
How to Use 4 pack 1s4p battery: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 4 pack 1s4p battery in Cirkit Designer
Design with 4 pack 1s4p battery in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 4 Pack 1S4P Battery is a configuration of four individual cells connected in parallel (4P) with a single series connection (1S). This arrangement increases the overall capacity of the battery while maintaining the same voltage as a single cell. The 1S4P configuration is ideal for applications requiring extended runtime without increasing the voltage level.
Explore Projects Built with 4 pack 1s4p battery
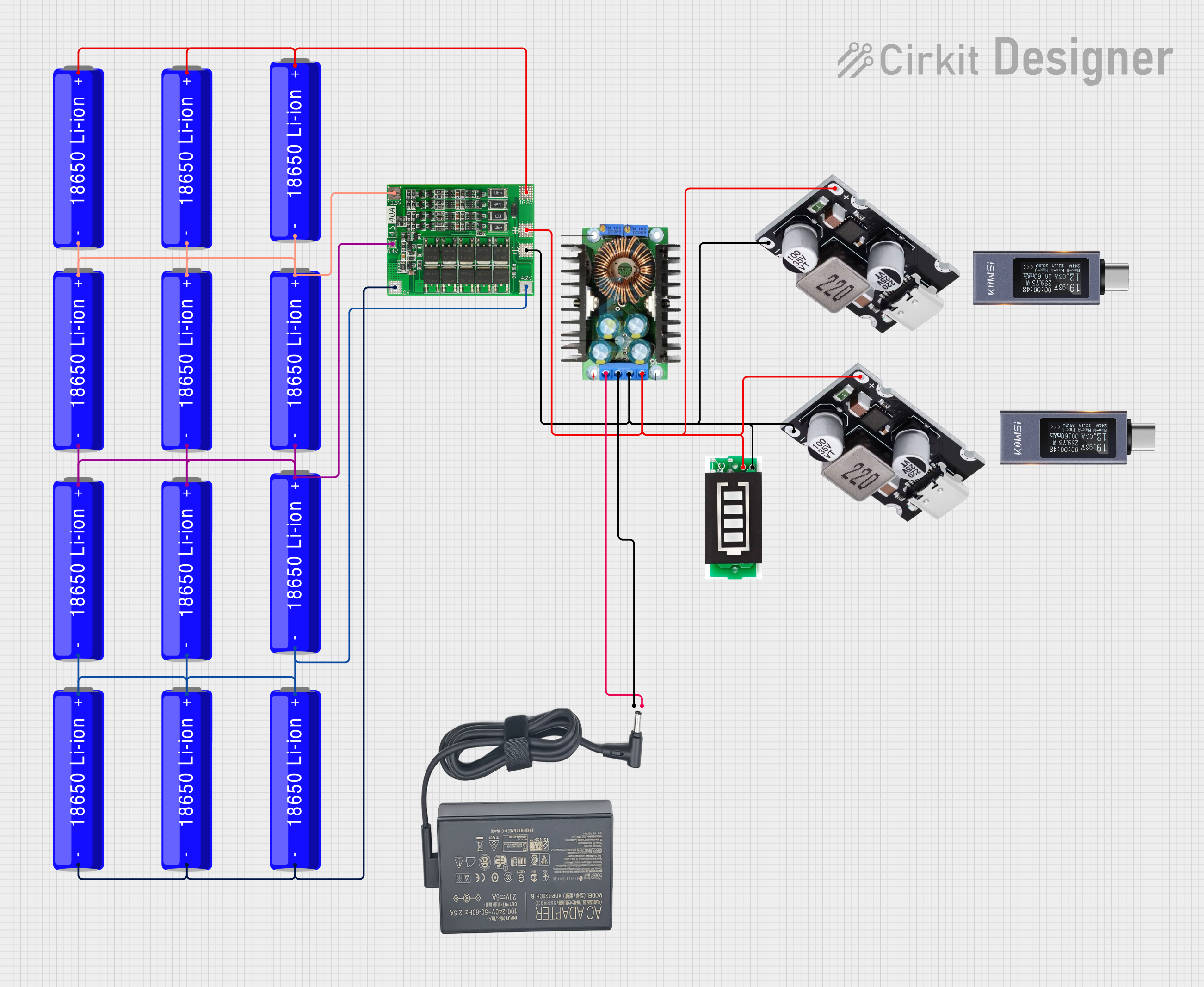
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer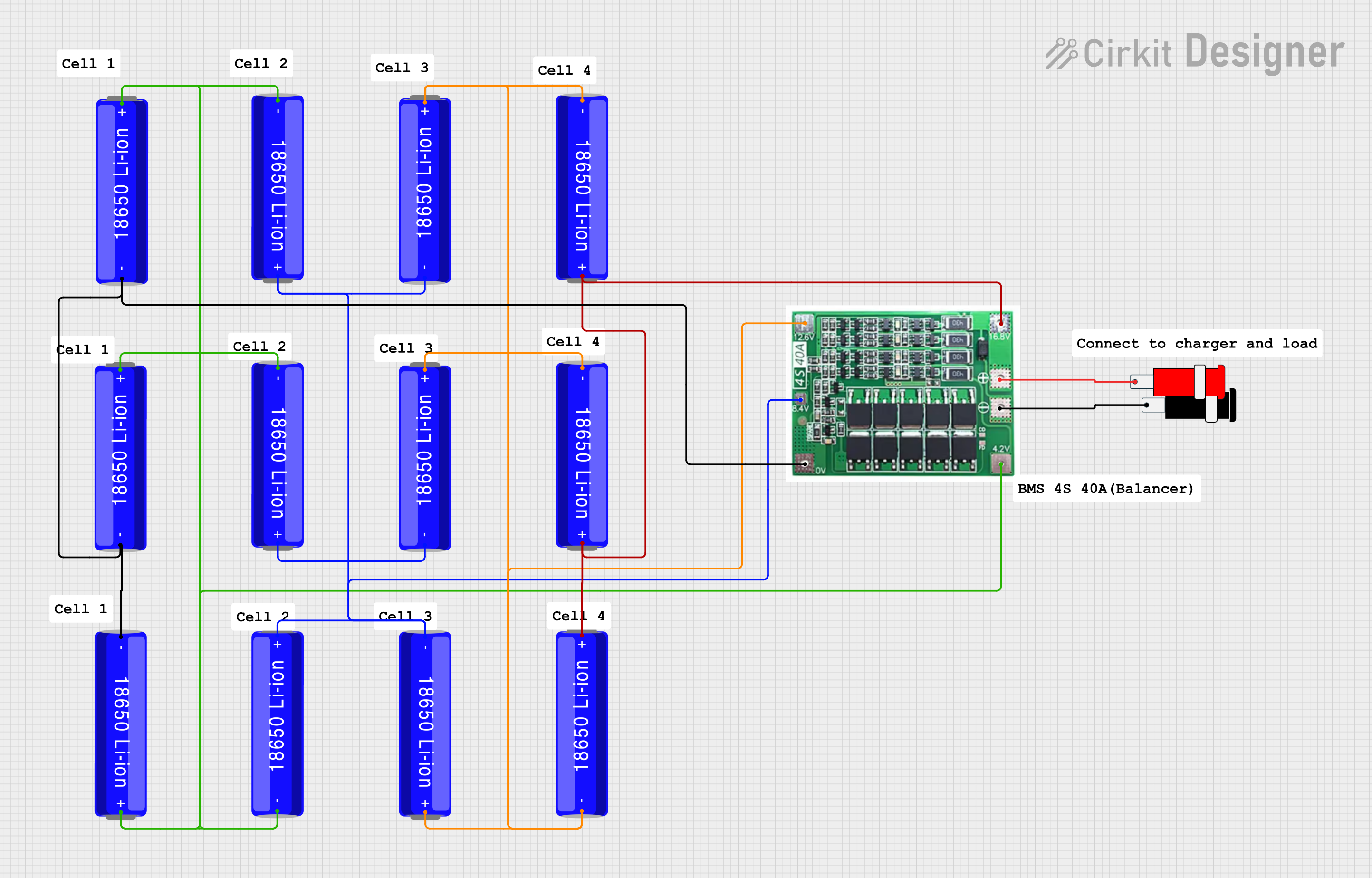
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 4 pack 1s4p battery

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Portable electronic devices (e.g., handheld tools, flashlights)
- Power banks and backup power systems
- Low-power robotics and IoT devices
- Renewable energy storage (e.g., solar-powered systems)
- Electric vehicles with low-voltage requirements
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical specifications of the 4 Pack 1S4P Battery:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Nominal Voltage | Same as a single cell (e.g., 3.7V for Li-ion) |
| Capacity | 4 times the capacity of a single cell |
| Configuration | 1 Series, 4 Parallel (1S4P) |
| Maximum Discharge Current | Sum of the maximum discharge currents of all cells |
| Charging Voltage | Same as a single cell (e.g., 4.2V for Li-ion) |
| Charging Current | Should not exceed the combined safe charging current of all cells |
| Dimensions | Varies based on cell size and packaging |
| Weight | Approximately 4 times the weight of a single cell |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The 4 Pack 1S4P Battery typically has two terminals for connection:
| Pin | Label | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Positive (+) | Positive terminal of the battery pack |
| 2 | Negative (-) | Negative terminal of the battery pack |
Some battery packs may include additional pins for features like temperature monitoring or balancing. Refer to the specific datasheet for such configurations.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the 4 Pack 1S4P Battery in a Circuit
- Connection: Connect the positive terminal of the battery pack to the positive rail of your circuit and the negative terminal to the ground rail.
- Charging: Use a charger designed for the specific chemistry of the cells (e.g., Li-ion, NiMH). Ensure the charger supports the combined capacity and voltage of the 1S4P configuration.
- Load Compatibility: Ensure the load does not exceed the maximum discharge current of the battery pack.
- Protection Circuit: Use a Battery Management System (BMS) to prevent overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Cell Matching: Ensure all cells in the pack have the same capacity, internal resistance, and state of charge to avoid imbalances.
- Thermal Management: Monitor the temperature of the battery pack during operation and charging to prevent overheating.
- Storage: Store the battery pack in a cool, dry place at a partial charge (e.g., 40-60%) to prolong its lifespan.
- Safety: Avoid puncturing, short-circuiting, or exposing the battery pack to water or fire.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
The 4 Pack 1S4P Battery can be used to power an Arduino UNO via its VIN pin. Ensure the battery voltage matches the Arduino's input voltage requirements (e.g., 5V with a step-up converter if necessary).
// Example: Reading battery voltage using Arduino UNO
// This code assumes the battery is connected to an analog pin via a voltage divider.
const int batteryPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the voltage divider
const float voltageDividerRatio = 2.0; // Adjust based on your resistor values
const float referenceVoltage = 5.0; // Arduino's reference voltage (5V for UNO)
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int rawValue = analogRead(batteryPin); // Read the analog value
float batteryVoltage = (rawValue / 1023.0) * referenceVoltage * voltageDividerRatio;
// Print the battery voltage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.print(batteryVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Note: Use a voltage divider to scale down the battery voltage if it exceeds the Arduino's analog input range (0-5V).
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Battery Pack Not Charging
- Cause: Charger not compatible with the battery chemistry or capacity.
- Solution: Use a charger specifically designed for the battery type and configuration.
Uneven Cell Voltages
- Cause: Cells are not properly matched or balanced.
- Solution: Use a BMS with cell balancing or manually balance the cells before assembly.
Overheating During Operation
- Cause: Excessive current draw or poor thermal management.
- Solution: Reduce the load or improve ventilation around the battery pack.
Short Runtime
- Cause: Degraded cells or excessive self-discharge.
- Solution: Replace damaged cells and ensure proper storage conditions.
FAQs
Q: Can I use different types of cells in a 1S4P configuration?
A: No, all cells should be of the same type, capacity, and internal resistance to ensure safe and efficient operation.
Q: How do I calculate the total capacity of the 1S4P battery pack?
A: Multiply the capacity of a single cell by the number of parallel cells (e.g., 4 cells × 2500mAh = 10,000mAh).
Q: Is a BMS necessary for a 1S4P battery pack?
A: Yes, a BMS is highly recommended to protect the battery pack from overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits.
Q: Can I connect multiple 1S4P packs in series?
A: Yes, but ensure each pack has a BMS and the same voltage and capacity to avoid imbalances.