
How to Use ESP-WROOM-32: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with ESP-WROOM-32 in Cirkit Designer
Design with ESP-WROOM-32 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ESP-WROOM-32 is a powerful Wi-Fi and Bluetooth module based on the ESP32 chip. It is designed for Internet of Things (IoT) applications, offering dual-core processing, low power consumption, and a wide range of GPIO options. This module is highly versatile and can be used in projects requiring wireless communication, sensor integration, or edge computing.
Explore Projects Built with ESP-WROOM-32
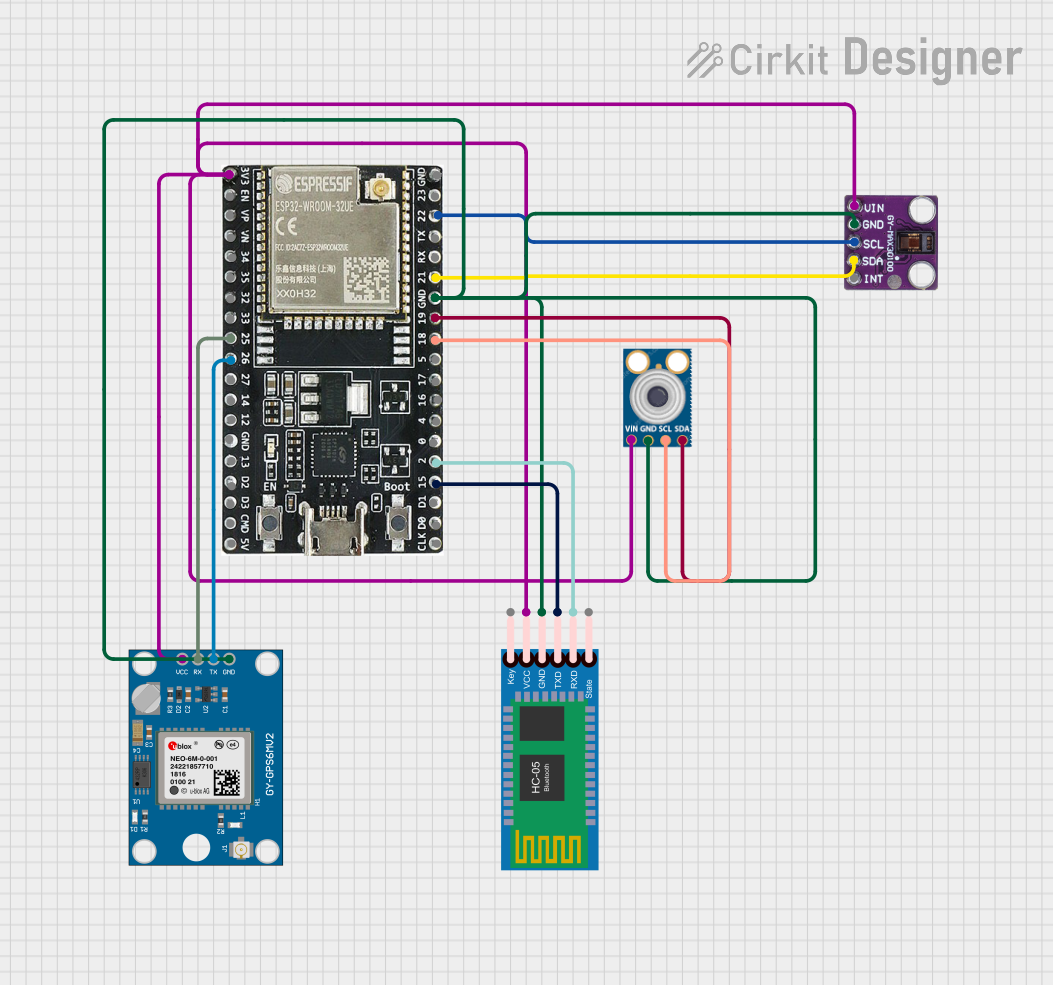
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer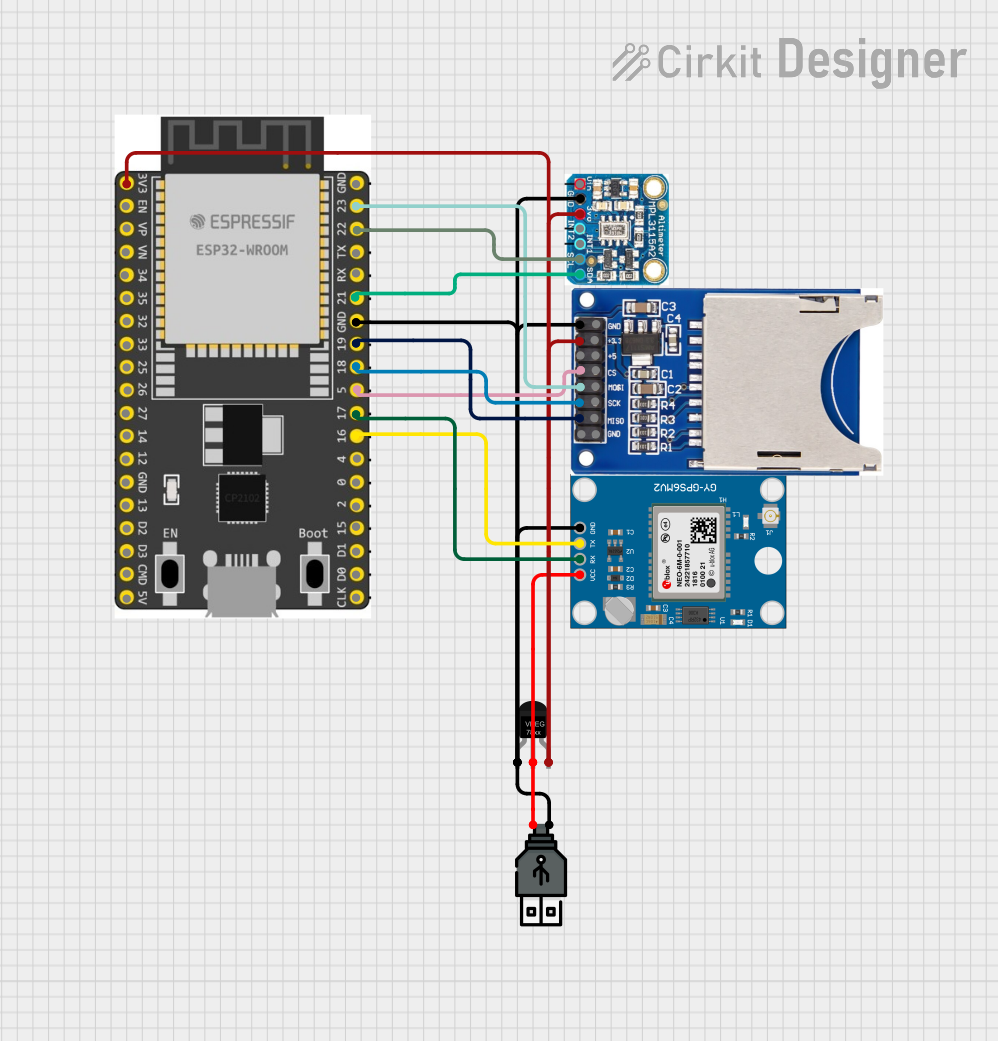
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer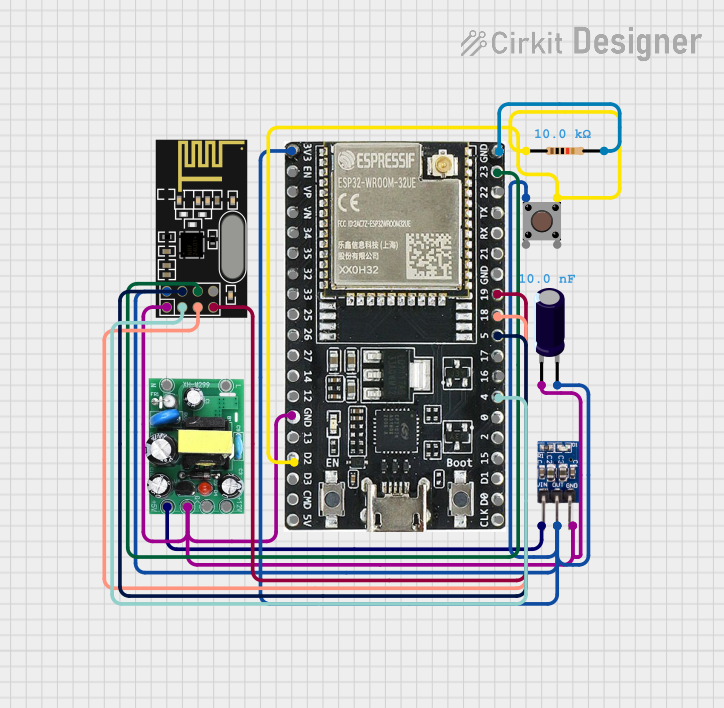
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with ESP-WROOM-32

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Smart home devices (e.g., smart lights, thermostats)
- Wearable technology
- Industrial IoT systems
- Wireless sensor networks
- Robotics and automation
- Prototyping and development of connected devices
Technical Specifications
The ESP-WROOM-32 module is built around the ESP32-D0WDQ6 chip, which integrates Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities. Below are the key technical details:
General Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Microcontroller | ESP32-D0WDQ6 |
| Wireless Connectivity | Wi-Fi 802.11 b/g/n, Bluetooth v4.2 BR/EDR |
| CPU | Dual-core Xtensa® 32-bit LX6 |
| Clock Speed | Up to 240 MHz |
| Flash Memory | 4 MB (default) |
| SRAM | 520 KB |
| Operating Voltage | 3.0V to 3.6V |
| Power Consumption | Ultra-low power modes available |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to 85°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The ESP-WROOM-32 module has 38 pins. Below is a table of the most commonly used pins:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Functionality |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | EN | Enable pin (active high) |
| 2 | IO0 | GPIO0, used for boot mode selection |
| 3 | IO2 | GPIO2, general-purpose I/O |
| 4 | IO4 | GPIO4, general-purpose I/O |
| 5 | IO5 | GPIO5, general-purpose I/O |
| 6 | IO12 | GPIO12, ADC2 channel 5 |
| 7 | IO13 | GPIO13, ADC2 channel 4 |
| 8 | IO14 | GPIO14, ADC2 channel 6 |
| 9 | IO15 | GPIO15, ADC2 channel 3 |
| 10 | IO16 | GPIO16, general-purpose I/O |
| 11 | IO17 | GPIO17, general-purpose I/O |
| 12 | GND | Ground |
| 13 | 3V3 | 3.3V power supply |
Note: Some GPIO pins have specific functions or limitations. For example, GPIO0 is used for boot mode selection, and certain pins are input-only or have pull-up/down resistors.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the ESP-WROOM-32 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the module to a stable 3.3V power source. Avoid exceeding 3.6V to prevent damage.
- Boot Mode: To upload code, connect GPIO0 to GND and reset the module. After uploading, disconnect GPIO0 from GND.
- Programming: Use the UART interface (TX/RX pins) to program the module via a USB-to-serial adapter or development board.
- GPIO Usage: Connect sensors, actuators, or other peripherals to the GPIO pins. Refer to the pin configuration table for details.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Levels: Ensure all connected peripherals operate at 3.3V logic levels. Use level shifters if necessary.
- Power Supply: Use a decoupling capacitor (e.g., 10 µF) near the power pins to stabilize the voltage.
- Antenna Placement: Avoid placing metal objects near the module's antenna to ensure optimal wireless performance.
- Deep Sleep Mode: Use the deep sleep mode to reduce power consumption in battery-powered applications.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
The ESP-WROOM-32 can be programmed using the Arduino IDE. Below is an example of how to connect the module to a Wi-Fi network:
#include <WiFi.h> // Include the Wi-Fi library for ESP32
const char* ssid = "Your_SSID"; // Replace with your Wi-Fi network name
const char* password = "Your_Password"; // Replace with your Wi-Fi password
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // Initialize serial communication at 115200 baud
delay(1000); // Wait for a moment to stabilize
Serial.println("Connecting to Wi-Fi...");
WiFi.begin(ssid, password); // Start connecting to the Wi-Fi network
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500); // Wait for connection
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("\nConnected to Wi-Fi!");
Serial.print("IP Address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); // Print the assigned IP address
}
void loop() {
// Add your main code here
}
Note: Replace
Your_SSIDandYour_Passwordwith your Wi-Fi credentials.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Module Not Responding
- Cause: Incorrect power supply or wiring.
- Solution: Ensure the module is powered with 3.3V and all connections are secure.
Wi-Fi Connection Fails
- Cause: Incorrect SSID or password.
- Solution: Double-check the Wi-Fi credentials in your code.
Upload Fails
- Cause: GPIO0 not connected to GND during boot mode.
- Solution: Connect GPIO0 to GND, reset the module, and try uploading again.
Random Resets
- Cause: Insufficient power supply or unstable voltage.
- Solution: Use a stable 3.3V power source and add decoupling capacitors.
FAQs
Q: Can the ESP-WROOM-32 operate on 5V?
A: No, the module operates at 3.3V. Use a voltage regulator or level shifter for 5V systems.Q: How do I reset the module?
A: Pull the EN pin low momentarily to reset the module.Q: Can I use the ESP-WROOM-32 with Bluetooth and Wi-Fi simultaneously?
A: Yes, the ESP32 chip supports simultaneous use of Wi-Fi and Bluetooth.Q: What is the maximum range of the Wi-Fi connection?
A: The range depends on environmental factors but typically extends up to 100 meters in open space.
This documentation provides a comprehensive guide to using the ESP-WROOM-32 module effectively in your projects.