
How to Use D-Pad: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with D-Pad in Cirkit Designer
Design with D-Pad in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The D-Pad, or Directional Pad, is a directional control interface commonly found on game controllers. It consists of four or more buttons arranged in a cross shape, enabling users to navigate menus or control movement in games. The D-Pad is widely used in gaming consoles, handheld devices, and custom electronics projects requiring directional input.
Explore Projects Built with D-Pad
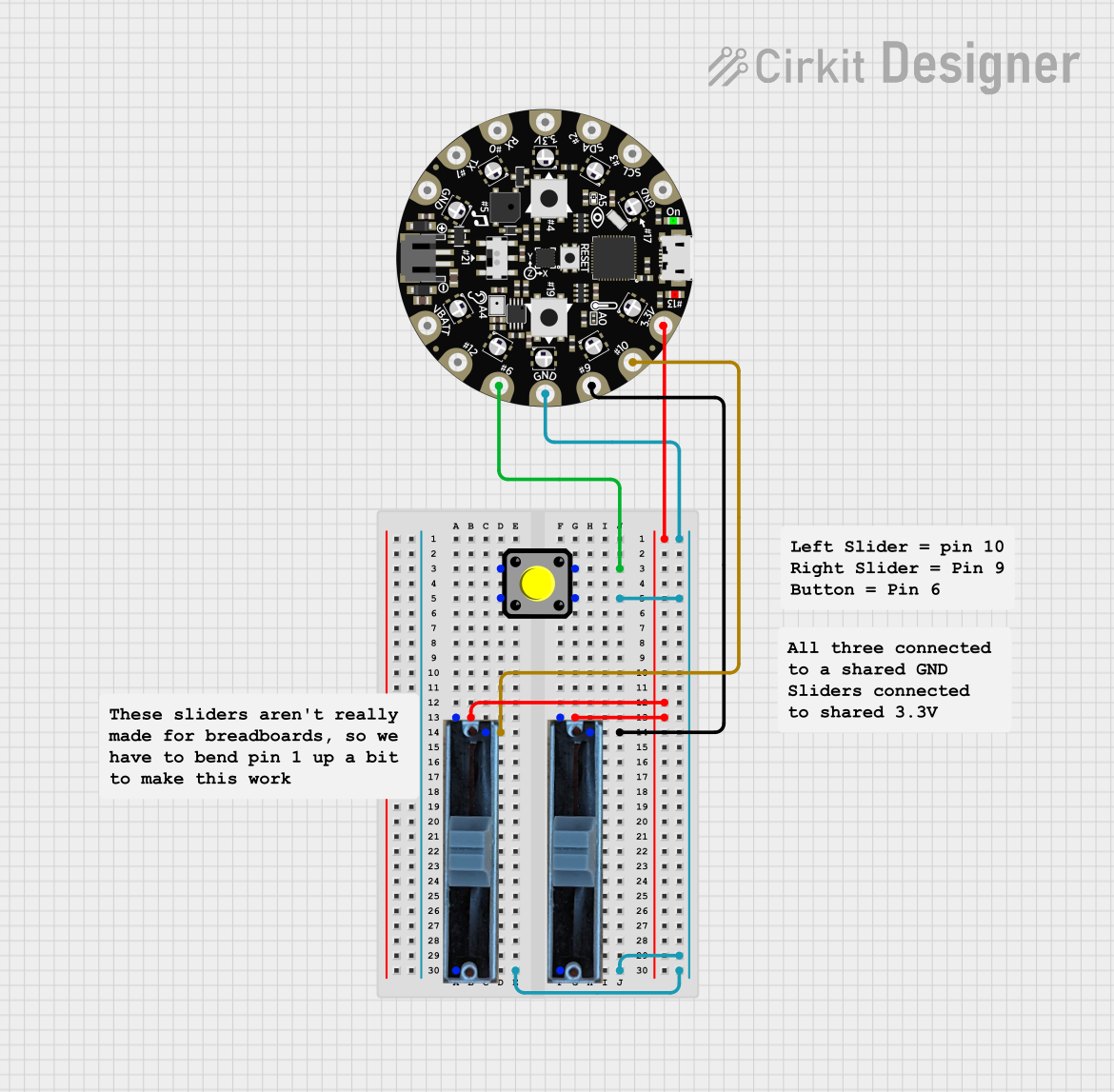
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer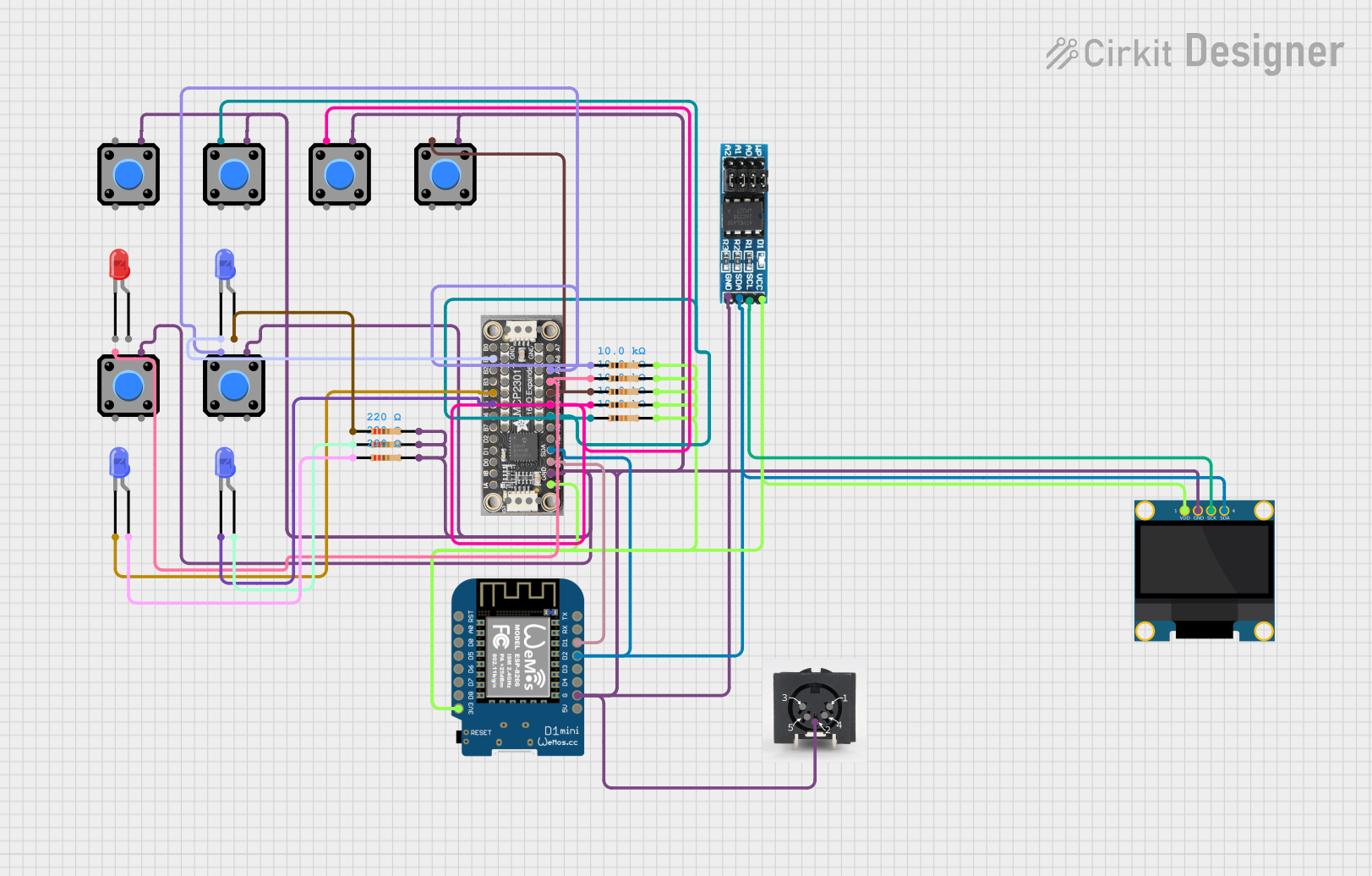
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer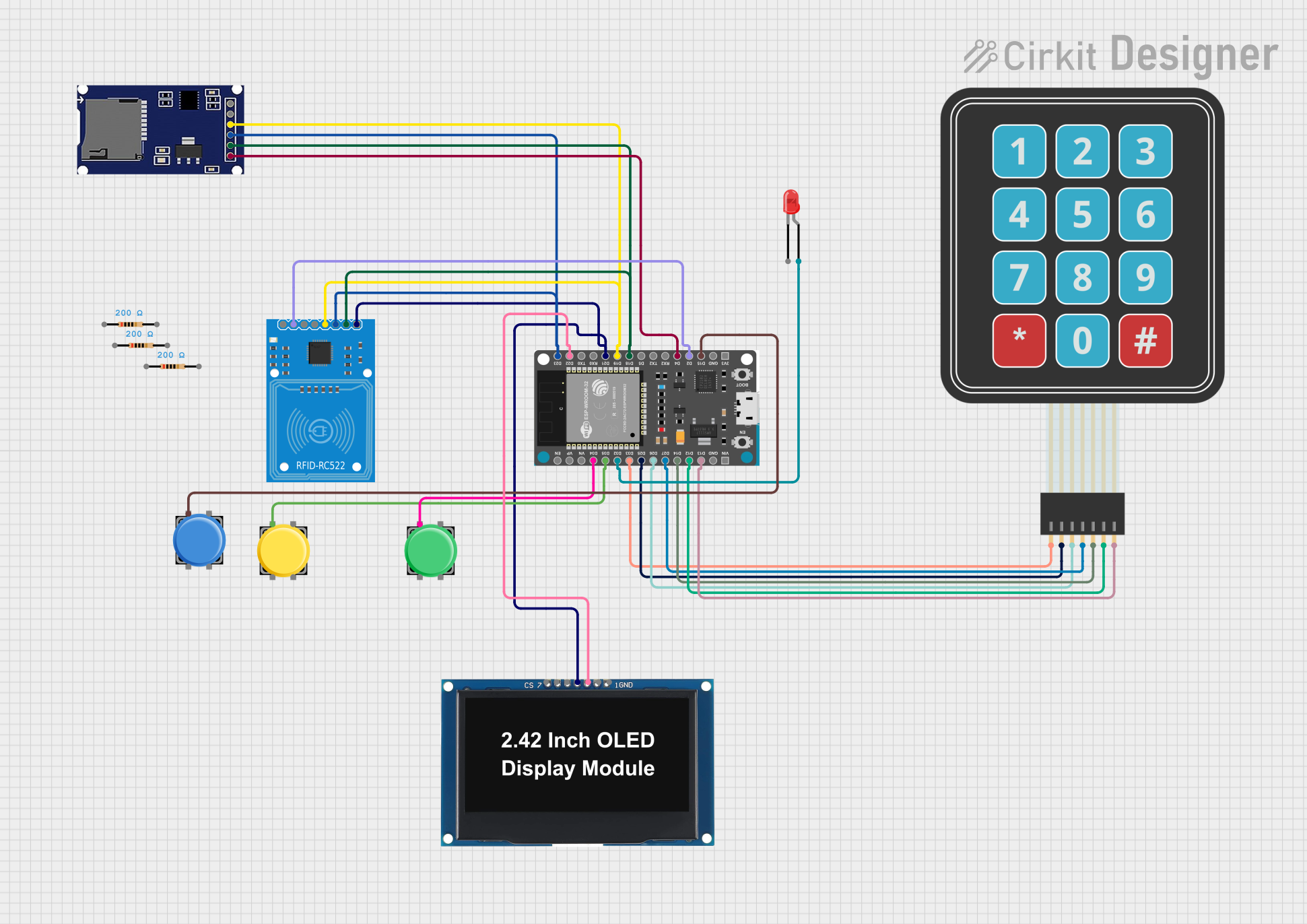
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with D-Pad

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Game controllers for consoles and PCs
- Navigation in user interfaces (e.g., menu selection)
- Robotics and remote control systems
- Custom DIY electronics projects for directional input
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Input Type: Digital (on/off for each direction)
- Number of Buttons: Typically 4 (Up, Down, Left, Right), with optional diagonals
- Voltage Range: 3.3V to 5V (compatible with most microcontrollers)
- Current Consumption: Minimal (depends on pull-up or pull-down resistors)
- Interface: Individual button outputs or matrix configuration
- Debouncing: May require external or software-based debouncing
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The D-Pad typically has 5 pins: one common ground and four directional outputs. Below is a table describing the pin configuration:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Common Ground | Shared ground connection for all buttons. |
| 2 | Up | Output pin for the "Up" button. Connects to ground when pressed. |
| 3 | Down | Output pin for the "Down" button. Connects to ground when pressed. |
| 4 | Left | Output pin for the "Left" button. Connects to ground when pressed. |
| 5 | Right | Output pin for the "Right" button. Connects to ground when pressed. |
Note: Some D-Pads may use a matrix configuration, where multiple buttons share rows and columns. In such cases, additional decoding logic is required.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the D-Pad in a Circuit
Connect the Pins:
- Connect the "Common Ground" pin to the ground (GND) of your circuit.
- Connect each directional pin (Up, Down, Left, Right) to a digital input pin on your microcontroller.
- Use pull-up or pull-down resistors to ensure stable signals when buttons are not pressed.
Read Button States:
- When a button is pressed, its corresponding pin will be pulled to ground.
- Use digital input pins on your microcontroller to detect the button press.
Debouncing:
- Mechanical buttons can produce noise or "bouncing" when pressed or released.
- Implement software-based debouncing or use external capacitors to filter out noise.
Example: Connecting a D-Pad to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect and read a D-Pad using an Arduino UNO:
Circuit Connections
- Connect the "Common Ground" pin of the D-Pad to the GND pin on the Arduino.
- Connect the "Up", "Down", "Left", and "Right" pins to Arduino digital pins 2, 3, 4, and 5, respectively.
- Use internal pull-up resistors in the Arduino code to simplify the circuit.
Arduino Code
// Define pin connections for the D-Pad
const int upPin = 2;
const int downPin = 3;
const int leftPin = 4;
const int rightPin = 5;
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
// Set D-Pad pins as inputs with internal pull-up resistors
pinMode(upPin, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(downPin, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(leftPin, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(rightPin, INPUT_PULLUP);
}
void loop() {
// Read the state of each button (LOW means pressed)
bool upPressed = digitalRead(upPin) == LOW;
bool downPressed = digitalRead(downPin) == LOW;
bool leftPressed = digitalRead(leftPin) == LOW;
bool rightPressed = digitalRead(rightPin) == LOW;
// Print the button states to the Serial Monitor
if (upPressed) {
Serial.println("Up button pressed");
}
if (downPressed) {
Serial.println("Down button pressed");
}
if (leftPressed) {
Serial.println("Left button pressed");
}
if (rightPressed) {
Serial.println("Right button pressed");
}
// Add a small delay to avoid flooding the Serial Monitor
delay(100);
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Debouncing: Always account for button bounce to avoid false triggers.
- Voltage Compatibility: Ensure the D-Pad operates within the voltage range of your microcontroller.
- Pull-Up Resistors: Use internal or external pull-up resistors to stabilize the signal.
- Durability: D-Pads are mechanical components and may wear out over time with heavy use.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Button presses are not detected | Loose or incorrect wiring | Verify all connections and ensure proper grounding. |
| Multiple buttons register simultaneously | Button bounce or matrix misconfiguration | Implement software debouncing or check matrix wiring. |
| Button state is unstable | Missing pull-up or pull-down resistors | Use internal pull-up resistors or add external resistors to stabilize inputs. |
| No response from the D-Pad | Voltage mismatch or damaged component | Ensure voltage compatibility and check for physical damage. |
FAQs
Can I use the D-Pad with a 3.3V microcontroller?
- Yes, most D-Pads are compatible with 3.3V and 5V systems. Verify the specifications of your specific D-Pad.
Do I need external resistors for the D-Pad?
- If your microcontroller supports internal pull-up resistors, external resistors are not necessary. Otherwise, use 10kΩ pull-up resistors.
How do I add diagonal inputs?
- Diagonal inputs can be detected by checking for simultaneous presses of two adjacent buttons (e.g., Up + Right for "Up-Right").
Can I use the D-Pad for analog input?
- No, the D-Pad is a digital input device. For analog input, consider using a joystick.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate a D-Pad into your projects for reliable directional input.