
How to Use tb6600 Micro Stepping Motor Driver: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
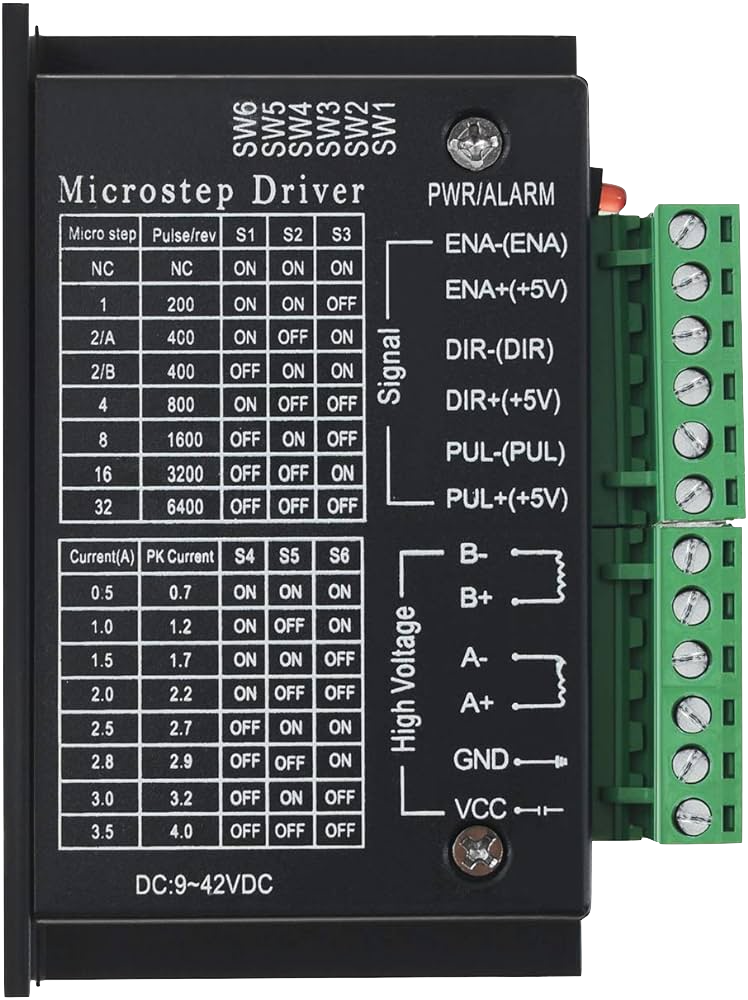
 Design with tb6600 Micro Stepping Motor Driver in Cirkit Designer
Design with tb6600 Micro Stepping Motor Driver in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The TB6600 Micro Stepping Motor Driver is a professional-grade driver module designed to control stepper motors with precision and efficiency. Manufactured by DFROBOT, this driver is capable of powering a wide range of stepper motors, making it suitable for applications such as CNC machines, 3D printers, and robotics. Its ability to micro-step allows for smoother and quieter motor operation, as well as increased accuracy in motion control.
Explore Projects Built with tb6600 Micro Stepping Motor Driver
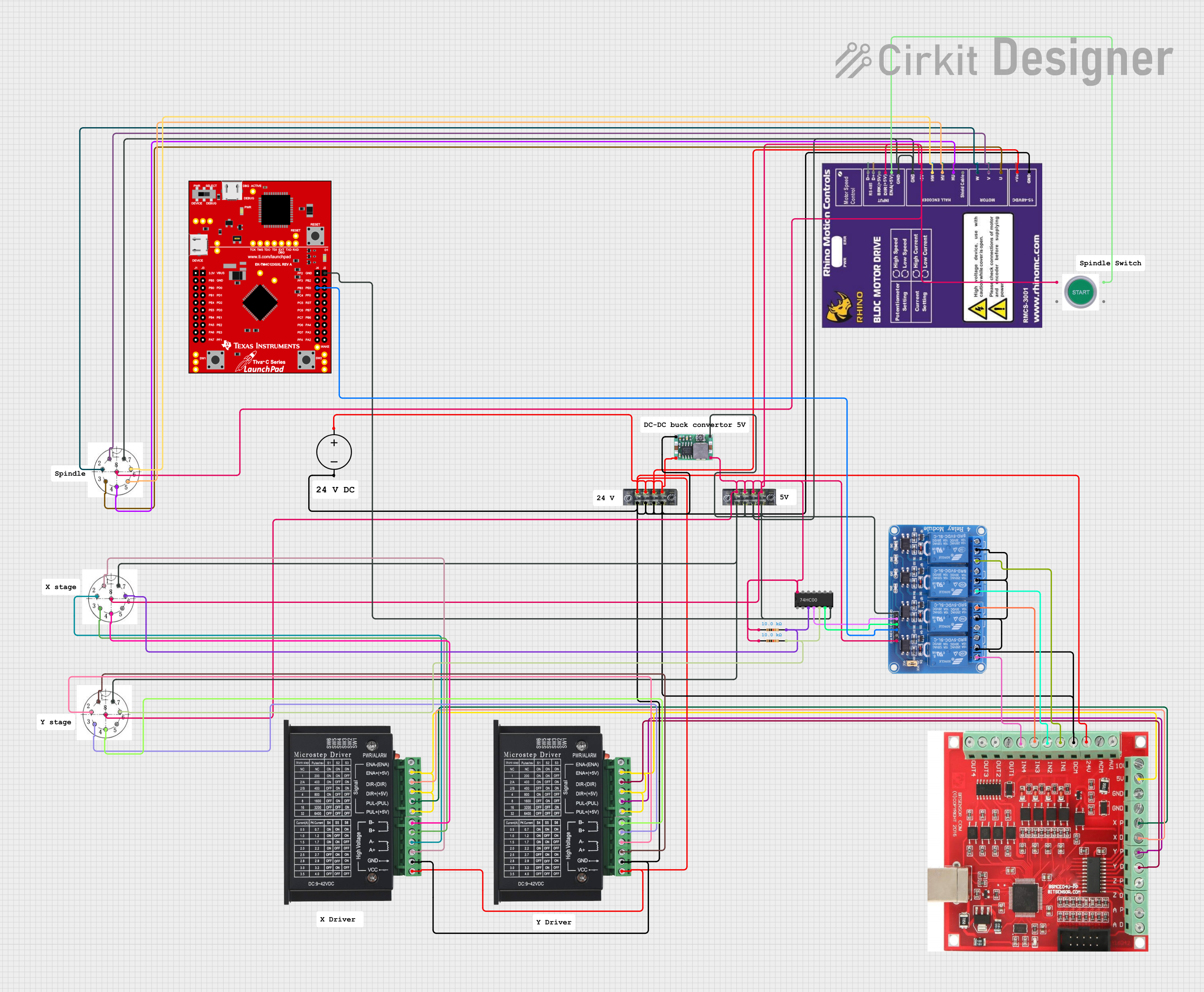
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer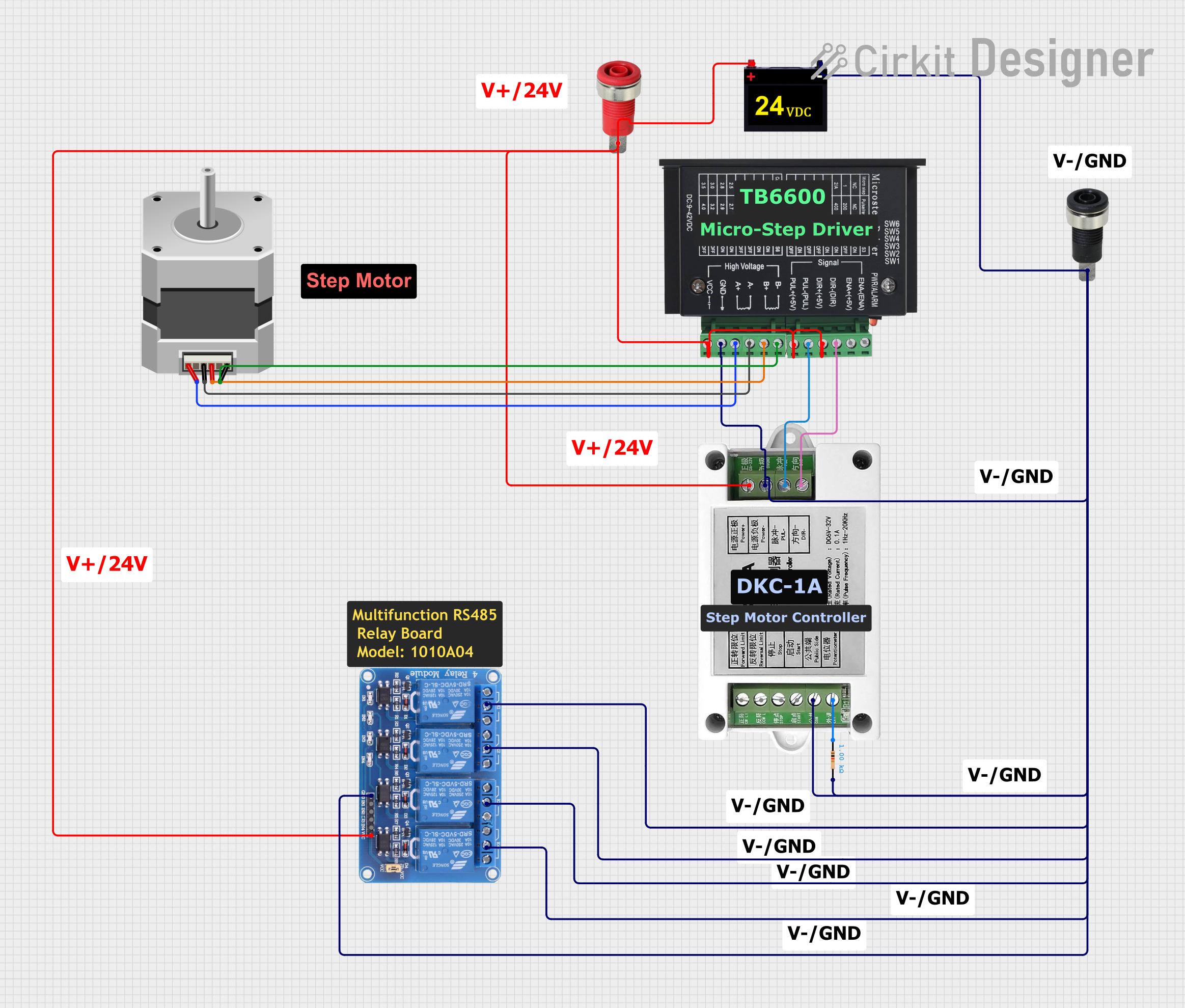
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer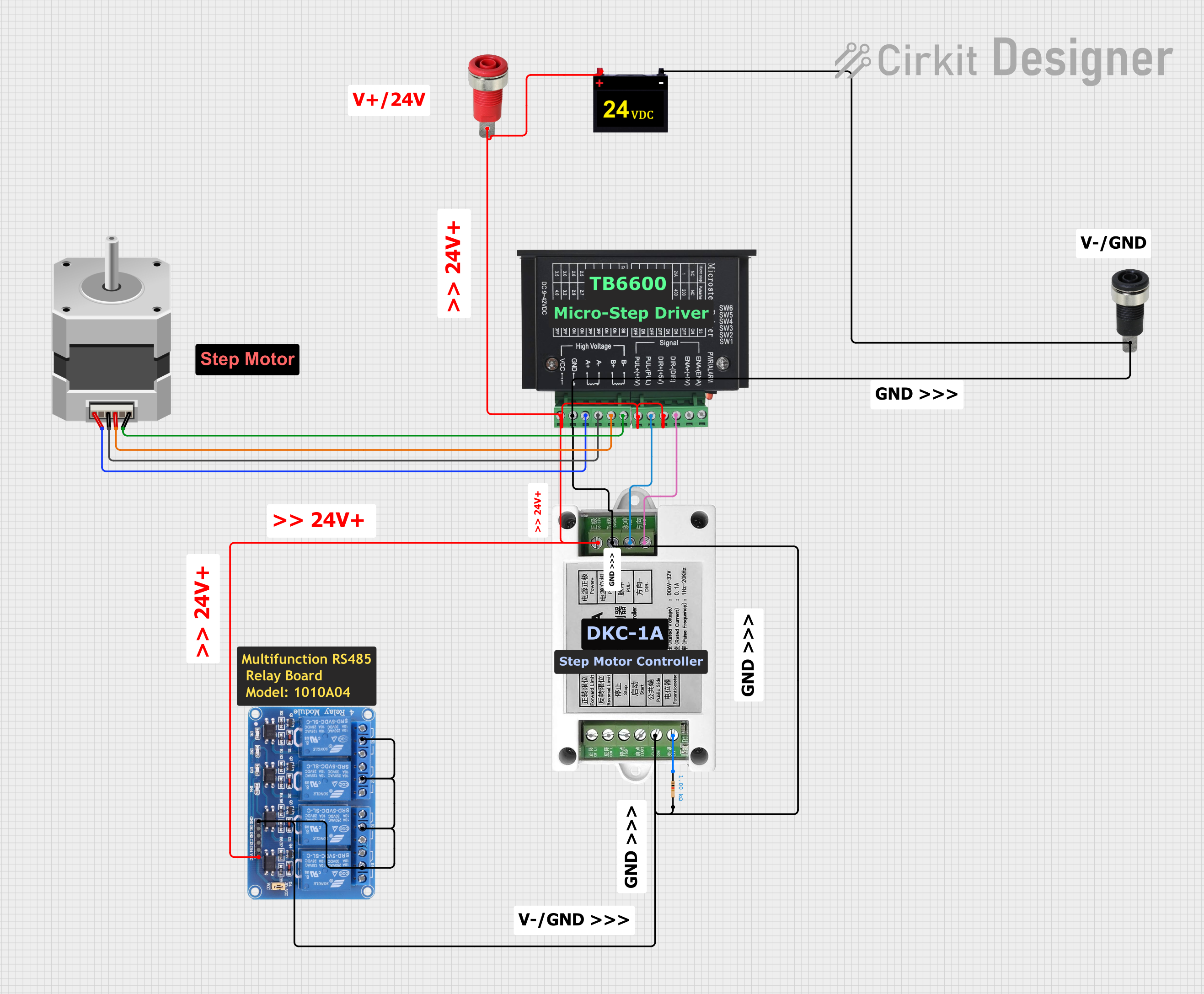
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer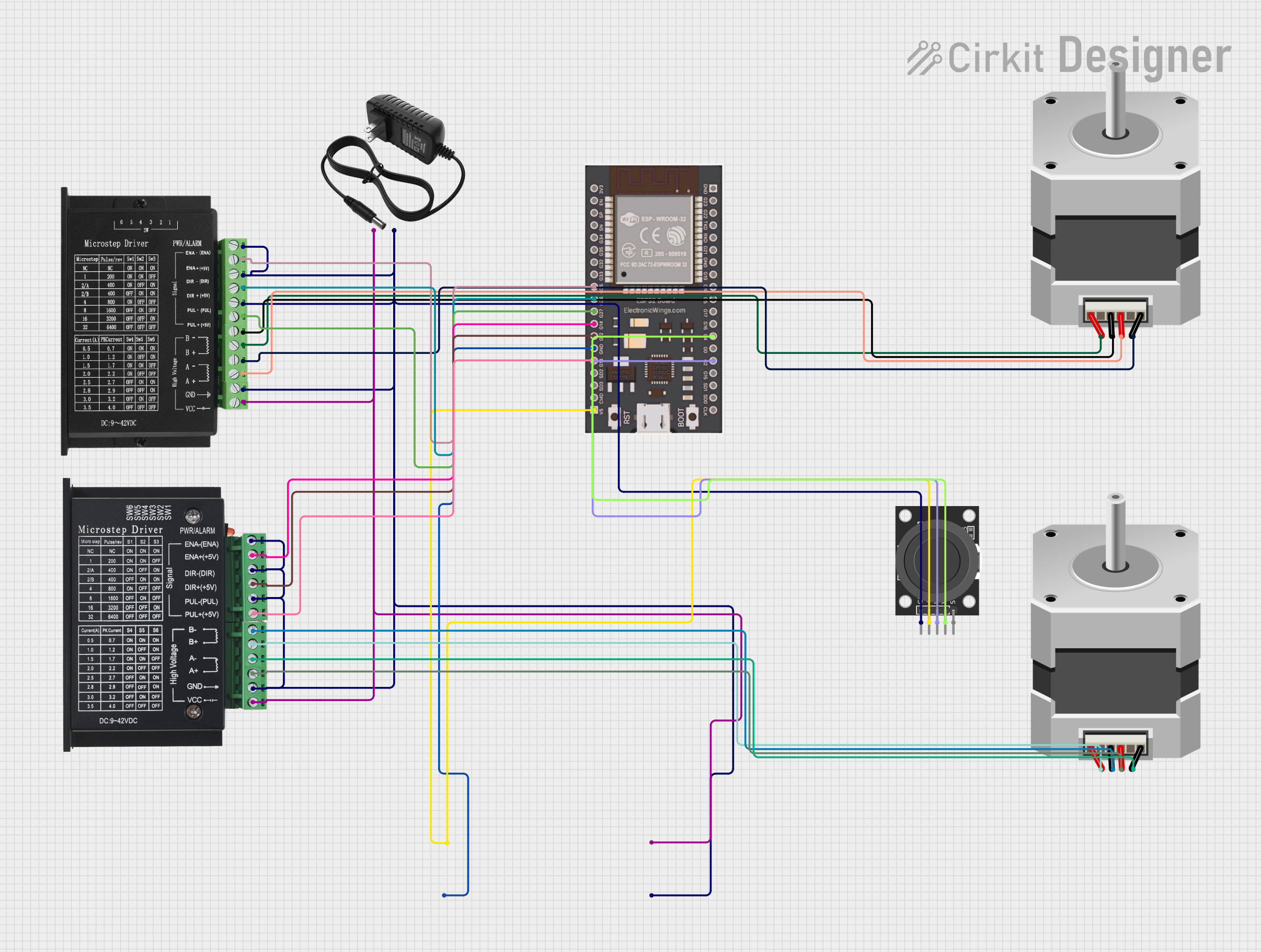
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with tb6600 Micro Stepping Motor Driver

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- CNC milling machines and lathes
- 3D printers
- Robotic arms and actuators
- Precision XY tables
- Automated equipment and assembly lines
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Input Voltage: 9V-42V DC
- Output Current: Adjustable from 0.2A to 4.0A
- Control Signal Voltage: 3.3V-24V
- Microstepping: Up to 1/32 micro steps
- Operating Temperature: -10°C to 45°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ENA+ | Enable signal positive |
| 2 | ENA- | Enable signal negative |
| 3 | DIR+ | Direction signal positive |
| 4 | DIR- | Direction signal negative |
| 5 | PUL+ | Pulse signal positive |
| 6 | PUL- | Pulse signal negative |
| 7 | VCC | Motor power supply positive |
| 8 | GND | Motor power supply negative |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Power Supply Connection: Connect a DC power supply to the VCC and GND pins, ensuring that the voltage is within the specified range (9V-42V).
Motor Connection: Connect the stepper motor wires to the motor output terminals on the TB6600 driver, observing the correct wiring sequence as per the motor's datasheet.
Control Signal Connection: Connect the ENA+, DIR+, and PUL+ pins to the corresponding output pins on your controller (e.g., Arduino UNO). Connect the ENA-, DIR-, and PUL- to the ground of the controller.
Microstep Configuration: Set the microstep resolution using the onboard DIP switches according to the desired step size.
Current Setting: Adjust the current setting using the onboard potentiometer to match the requirements of the stepper motor.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Always ensure the power supply is turned off before making any connections to prevent damage.
- Use a suitable heatsink to dissipate heat during operation.
- Avoid running the motor driver at its maximum current rating for extended periods to prevent overheating.
- Ensure that the control signals from the microcontroller are within the acceptable voltage range.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
// Define the stepper motor control pins
#define ENA 8
#define DIR 9
#define PUL 10
void setup() {
// Set the control pins as outputs
pinMode(ENA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(DIR, OUTPUT);
pinMode(PUL, OUTPUT);
// Enable the stepper motor driver
digitalWrite(ENA, LOW);
}
void loop() {
// Set the direction of the motor
digitalWrite(DIR, HIGH); // Set to LOW to change direction
// Pulse the PUL pin to move the motor
digitalWrite(PUL, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(500); // Adjust the speed by changing the delay
digitalWrite(PUL, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(500);
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- Motor not moving: Check power supply connections, ensure the motor driver is enabled, and verify that the control signals are being sent correctly.
- Motor stalling or vibrating: Adjust the current setting, check for proper microstep configuration, and ensure the motor is not overloaded.
- Overheating: Ensure adequate cooling, reduce the operating current, or check for short circuits.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Double-check all connections and ensure they are secure and correct.
- Use a multimeter to verify the voltage levels at the power supply and the control signals.
- Consult the stepper motor's datasheet to ensure compatibility with the driver settings.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the TB6600 driver with a 5V control signal? A: Yes, the TB6600 can accept control signal voltages from 3.3V to 24V.
Q: What is the maximum motor current that the TB6600 can handle? A: The TB6600 can handle up to 4.0A of output current with proper cooling.
Q: How do I set the microstepping resolution? A: Use the onboard DIP switches to select the desired microstepping resolution according to the driver's manual.
Q: Can I run two motors simultaneously with one TB6600 driver? A: No, the TB6600 is designed to control a single stepper motor. Each motor requires its own driver.
Remember to always refer to the manufacturer's datasheet and manual for the most accurate and detailed information about the TB6600 Micro Stepping Motor Driver.