
How to Use ULTASONIC: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with ULTASONIC in Cirkit Designer
Design with ULTASONIC in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ultrasonic sensor is a versatile electronic component that uses high-frequency sound waves to measure distances or detect objects. It operates by emitting ultrasonic pulses and calculating the time it takes for the echo to return after bouncing off an object. This time-of-flight measurement allows for precise distance calculations, making the ultrasonic sensor a popular choice in a wide range of applications.
Explore Projects Built with ULTASONIC
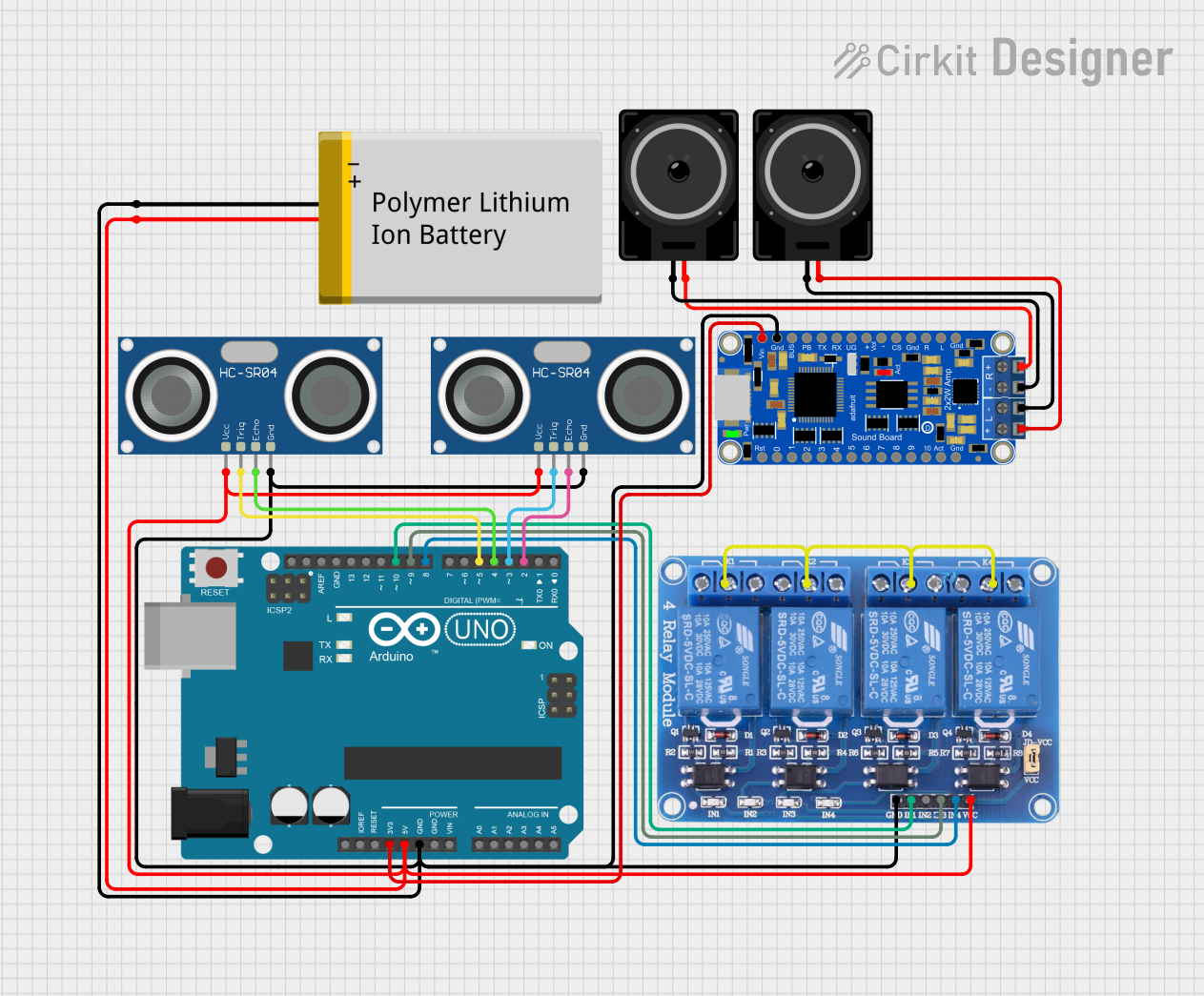
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer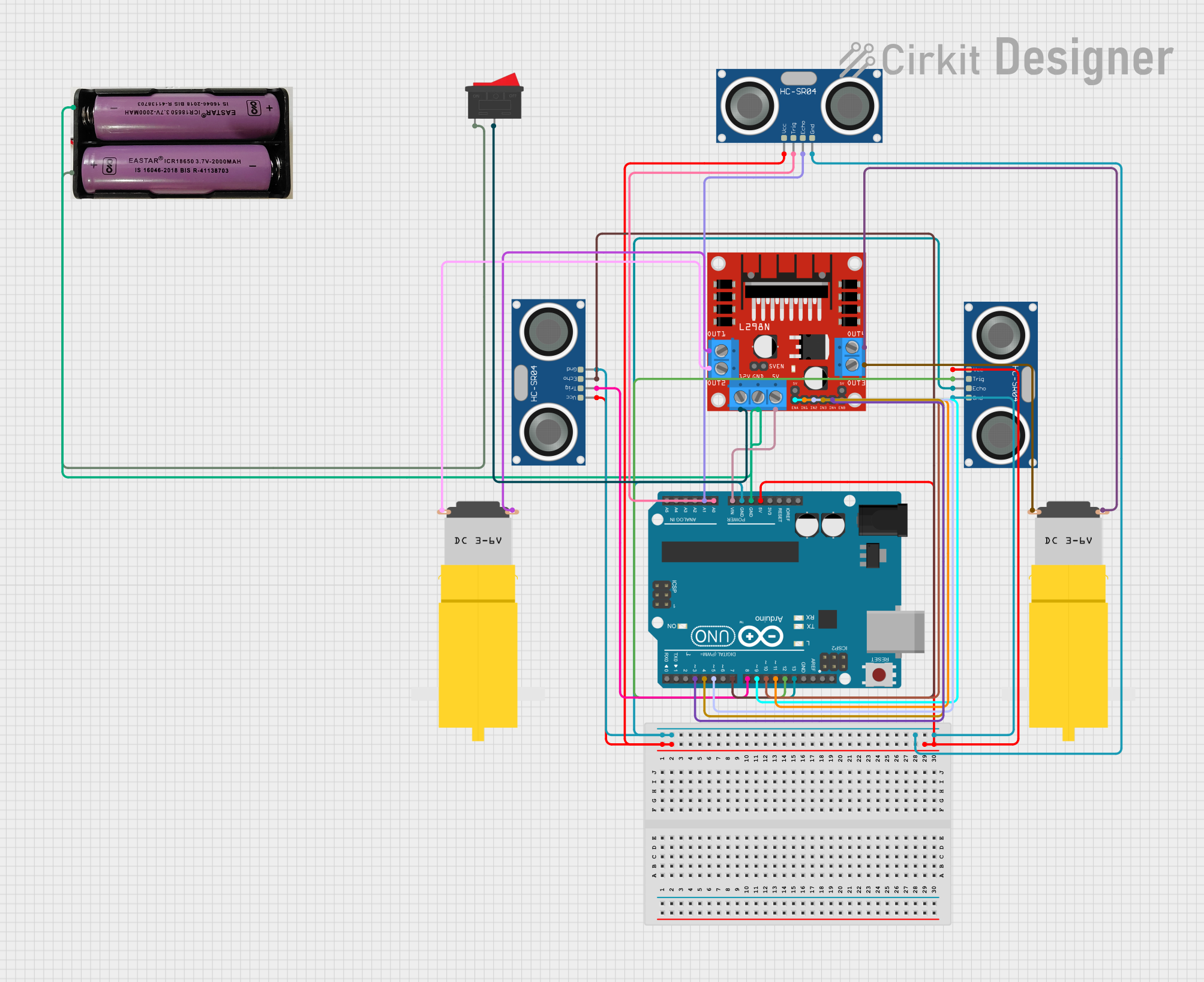
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer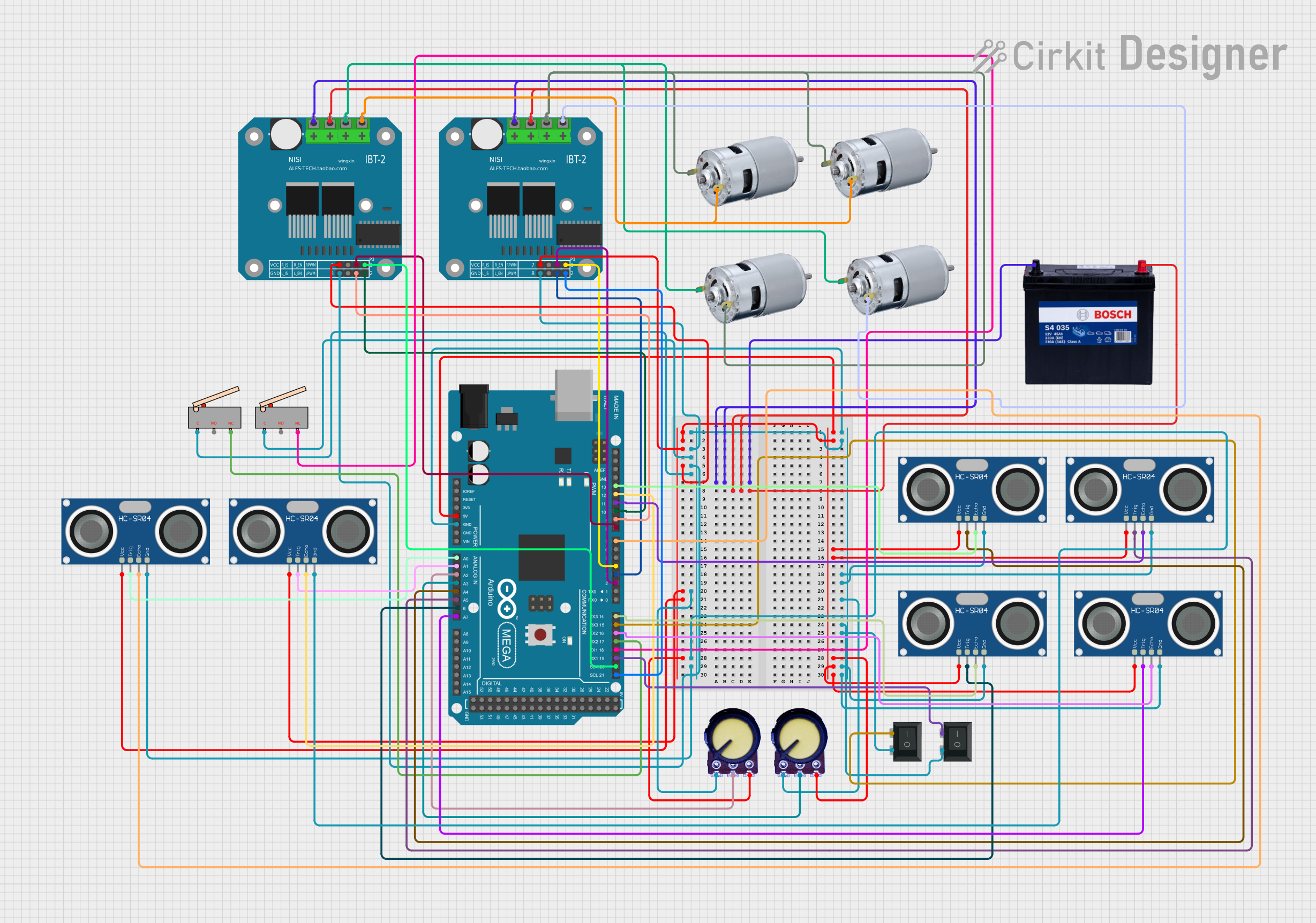
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with ULTASONIC

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Obstacle detection in robotics and autonomous vehicles
- Distance measurement in industrial automation
- Level sensing in liquid tanks
- Proximity detection in security systems
- Gesture recognition in interactive devices
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of a typical ultrasonic sensor (e.g., HC-SR04):
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 5V DC |
| Operating Current | 15 mA |
| Operating Frequency | 40 kHz |
| Measuring Range | 2 cm to 400 cm |
| Accuracy | ±3 mm |
| Trigger Input Signal | 10 µs TTL pulse |
| Echo Output Signal | Pulse width proportional to distance |
| Dimensions | 45 mm x 20 mm x 15 mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Name | Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VCC | 1 | Power supply pin (5V DC) |
| Trig | 2 | Trigger pin: Sends the ultrasonic pulse |
| Echo | 3 | Echo pin: Outputs a pulse proportional to distance |
| GND | 4 | Ground pin |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Ultrasonic Sensor in a Circuit
Connect the Pins:
- Connect the VCC pin to a 5V power source.
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of the circuit.
- Connect the Trig pin to a digital output pin of your microcontroller.
- Connect the Echo pin to a digital input pin of your microcontroller.
Trigger the Sensor:
- Send a 10 µs HIGH pulse to the Trig pin to initiate the ultrasonic pulse.
Measure the Echo:
- Measure the duration of the HIGH pulse on the Echo pin. This duration is proportional to the distance of the object.
Calculate the Distance:
- Use the formula:
[ \text{Distance (cm)} = \frac{\text{Pulse Duration (µs)} \times 0.034}{2} ] The factor 0.034 accounts for the speed of sound (343 m/s) in air.
- Use the formula:
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure there are no obstructions between the sensor and the target object.
- Avoid using the sensor in environments with high noise or vibrations, as these can interfere with measurements.
- Use a capacitor (e.g., 10 µF) across the VCC and GND pins to stabilize the power supply.
- For best results, ensure the target object has a flat, hard surface to reflect the ultrasonic waves effectively.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the ultrasonic sensor with an Arduino UNO:
// Define the pins for the ultrasonic sensor
const int trigPin = 9; // Trigger pin connected to digital pin 9
const int echoPin = 10; // Echo pin connected to digital pin 10
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
// Set the trigPin as an output and echoPin as an input
pinMode(trigPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(echoPin, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Send a 10 µs HIGH pulse to the trigPin
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(trigPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
// Measure the duration of the HIGH pulse on the echoPin
long duration = pulseIn(echoPin, HIGH);
// Calculate the distance in cm
float distance = (duration * 0.034) / 2;
// Print the distance to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Distance: ");
Serial.print(distance);
Serial.println(" cm");
// Wait for a short period before the next measurement
delay(500);
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output or Incorrect Readings:
- Cause: Loose or incorrect wiring.
- Solution: Double-check all connections, ensuring the pins are connected to the correct microcontroller pins.
Unstable or Fluctuating Measurements:
- Cause: Electrical noise or unstable power supply.
- Solution: Add a decoupling capacitor (e.g., 10 µF) across the VCC and GND pins.
Sensor Not Detecting Objects:
- Cause: Target object is too far, too close, or has a poor reflective surface.
- Solution: Ensure the object is within the sensor's range (2 cm to 400 cm) and has a flat, hard surface.
Echo Pin Always LOW:
- Cause: Trigger signal not sent correctly.
- Solution: Verify that the Trig pin is receiving a 10 µs HIGH pulse.
FAQs
Q: Can the ultrasonic sensor detect transparent objects?
A: No, the sensor may struggle to detect transparent or soft objects as they do not reflect ultrasonic waves effectively.Q: Can I use the sensor with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, but you may need a logic level shifter for the Echo pin to avoid damaging the microcontroller.Q: What is the maximum angle of detection?
A: The sensor typically has a detection angle of about 15 degrees.Q: Can the sensor work outdoors?
A: While it can work outdoors, environmental factors like wind, temperature, and rain may affect its performance.