
How to Use GNSS: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with GNSS in Cirkit Designer
Design with GNSS in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) is a satellite-based navigation system that provides precise geolocation and time information to a GNSS receiver anywhere on Earth. It operates under all weather conditions, making it a reliable solution for a wide range of applications. GNSS is widely used in navigation, mapping, surveying, autonomous vehicles, agriculture, and timing synchronization for telecommunications and power grids.
Common applications and use cases include:
- Vehicle navigation systems
- Geospatial mapping and surveying
- Precision agriculture
- Autonomous drones and robotics
- Timing synchronization for critical infrastructure
Explore Projects Built with GNSS
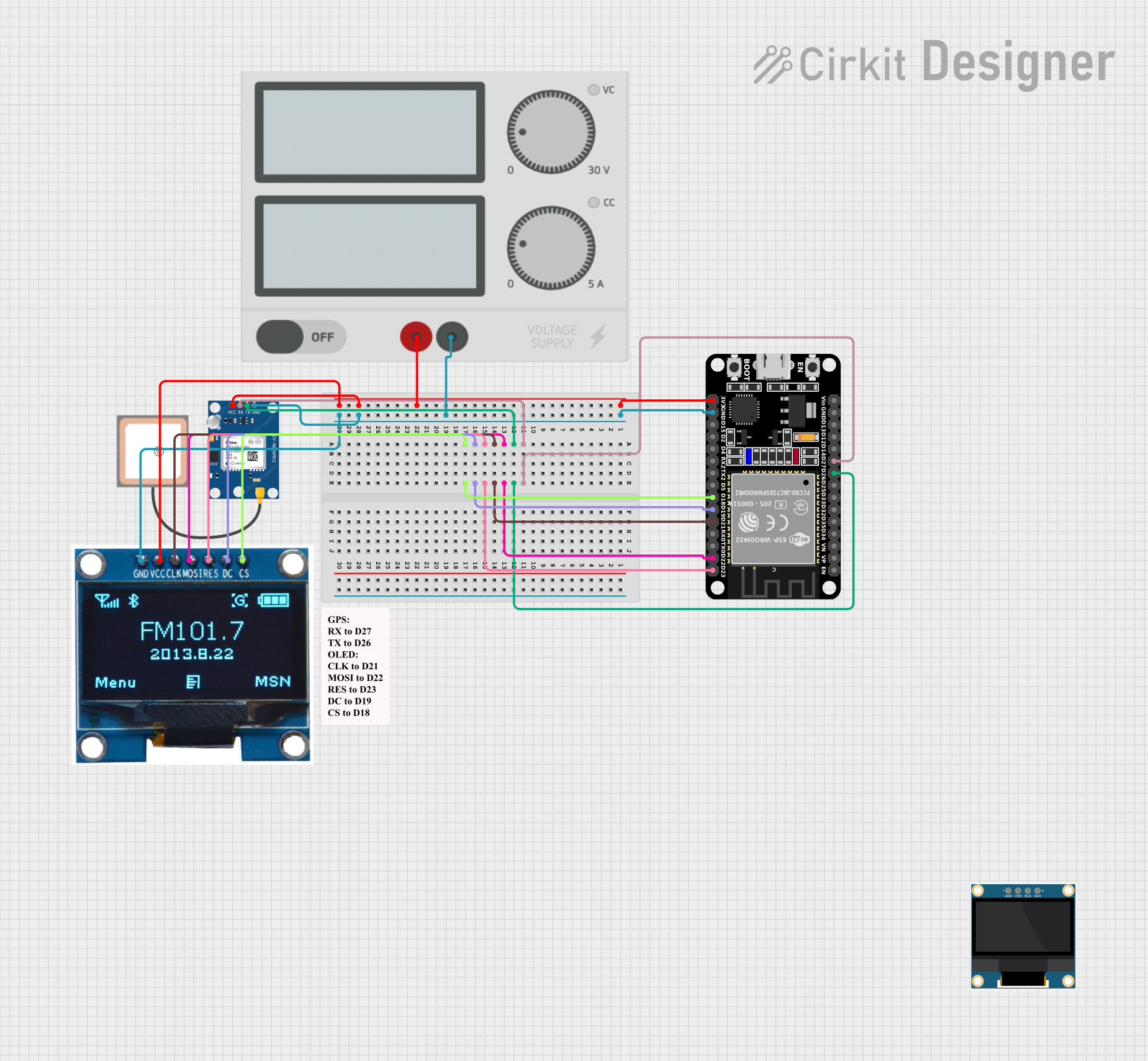
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer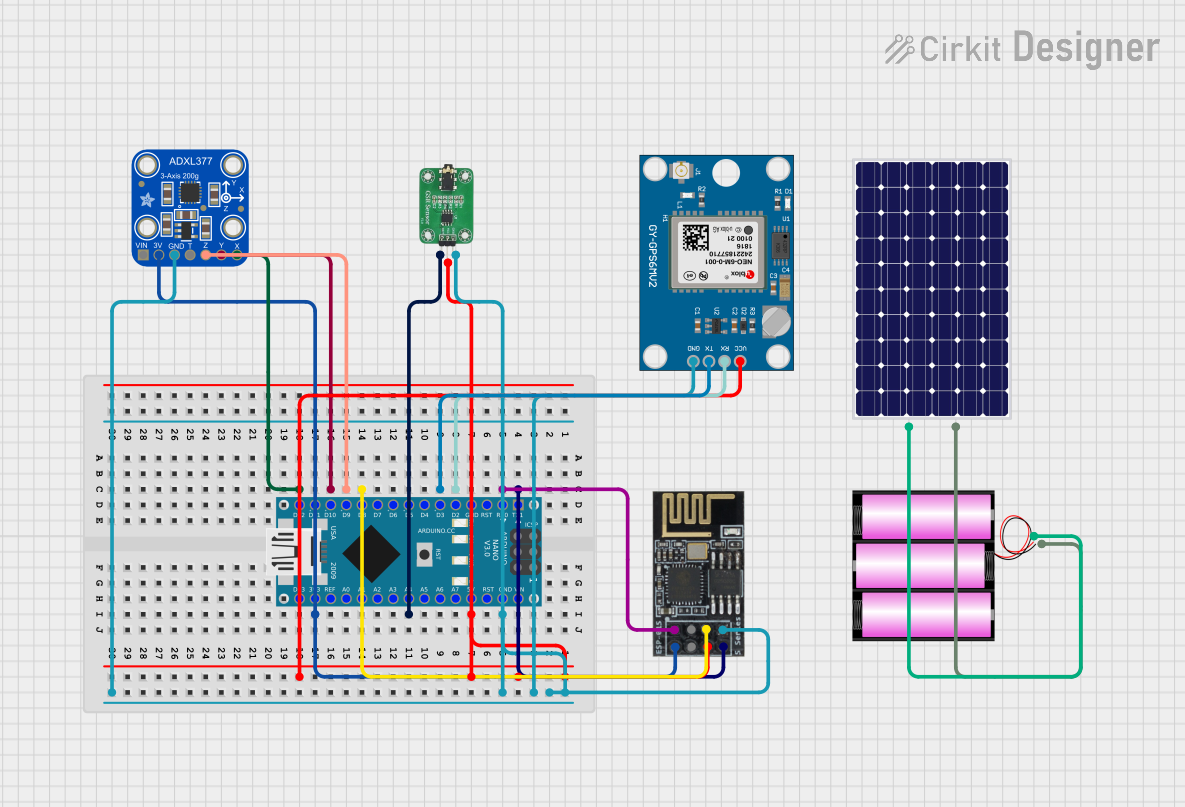
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer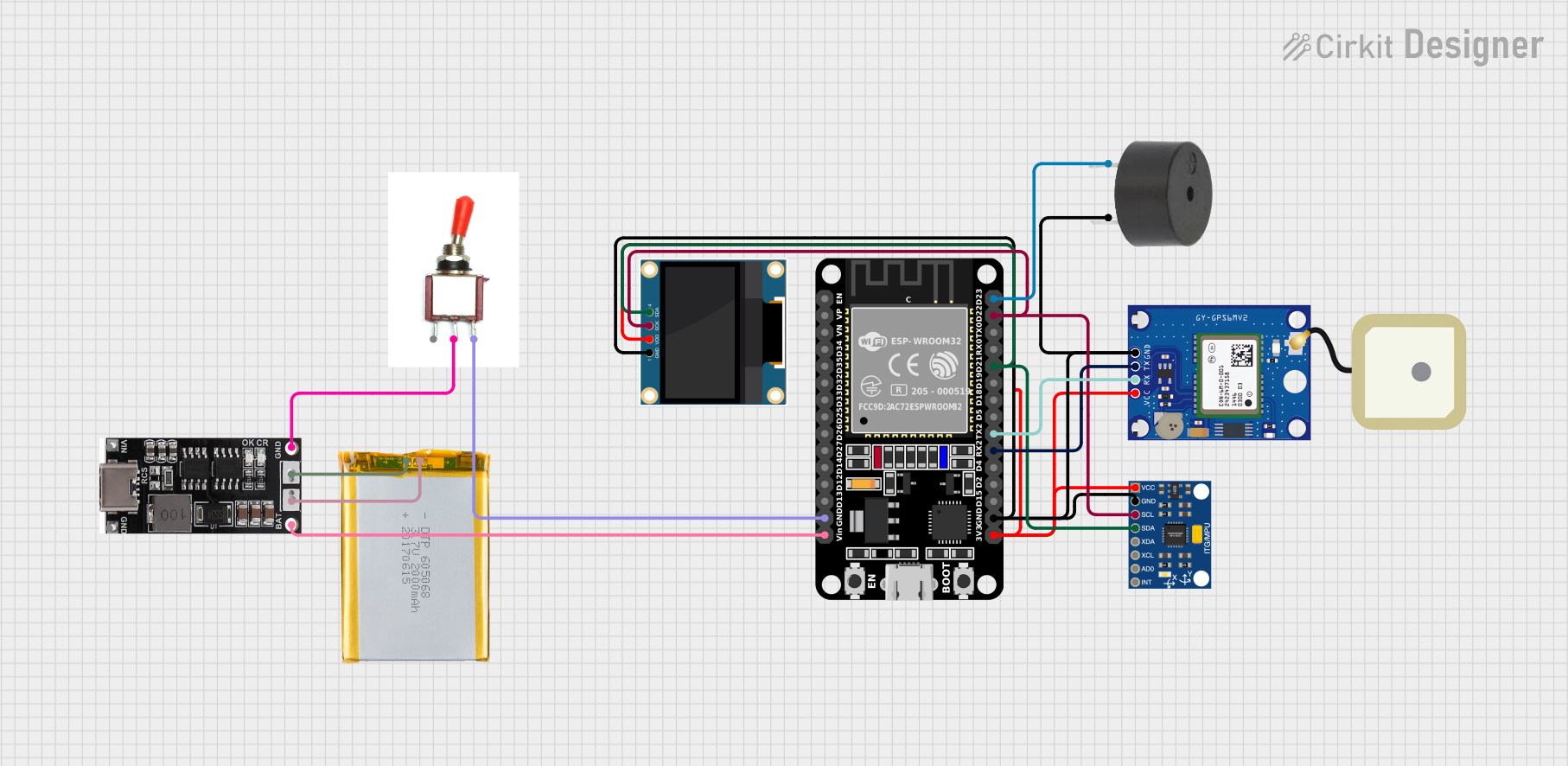
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with GNSS

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Below are the key technical details and pin configuration for a typical GNSS module:
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V to 5V |
| Current Consumption | 20mA to 50mA (varies by module) |
| Positioning Accuracy | Typically 2.5m CEP (Circular Error Probable) |
| Time to First Fix (TTFF) | Cold Start: ~30s, Hot Start: ~1s |
| Communication Interface | UART, I2C, or SPI |
| Frequency Bands | L1 (1575.42 MHz), L2, L5 (varies by system) |
| Supported Systems | GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, BeiDou, QZSS |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Name | Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VCC | 1 | Power supply input (3.3V to 5V) |
| GND | 2 | Ground connection |
| TX | 3 | UART Transmit pin (data output) |
| RX | 4 | UART Receive pin (data input) |
| PPS | 5 | Pulse Per Second output for timing |
| EN | 6 | Enable pin (active high) |
| SDA | 7 | I2C Data line (optional, module-specific) |
| SCL | 8 | I2C Clock line (optional, module-specific) |
Note: Pin configuration may vary depending on the specific GNSS module. Always refer to the datasheet of your module for exact details.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the GNSS Module in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the
VCCpin to a 3.3V or 5V power source, depending on the module's requirements. Connect theGNDpin to the ground of your circuit. - Data Communication: Use the
TXandRXpins for UART communication. ConnectTXto the RX pin of your microcontroller andRXto the TX pin of your microcontroller. - Optional Connections: If your module supports I2C, connect the
SDAandSCLpins to the corresponding pins on your microcontroller. Use pull-up resistors (typically 4.7kΩ) on these lines. - Antenna: Attach an external GNSS antenna to the module's antenna port for better signal reception.
- Enable Pin: If the module has an
ENpin, ensure it is pulled high to enable the module.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Antenna Placement: Place the antenna in an open area with a clear view of the sky for optimal satellite reception.
- Power Supply: Use a stable and noise-free power supply to avoid interference with GNSS signals.
- Baud Rate: Configure the UART baud rate of the GNSS module to match your microcontroller's settings (commonly 9600 bps).
- Signal Interference: Avoid placing the module near high-frequency components or metal enclosures that can block signals.
Example: Connecting GNSS to Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to interface a GNSS module with an Arduino UNO using UART communication:
Circuit Connections
| GNSS Pin | Arduino Pin |
|---|---|
| VCC | 5V |
| GND | GND |
| TX | Pin 4 |
| RX | Pin 3 |
Arduino Code
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Define RX and TX pins for SoftwareSerial
SoftwareSerial GNSS(3, 4); // RX = Pin 3, TX = Pin 4
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize Serial Monitor at 9600 bps
GNSS.begin(9600); // Initialize GNSS module at 9600 bps
Serial.println("GNSS Module Initialized");
}
void loop() {
// Check if data is available from the GNSS module
if (GNSS.available()) {
// Read data from GNSS and send it to Serial Monitor
while (GNSS.available()) {
char c = GNSS.read();
Serial.print(c);
}
}
}
Note: The above code reads raw NMEA sentences from the GNSS module and outputs them to the Serial Monitor. You can use libraries like TinyGPS++ to parse and extract specific data such as latitude, longitude, and time.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Data Output from GNSS Module
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or baud rate mismatch.
- Solution: Double-check the connections and ensure the UART baud rate matches the module's default setting.
Poor Signal Reception
- Cause: Antenna placement or environmental obstructions.
- Solution: Place the antenna in an open area with a clear view of the sky. Avoid indoor use or areas with tall buildings.
Module Not Powering On
- Cause: Insufficient power supply or incorrect voltage.
- Solution: Verify the power supply voltage and current requirements. Ensure proper connections to
VCCandGND.
Intermittent Data Loss
- Cause: Electrical noise or interference.
- Solution: Use decoupling capacitors near the power pins and keep the module away from high-frequency components.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the GNSS module indoors?
A: GNSS modules generally require a clear view of the sky for accurate positioning. Indoor use may result in poor or no signal reception.
Q: What is the difference between GPS and GNSS?
A: GPS is a specific satellite navigation system operated by the United States, while GNSS refers to a broader term encompassing multiple systems like GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou.
Q: How do I parse NMEA sentences from the GNSS module?
A: You can use libraries like TinyGPS++ or Adafruit GPS to parse NMEA sentences and extract useful data such as latitude, longitude, and time.
Q: What is the purpose of the PPS pin?
A: The Pulse Per Second (PPS) pin provides a precise timing signal that can be used for synchronization in time-sensitive applications.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate and troubleshoot a GNSS module in your projects.