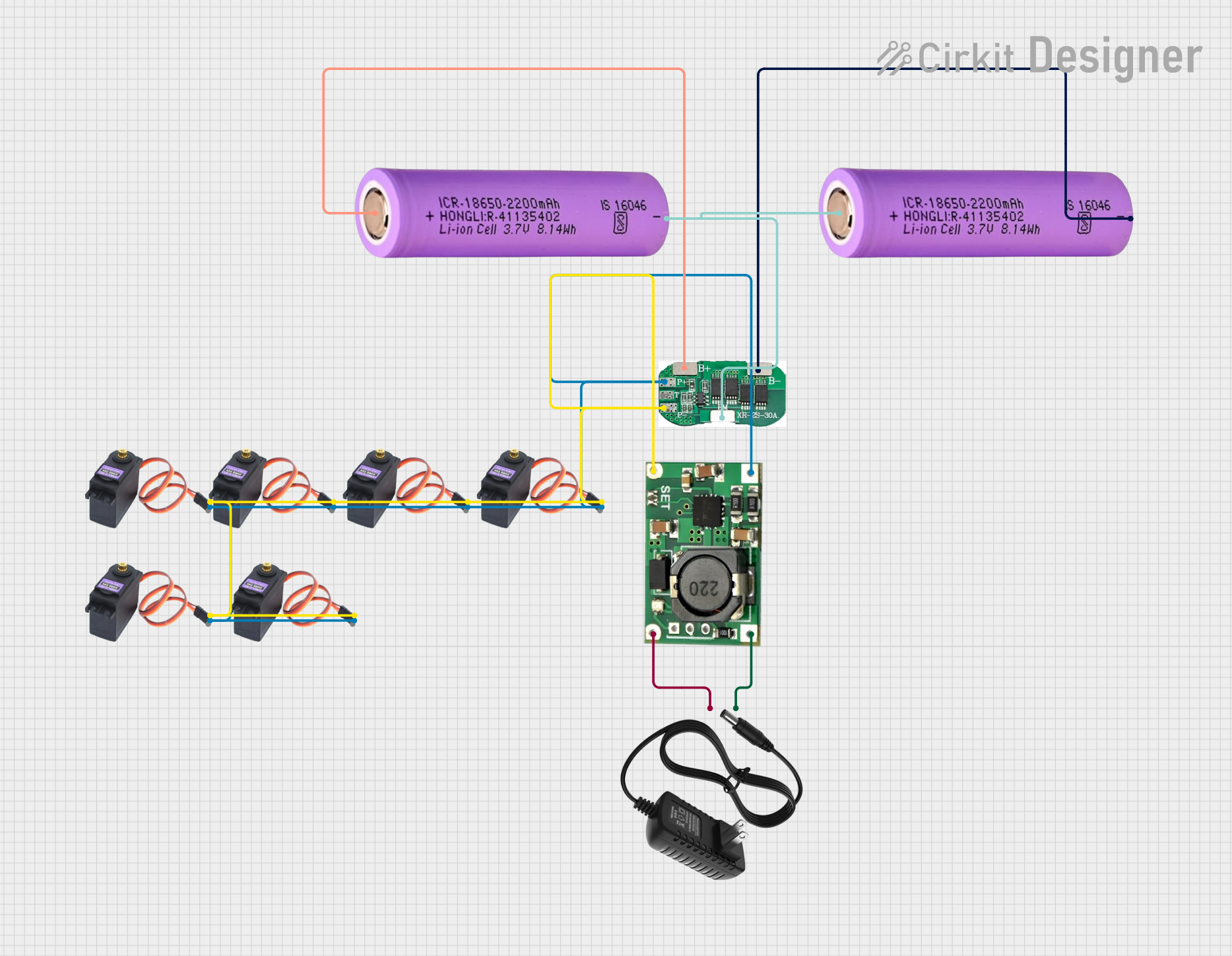
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer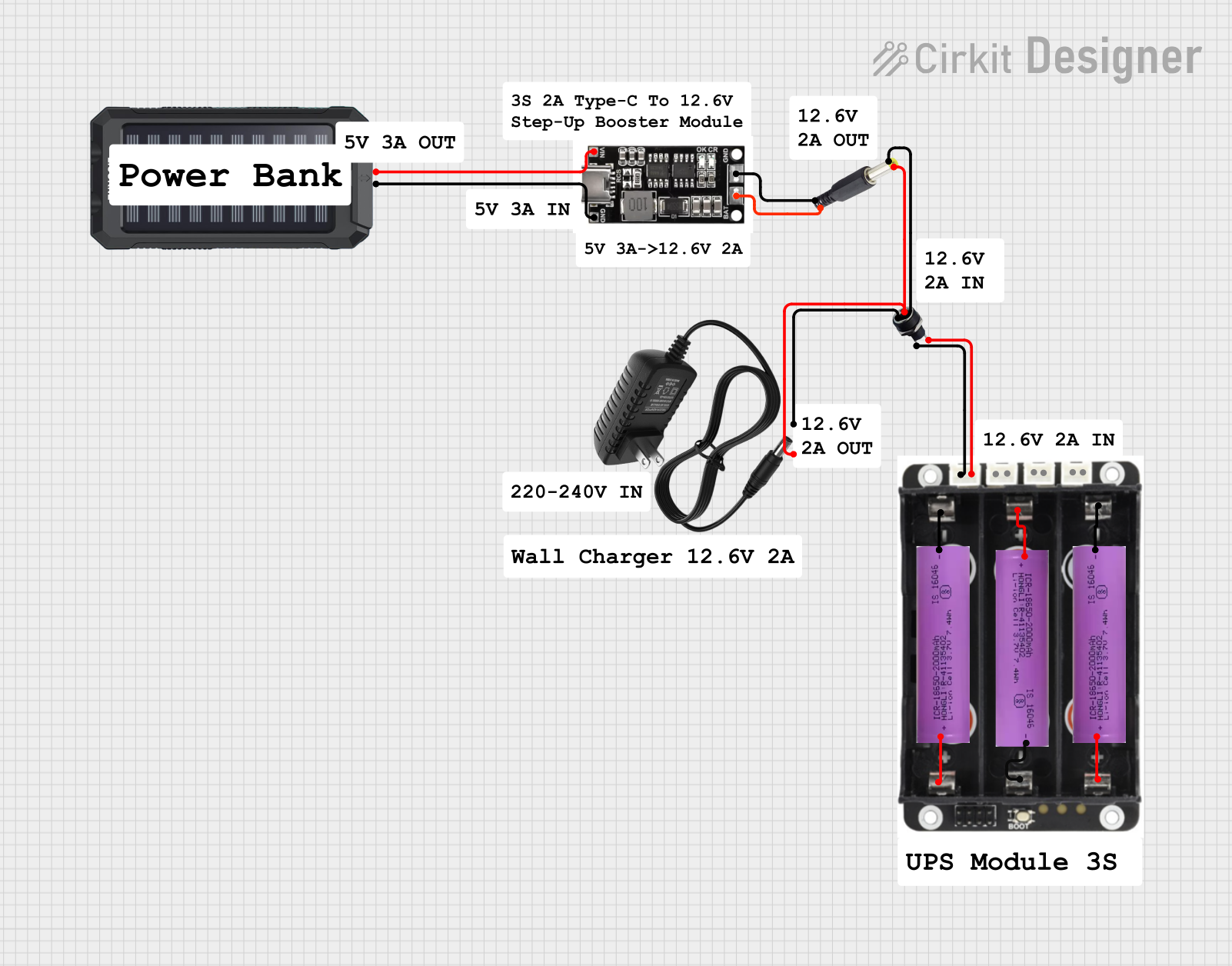
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with SLA BATTERY SMART CHARGER

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Charging SLA batteries used in uninterruptible power supplies (UPS)
- Maintaining batteries in emergency lighting systems
- Charging batteries for mobility scooters, golf carts, and wheelchairs
- Powering backup systems for solar energy storage
- Maintaining automotive and marine SLA batteries
Technical Specifications
The SLA Battery Smart Charger is designed to handle a wide range of SLA battery capacities and includes features to ensure safe and efficient operation.
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage | 100-240V AC, 50/60Hz |
| Output Voltage | 6V/12V DC (selectable) |
| Output Current | 1A, 2A, or 4A (depending on model) |
| Charging Algorithm | 3-stage (Bulk, Absorption, Float) |
| Temperature Compensation | Yes |
| Overcharge Protection | Yes |
| Reverse Polarity Protection | Yes |
| Operating Temperature Range | -10°C to 40°C |
| Dimensions | 120mm x 70mm x 40mm |
| Weight | 300g |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The SLA Battery Smart Charger typically uses a two-pin output connector for connecting to the battery terminals. Below is the description of the pins:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Positive (+) | Connects to the positive terminal of the battery |
| Negative (-) | Connects to the negative terminal of the battery |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Select the Correct Voltage: Ensure the charger is set to the correct output voltage (6V or 12V) based on your SLA battery's specifications.
- Connect the Charger:
- Attach the positive output pin of the charger to the positive terminal of the battery.
- Attach the negative output pin of the charger to the negative terminal of the battery.
- Power On the Charger: Plug the charger into an AC power outlet. The charger will automatically detect the battery's state and begin the charging process.
- Monitor the Charging Status: Most smart chargers have LED indicators to show the charging status:
- Red LED: Charging in progress (Bulk or Absorption stage).
- Green LED: Charging complete (Float stage).
- Disconnect Safely: Once the battery is fully charged, unplug the charger from the AC outlet and disconnect it from the battery.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Battery Compatibility: Ensure the charger is compatible with the capacity and voltage of your SLA battery.
- Ventilation: Use the charger in a well-ventilated area to prevent overheating.
- Temperature Compensation: If the charger has a temperature sensor, place it near the battery to ensure accurate compensation.
- Avoid Overcharging: Do not leave the charger connected to the battery for extended periods unless it has a float mode.
- Polarity Check: Always double-check the polarity of the connections to avoid damage to the battery or charger.
Example: Using the Charger with an Arduino UNO
If you are using the SLA battery to power an Arduino UNO, you can monitor the battery's voltage using the Arduino's analog input. Below is an example code snippet:
// Define the analog pin connected to the battery voltage divider
const int batteryPin = A0;
// Define the reference voltage and voltage divider ratio
const float referenceVoltage = 5.0; // Arduino's reference voltage
const float voltageDividerRatio = 11.0; // Example: 10k and 1k resistors
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int analogValue = analogRead(batteryPin); // Read the analog input
// Calculate the battery voltage
float batteryVoltage = (analogValue * referenceVoltage / 1023.0) * voltageDividerRatio;
// Print the battery voltage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.print(batteryVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Note: Use a voltage divider circuit to step down the battery voltage to a safe level for the Arduino's analog input (0-5V). Adjust the
voltageDividerRatioin the code based on your resistor values.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
Charger Not Powering On:
- Cause: No AC power or faulty power cord.
- Solution: Check the AC outlet and ensure the power cord is securely connected.
Battery Not Charging:
- Cause: Incorrect voltage setting or loose connections.
- Solution: Verify the voltage setting matches the battery and check all connections.
Overheating:
- Cause: Poor ventilation or high ambient temperature.
- Solution: Ensure the charger is used in a well-ventilated area and within the specified temperature range.
Reverse Polarity Warning:
- Cause: Battery terminals are connected incorrectly.
- Solution: Disconnect the charger and reconnect with the correct polarity.
LED Indicators Not Working:
- Cause: Faulty charger or LED malfunction.
- Solution: Test the charger with a different battery. If the issue persists, contact the manufacturer.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Always refer to the user manual provided with the charger for specific troubleshooting steps.
- Use a multimeter to verify the output voltage of the charger and the battery's state of charge.
- If the charger has a fuse, check and replace it if necessary.
By following this documentation, you can safely and effectively use the SLA Battery Smart Charger to maintain and extend the life of your SLA batteries.