
How to Use arduino uno: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
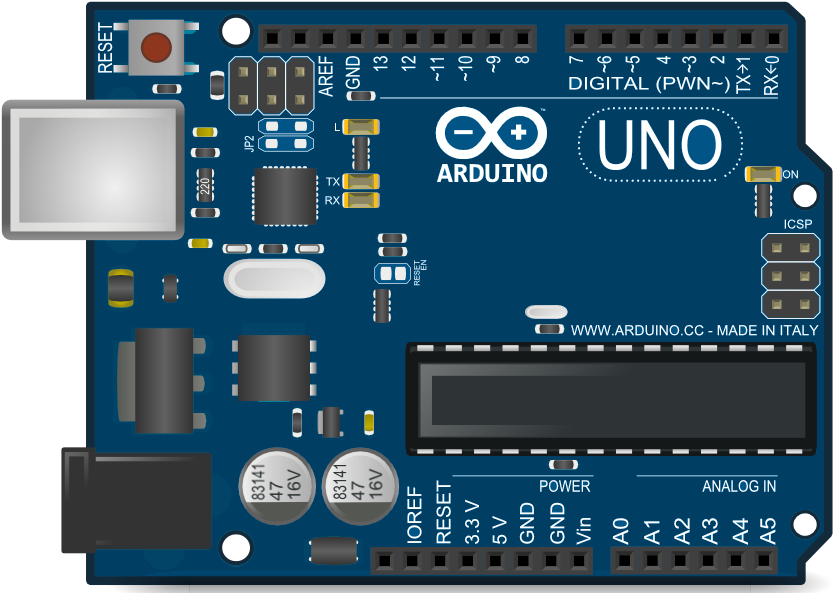
 Design with arduino uno in Cirkit Designer
Design with arduino uno in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Arduino Uno is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P. It is one of the most popular and versatile development boards in the Arduino ecosystem, widely used for building digital devices and interactive objects that can sense and control the physical world. Its simplicity, open-source nature, and extensive community support make it an excellent choice for both beginners and experienced developers.
Explore Projects Built with arduino uno
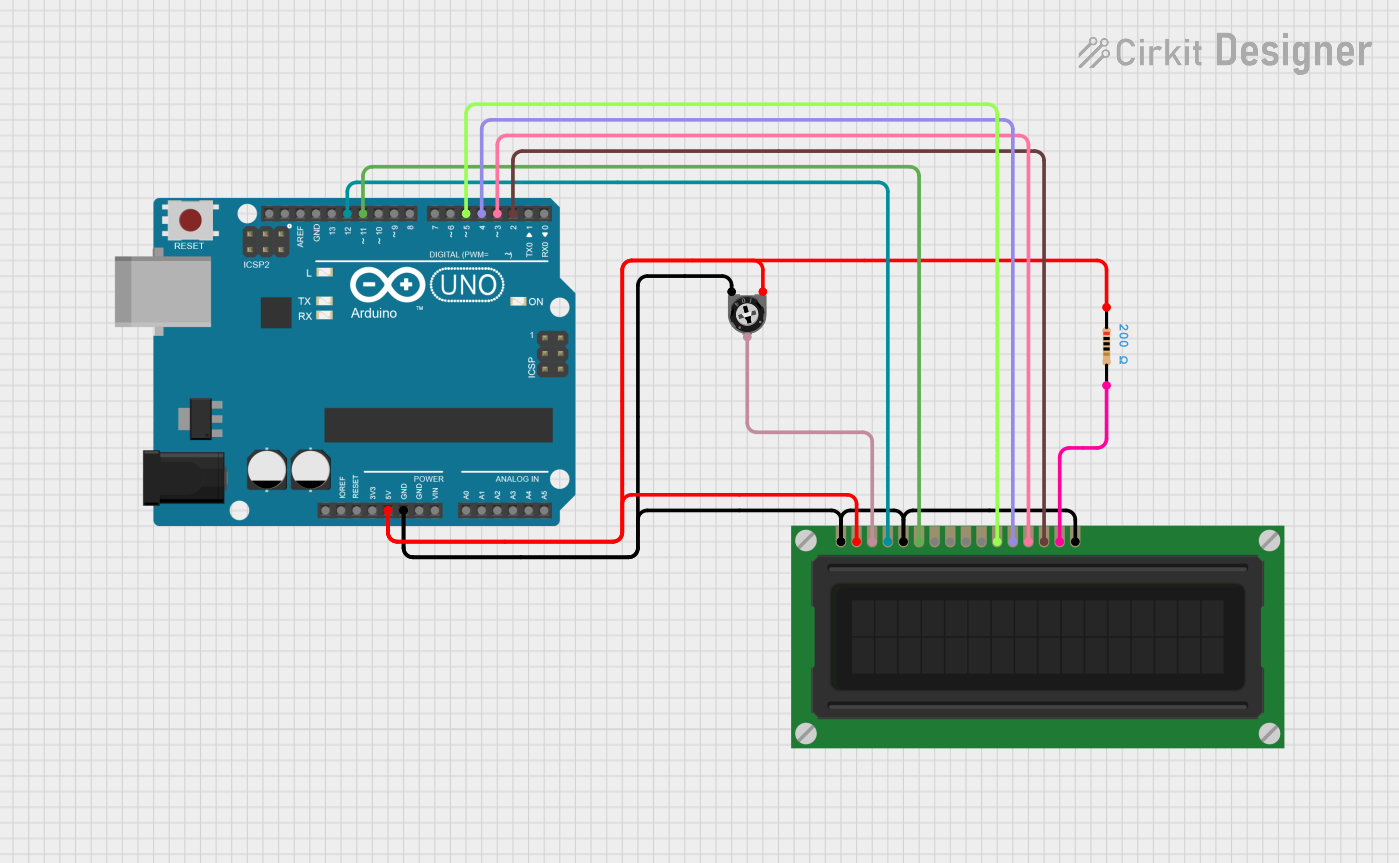
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer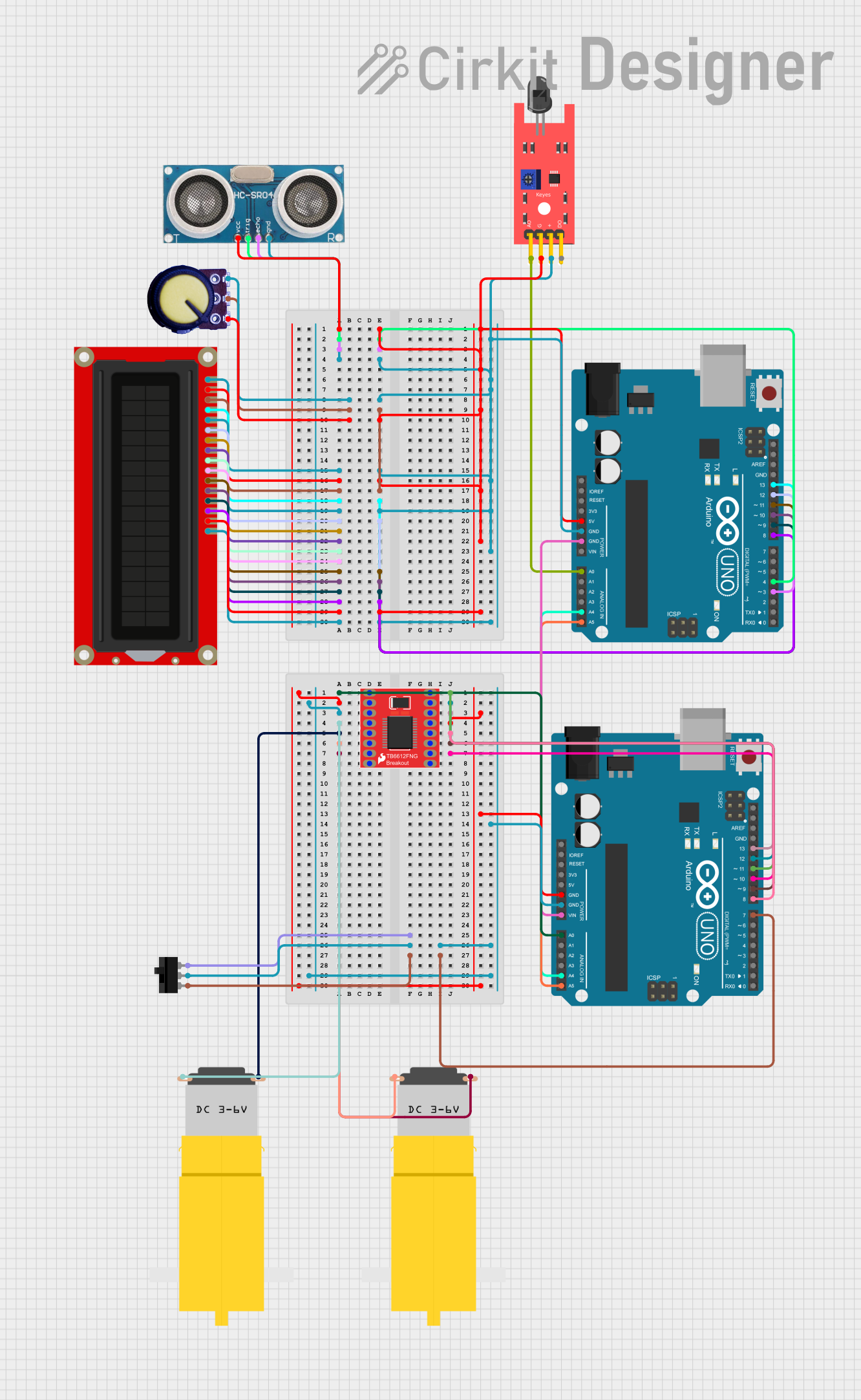
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer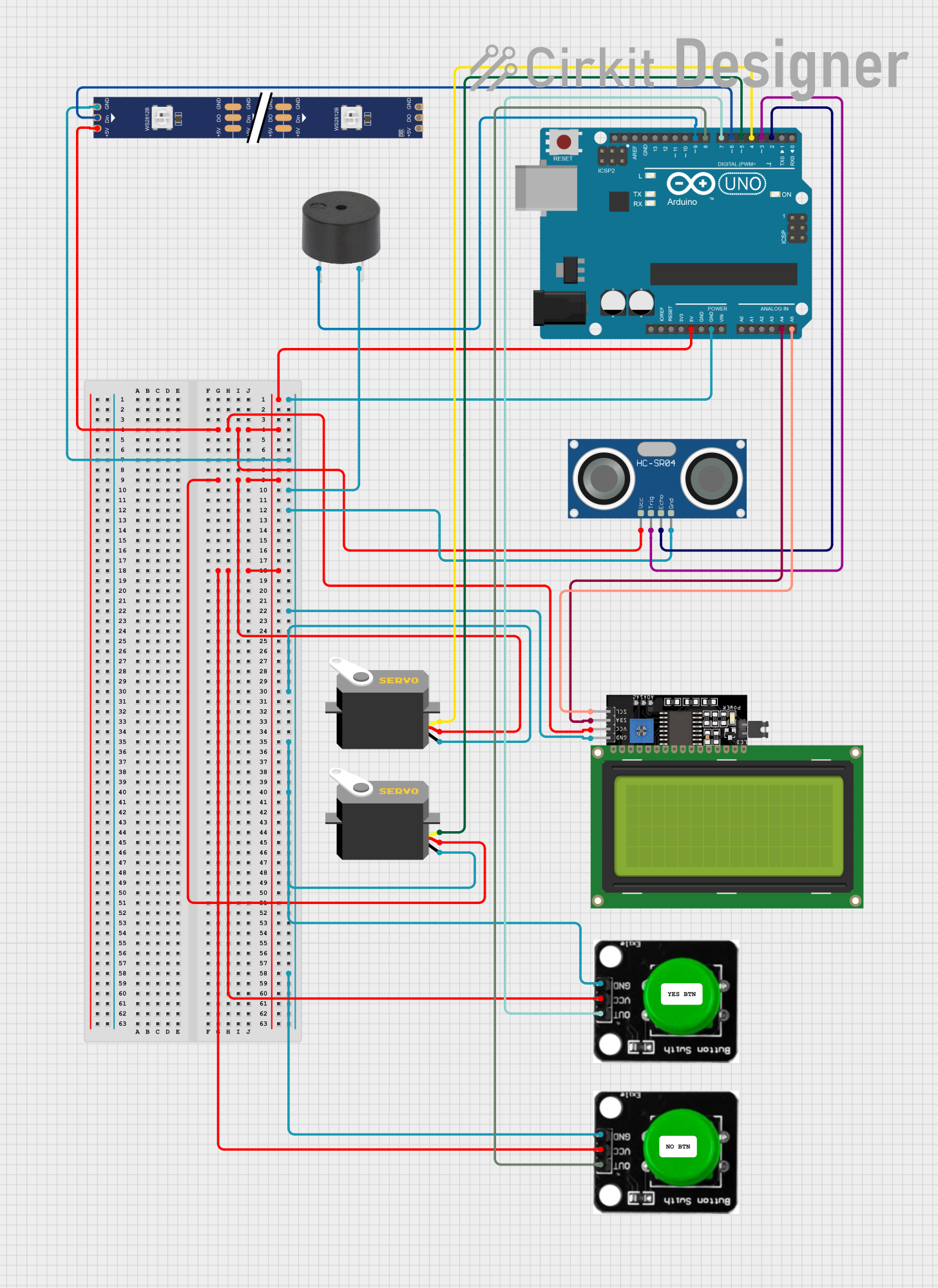
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer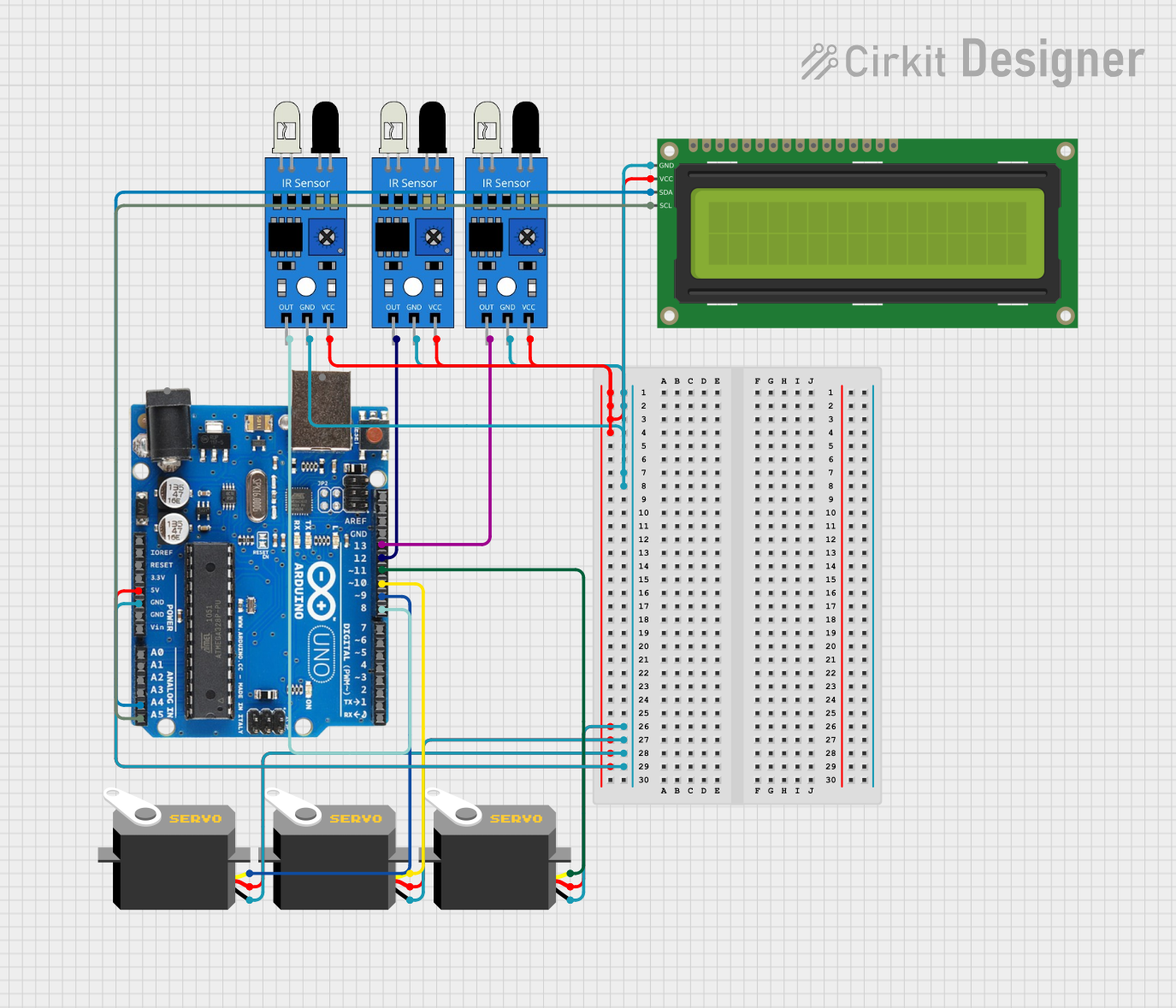
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with arduino uno

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Prototyping and testing electronic circuits
- Building IoT (Internet of Things) devices
- Robotics and automation projects
- Data logging and environmental monitoring
- Interactive art installations
- Educational purposes for learning programming and electronics
Technical Specifications
The Arduino Uno is designed to provide a balance of functionality and ease of use. Below are its key technical details:
Key Technical Details
- Microcontroller: ATmega328P
- Operating Voltage: 5V
- Input Voltage (recommended): 7-12V
- Input Voltage (limit): 6-20V
- Digital I/O Pins: 14 (6 of which provide PWM output)
- Analog Input Pins: 6
- DC Current per I/O Pin: 20 mA
- Flash Memory: 32 KB (0.5 KB used by bootloader)
- SRAM: 2 KB
- EEPROM: 1 KB
- Clock Speed: 16 MHz
- USB Connector: Type-B
- Dimensions: 68.6 mm x 53.4 mm
- Weight: 25 g
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Arduino Uno has a total of 28 pins, including digital, analog, power, and communication pins. Below is a detailed breakdown:
Digital Pins
| Pin Number | Functionality | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 (RX) | UART Receive | Used for serial communication (RXD). |
| 1 (TX) | UART Transmit | Used for serial communication (TXD). |
| 2-13 | General Purpose Digital I/O | Configurable as input or output. |
| 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 11 | PWM Output | Provides Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) output. |
Analog Pins
| Pin Number | Functionality | Description |
|---|---|---|
| A0-A5 | Analog Input | Reads analog signals (0-5V). |
Power Pins
| Pin Name | Functionality | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VIN | Input Voltage | External power input (7-12V recommended). |
| 5V | Regulated 5V Output | Powers external components. |
| 3.3V | Regulated 3.3V Output | Powers low-voltage components. |
| GND | Ground | Common ground for the circuit. |
| IOREF | I/O Reference Voltage | Provides voltage reference for I/O pins. |
| RESET | Reset | Resets the microcontroller. |
Communication Pins
| Pin Name | Functionality | Description |
|---|---|---|
| SDA | I2C Data Line | Used for I2C communication. |
| SCL | I2C Clock Line | Used for I2C communication. |
| SPI (10-13) | SPI Communication | Used for SPI communication. |
Usage Instructions
The Arduino Uno is straightforward to use and can be programmed using the Arduino IDE. Below are the steps to get started and some best practices:
How to Use the Arduino Uno in a Circuit
Power the Board:
- Connect the Arduino Uno to your computer using a USB Type-B cable.
- Alternatively, use an external power supply (7-12V) via the VIN pin or DC barrel jack.
Install the Arduino IDE:
- Download and install the Arduino IDE from the official Arduino website.
- Ensure the correct drivers are installed for the Arduino Uno.
Write and Upload Code:
- Open the Arduino IDE and select the correct board (
Arduino Uno) and port from theToolsmenu. - Write your code in the IDE or use one of the built-in examples.
- Click the "Upload" button to transfer the code to the board.
- Open the Arduino IDE and select the correct board (
Connect Components:
- Use jumper wires to connect sensors, actuators, and other components to the appropriate pins.
- Ensure proper grounding and voltage levels to avoid damage.
Test the Circuit:
- Power the board and observe the behavior of your circuit.
- Use the Serial Monitor in the Arduino IDE for debugging and data visualization.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid drawing more than 20 mA from any single I/O pin to prevent damage.
- Use external pull-up or pull-down resistors for stable digital input signals.
- When using motors or high-power devices, use a separate power supply and appropriate driver circuits.
- Always double-check connections to avoid short circuits or incorrect wiring.
- Use the onboard LED (connected to pin 13) for quick testing and debugging.
Example Code for Arduino Uno
Below is a simple example to blink the onboard LED:
// This program blinks the onboard LED connected to pin 13
// at a 1-second interval.
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output pin
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
The Arduino Uno is not detected by the computer:
- Ensure the USB cable is properly connected and functional.
- Check if the correct drivers are installed for the Arduino Uno.
- Try a different USB port or cable.
Code does not upload to the board:
- Verify that the correct board (
Arduino Uno) and port are selected in the Arduino IDE. - Ensure no other program is using the COM port.
- Press the reset button on the board before uploading.
- Verify that the correct board (
The board is not powering on:
- Check the power source and ensure it meets the voltage requirements.
- Inspect the USB cable or external power supply for faults.
Components connected to the board are not working:
- Double-check the wiring and connections.
- Ensure the components are compatible with the Arduino Uno's voltage and current ratings.
FAQs
Can I power the Arduino Uno with batteries? Yes, you can use a 9V battery connected to the DC barrel jack or VIN pin.
What is the maximum current the Arduino Uno can supply? The 5V pin can supply up to 500 mA when powered via USB, but it is recommended to stay below this limit.
Can I use the Arduino Uno for wireless communication? Yes, you can use external modules like Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or RF transceivers for wireless communication.
Is the Arduino Uno compatible with shields? Yes, the Arduino Uno is compatible with a wide range of shields designed for the Arduino ecosystem.