
How to Use HRB Propulsion Battery: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with HRB Propulsion Battery in Cirkit Designer
Design with HRB Propulsion Battery in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The HRB Propulsion Battery is a high-performance lithium polymer (LiPo) battery specifically designed for propulsion systems in remote-controlled (RC) vehicles and drones. Known for its lightweight construction and high discharge rates, this battery ensures optimal power delivery for demanding applications. Its robust design and reliable performance make it a popular choice for hobbyists and professionals alike.
Explore Projects Built with HRB Propulsion Battery
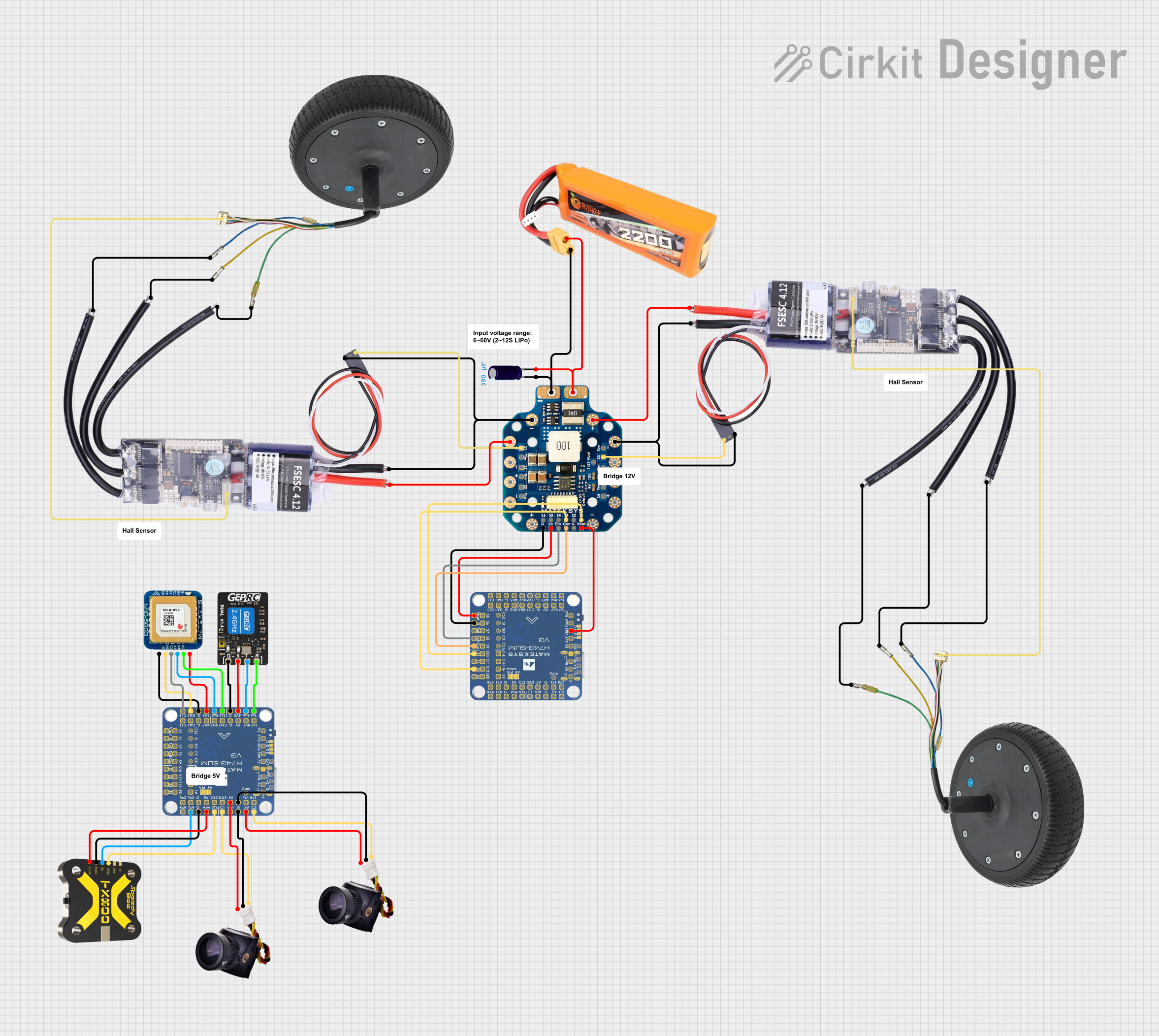
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer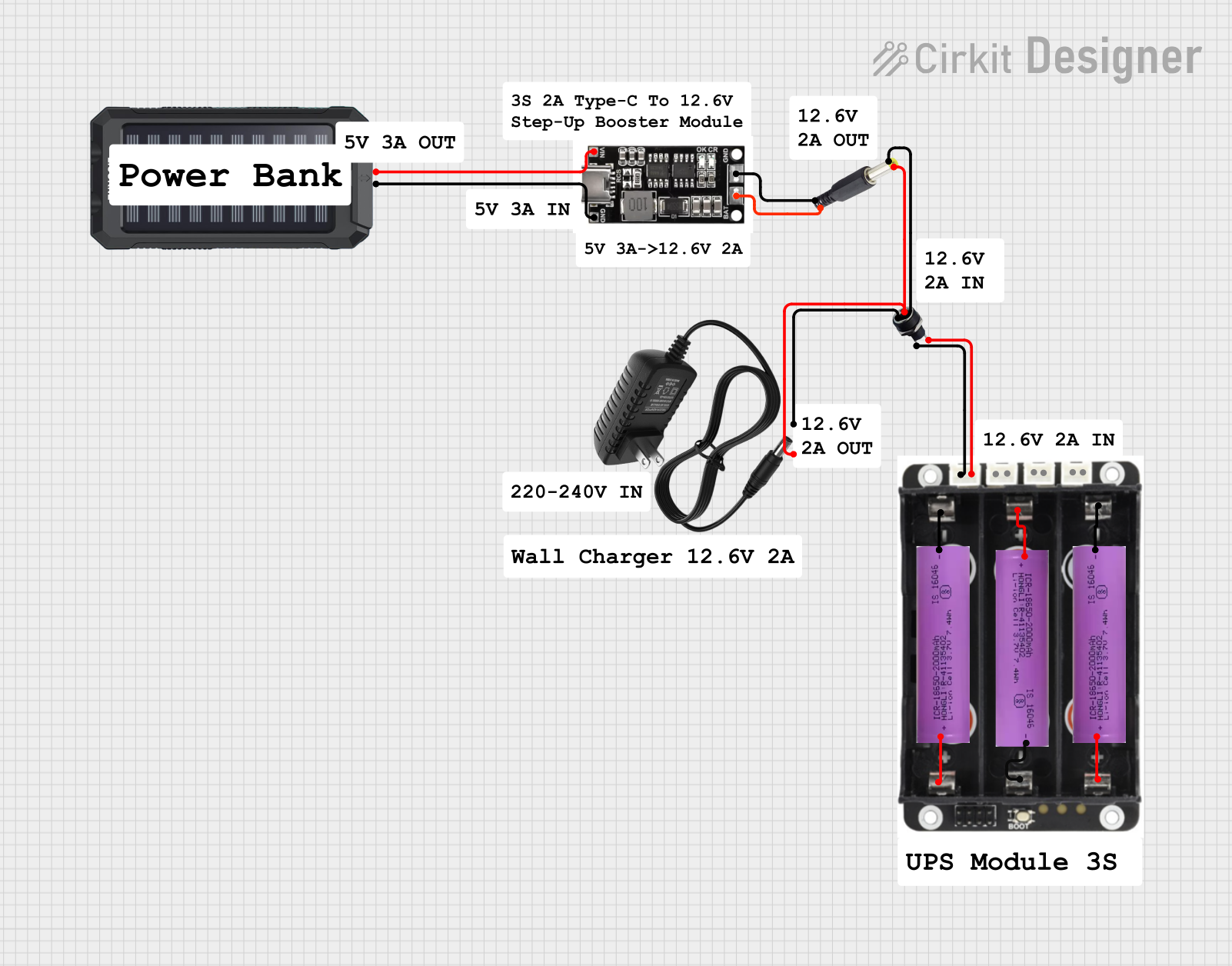
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer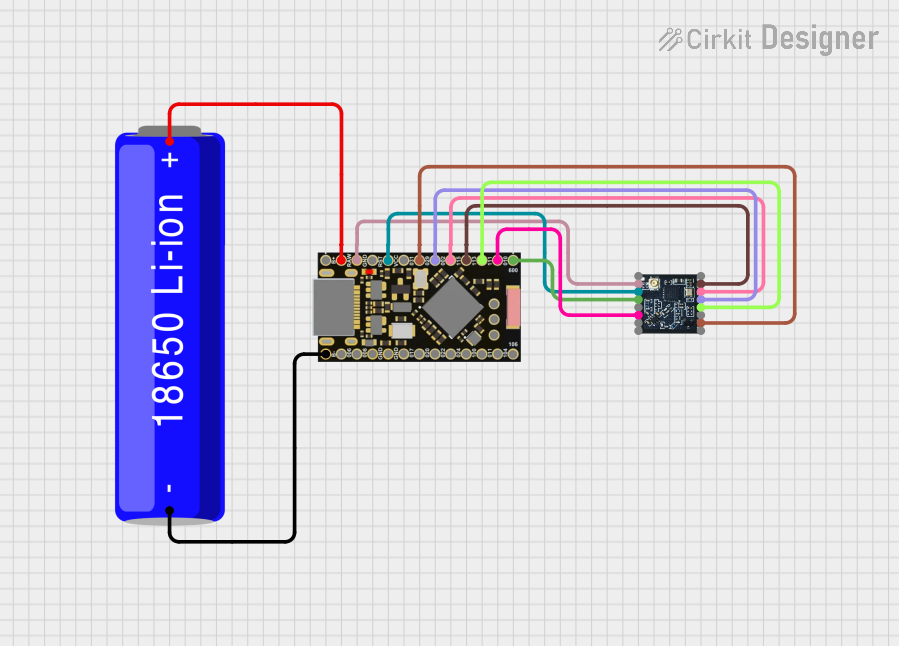
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with HRB Propulsion Battery

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Powering RC cars, boats, and airplanes
- Providing energy for drones and quadcopters
- Supporting high-performance robotics projects
- Used in DIY electric propulsion systems
Technical Specifications
The HRB Propulsion Battery is available in various configurations. Below are the general specifications for a typical model:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Battery Type | Lithium Polymer (LiPo) |
| Nominal Voltage | 11.1V (3S) / 14.8V (4S) / 22.2V (6S) |
| Capacity Range | 2200mAh to 6000mAh |
| Discharge Rate (C-Rating) | 50C to 100C |
| Maximum Charge Voltage | 4.2V per cell |
| Minimum Discharge Voltage | 3.0V per cell |
| Connector Type | XT60, XT90, or Deans T-Plug |
| Weight | Varies by model (e.g., ~400g for 4S) |
| Dimensions | Varies by model (e.g., 140x45x35mm) |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to 60°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The HRB Propulsion Battery typically includes two types of connectors: a power connector and a balance connector. Below is a description of each:
Power Connector (e.g., XT60 or XT90)
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| + | Positive terminal |
| - | Negative terminal |
Balance Connector (JST-XH)
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Negative terminal of Cell 1 |
| 2 | Positive terminal of Cell 1 / Negative of Cell 2 |
| 3 | Positive terminal of Cell 2 / Negative of Cell 3 |
| 4 | Positive terminal of Cell 3 (for 3S battery) |
| 5+ | Additional pins for higher cell counts |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the HRB Propulsion Battery in a Circuit
- Connect the Power Connector: Attach the XT60/XT90 connector to the power input of your RC vehicle, drone, or other propulsion system.
- Balance Charging: Always use a LiPo-compatible balance charger to charge the battery. Connect the balance connector to the charger to ensure all cells are charged evenly.
- Voltage Monitoring: Use a LiPo voltage alarm or monitor to prevent over-discharging, which can damage the battery.
- Secure Mounting: Secure the battery in your vehicle or drone using straps or a battery holder to prevent movement during operation.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Charging Safety: Always charge the battery on a fireproof surface and never leave it unattended while charging.
- Storage: Store the battery at a voltage of 3.7V to 3.85V per cell for long-term storage. Avoid storing in extreme temperatures.
- Discharge Limits: Do not discharge the battery below 3.0V per cell to prevent permanent damage.
- Inspect Regularly: Check for physical damage, swelling, or puffing before each use. Do not use a damaged battery.
- Compatibility: Ensure the battery's voltage and connector type are compatible with your device.
Example: Using the HRB Propulsion Battery with an Arduino UNO
While the HRB Propulsion Battery is primarily used for propulsion systems, it can also power Arduino-based projects with proper voltage regulation. Below is an example of connecting the battery to an Arduino UNO using a voltage regulator:
Circuit Setup
- Use a step-down voltage regulator (e.g., LM2596) to reduce the battery voltage to 5V.
- Connect the regulator's output to the Arduino's 5V and GND pins.
Sample Code
// Example code to read battery voltage using an Arduino UNO
// Ensure a voltage divider is used to step down the battery voltage
// to a safe level for the Arduino's analog input (max 5V).
const int batteryPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the voltage divider
const float voltageDividerRatio = 5.7; // Adjust based on your resistor values
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int rawValue = analogRead(batteryPin); // Read the analog input
float batteryVoltage = (rawValue / 1023.0) * 5.0 * voltageDividerRatio;
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.print(batteryVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Battery Not Charging
- Cause: Faulty charger or damaged balance connector.
- Solution: Check the charger and connectors for damage. Ensure the charger is set to the correct LiPo mode.
Battery Swelling or Puffing
- Cause: Overcharging, over-discharging, or physical damage.
- Solution: Stop using the battery immediately. Dispose of it safely according to local regulations.
Short Runtime
- Cause: Battery capacity is too low for the application or the battery is aging.
- Solution: Use a higher-capacity battery or replace the old battery.
Overheating During Use
- Cause: Excessive current draw or poor ventilation.
- Solution: Ensure the battery's discharge rate (C-rating) matches the application's requirements. Improve airflow around the battery.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the HRB Propulsion Battery for non-propulsion applications?
A: Yes, the battery can be used for any application requiring high-performance LiPo batteries, provided the voltage and current requirements are met.
Q: How do I safely dispose of a damaged LiPo battery?
A: Discharge the battery completely, submerge it in saltwater for 24 hours, and then dispose of it at a designated battery recycling facility.
Q: What is the difference between 3S, 4S, and 6S batteries?
A: The "S" refers to the number of cells in series. A 3S battery has 3 cells (11.1V nominal), a 4S has 4 cells (14.8V nominal), and a 6S has 6 cells (22.2V nominal). Higher cell counts provide higher voltage.