
How to Use PCM1808: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
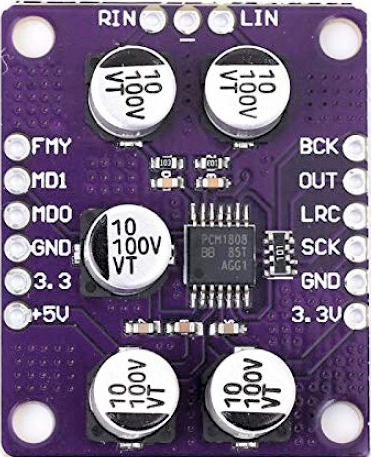
 Design with PCM1808 in Cirkit Designer
Design with PCM1808 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The PCM1808 is a 24-bit audio analog-to-digital converter (ADC) designed for high-performance audio applications. It converts analog audio signals into high-resolution digital data, ensuring low distortion and high dynamic range. This makes the PCM1808 an ideal choice for professional audio equipment, consumer electronics, and other audio processing systems.
Explore Projects Built with PCM1808

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer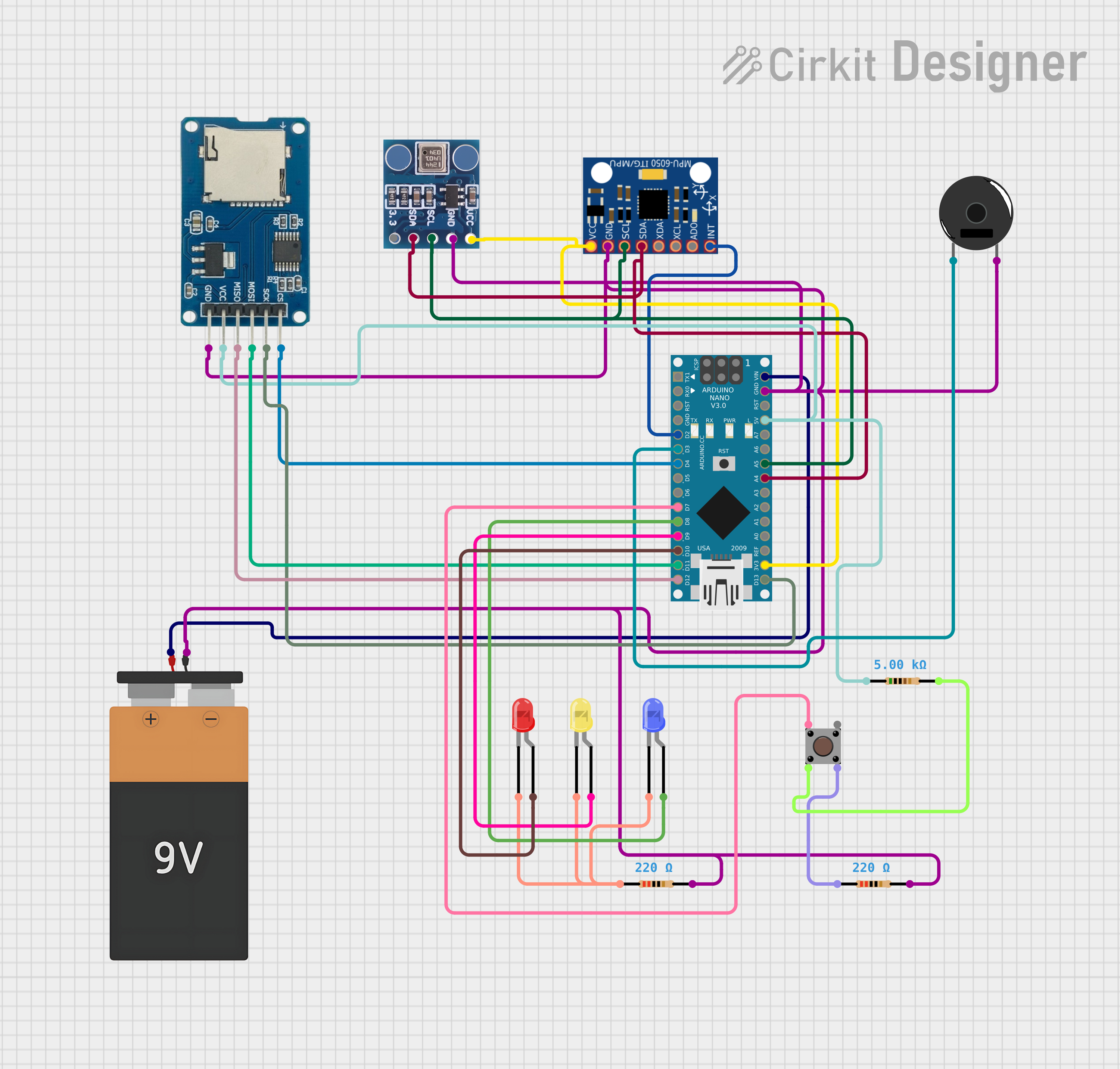
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer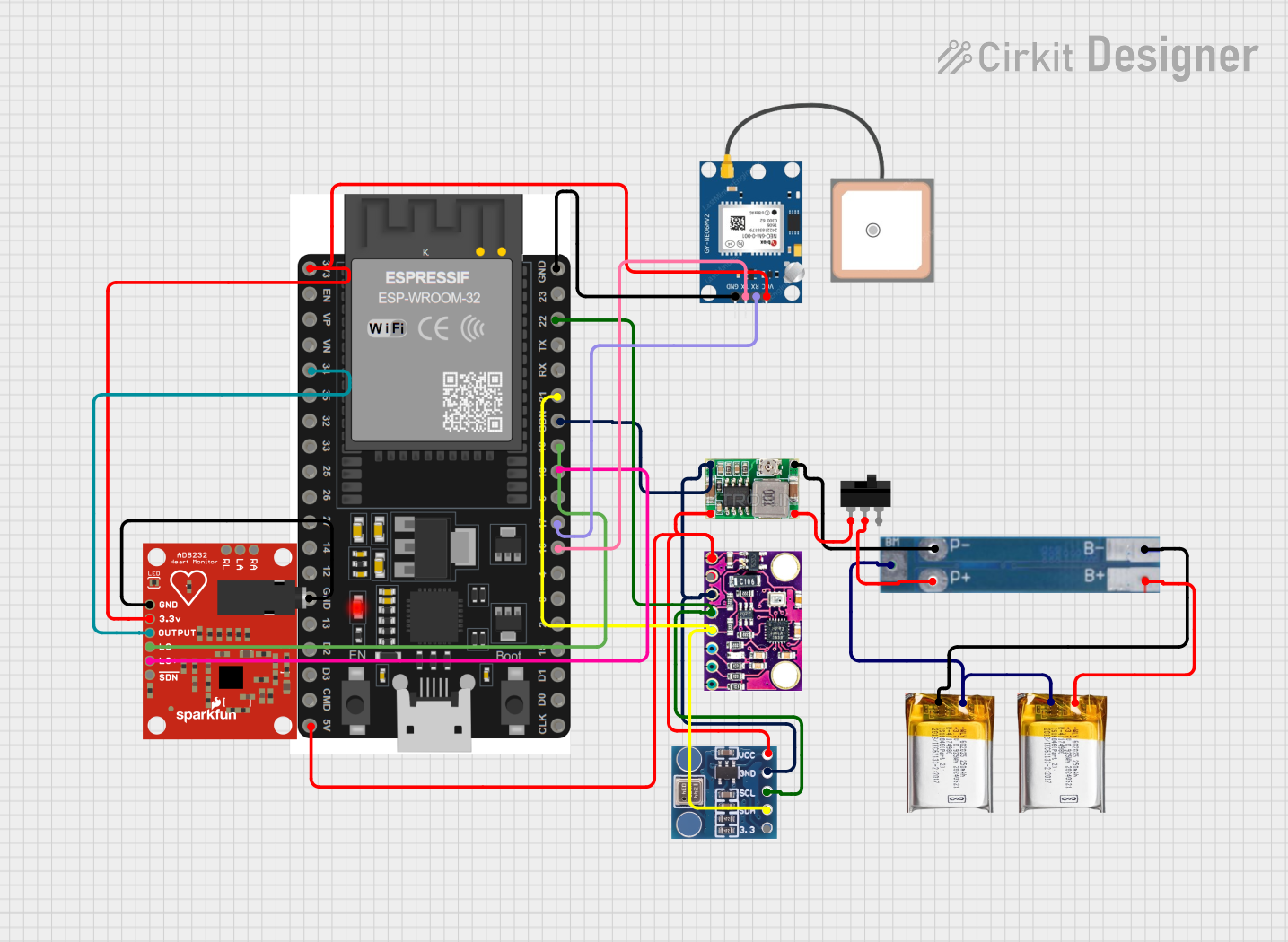
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with PCM1808

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Professional audio recording equipment
- Consumer audio devices (e.g., home theater systems, audio interfaces)
- Digital audio processing systems
- Musical instruments with digital output
- Voice recognition systems
Technical Specifications
The PCM1808 is a highly efficient ADC with the following key technical details:
Key Technical Details
- Resolution: 24-bit
- Sampling Rate: Supports up to 96 kHz
- Dynamic Range: 99 dB (typical)
- Total Harmonic Distortion (THD+N): -93 dB (typical)
- Input Voltage Range: 0.6 Vpp to 2.1 Vpp (differential)
- Power Supply Voltage:
- Analog: 5 V
- Digital: 3.3 V
- Power Consumption: 20 mW (typical)
- Interface: I²S (Inter-IC Sound) or Left-Justified Serial Audio Data
- Package: 14-pin TSSOP (Thin Shrink Small Outline Package)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The PCM1808 comes in a 14-pin TSSOP package. Below is the pin configuration and description:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | VINL | Analog Input | Left-channel analog audio input (differential positive) |
| 2 | VINR | Analog Input | Right-channel analog audio input (differential positive) |
| 3 | VREF1 | Analog Output | Reference voltage output 1 |
| 4 | VREF2 | Analog Output | Reference voltage output 2 |
| 5 | VCOM | Analog Output | Common voltage output for decoupling |
| 6 | AGND | Ground | Analog ground |
| 7 | VCC | Power Supply | Analog power supply (5 V) |
| 8 | DGND | Ground | Digital ground |
| 9 | SCKI | Digital Input | System clock input |
| 10 | BCK | Digital Input | Bit clock for serial audio data |
| 11 | LRCK | Digital Input | Left-right clock for serial audio data |
| 12 | DOUT | Digital Output | Serial audio data output |
| 13 | FORMAT | Digital Input | Audio data format selection (I²S or Left-Justified) |
| 14 | VDD | Power Supply | Digital power supply (3.3 V) |
Usage Instructions
The PCM1808 is straightforward to use in audio applications. Below are the steps and considerations for integrating it into a circuit:
How to Use the PCM1808 in a Circuit
- Power Supply:
- Connect the analog power supply (5 V) to the VCC pin and the digital power supply (3.3 V) to the VDD pin.
- Ensure proper decoupling capacitors are placed near the power supply pins to reduce noise.
- Analog Inputs:
- Connect the left and right analog audio signals to the VINL and VINR pins, respectively.
- Use differential input signals for optimal performance.
- Clock Signals:
- Provide a system clock (SCKI) to the PCM1808. A typical clock frequency is 256x, 384x, or 512x the sampling rate.
- Connect the bit clock (BCK) and left-right clock (LRCK) to synchronize the audio data.
- Audio Data Output:
- The digital audio data is output through the DOUT pin in the selected format (I²S or Left-Justified).
- Use the FORMAT pin to configure the desired audio data format.
- Reference and Ground:
- Connect the VREF1, VREF2, and VCOM pins to appropriate decoupling capacitors as specified in the datasheet.
- Ensure proper grounding by connecting AGND and DGND to a common ground plane.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Use high-quality capacitors for decoupling to minimize noise and interference.
- Ensure the system clock (SCKI) is stable and within the specified frequency range.
- Avoid long traces for analog input signals to reduce noise pickup.
- Match the impedance of differential input signals for optimal performance.
- If using an Arduino or microcontroller, ensure it supports I²S or Left-Justified audio data formats.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
The PCM1808 can be interfaced with an Arduino UNO using an I²S-compatible module (e.g., I²S breakout board). Below is an example code snippet for reading audio data:
#include <I2S.h> // Include the I2S library for Arduino
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
// Start the I2S interface in receiver mode
if (!I2S.begin(I2S_PHILIPS_MODE, 44100)) {
Serial.println("Failed to initialize I2S!");
while (1); // Halt if initialization fails
}
Serial.println("I2S initialized successfully.");
}
void loop() {
// Check if audio data is available
if (I2S.available()) {
int sample = I2S.read(); // Read a 32-bit audio sample
Serial.println(sample); // Print the sample to the serial monitor
}
}
Note: The Arduino UNO does not natively support I²S. Use an external I²S module or a microcontroller with built-in I²S support (e.g., ESP32).
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Audio Output:
- Ensure the system clock (SCKI) is connected and operating at the correct frequency.
- Verify that the analog input signals are within the specified voltage range.
- Check the connections for the bit clock (BCK) and left-right clock (LRCK).
Distorted Audio:
- Verify that the differential input signals are properly matched and free of noise.
- Ensure the decoupling capacitors are correctly placed and of the recommended value.
No Data on DOUT Pin:
- Confirm that the FORMAT pin is set to the correct audio data format.
- Check the power supply voltages (VCC and VDD) and ensure they are stable.
High Noise or Interference:
- Use a proper ground plane and minimize the length of analog signal traces.
- Shield the analog input signals if operating in a noisy environment.
FAQs
Q1: Can the PCM1808 operate with a single-ended input?
A1: No, the PCM1808 is designed for differential input signals. Single-ended inputs may result in degraded performance.
Q2: What is the maximum sampling rate supported by the PCM1808?
A2: The PCM1808 supports a maximum sampling rate of 96 kHz.
Q3: Can I use the PCM1808 with a 3.3 V analog power supply?
A3: No, the analog power supply (VCC) must be 5 V. The digital power supply (VDD) operates at 3.3 V.
Q4: How do I select between I²S and Left-Justified formats?
A4: Use the FORMAT pin to select the desired format. Refer to the datasheet for the specific pin configuration.
Q5: Is the PCM1808 suitable for battery-powered devices?
A5: Yes, the PCM1808 has low power consumption (20 mW typical), making it suitable for battery-powered applications.