
How to Use PURE SINE WAVE: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
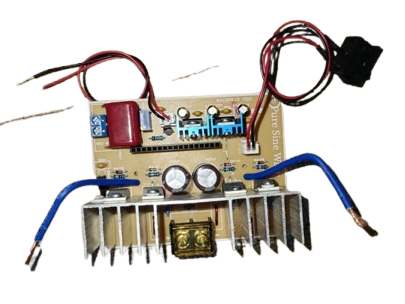
 Design with PURE SINE WAVE in Cirkit Designer
Design with PURE SINE WAVE in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A pure sine wave is a smooth, periodic oscillation that represents a constant frequency and amplitude. It is widely used in AC power supplies and signal generation due to its ideal characteristics for powering sensitive electronic devices. Unlike modified or square waveforms, a pure sine wave ensures minimal harmonic distortion, making it suitable for applications requiring clean and stable power.
Explore Projects Built with PURE SINE WAVE
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer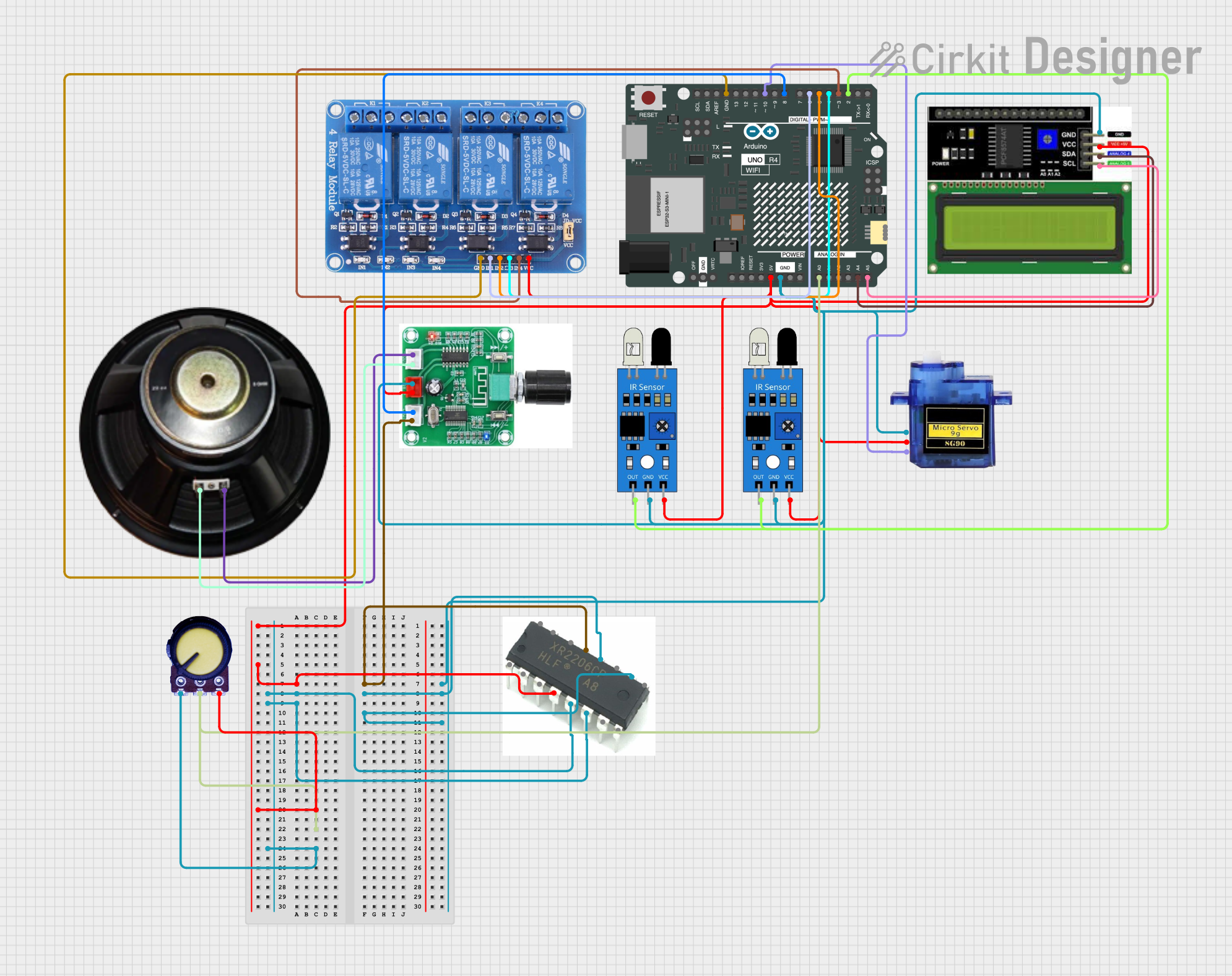
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with PURE SINE WAVE

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Inverters: Powering household appliances, medical equipment, and sensitive electronics.
- Signal Generators: Used in testing and calibration of electronic circuits.
- Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS): Providing backup power with minimal interference.
- Audio Equipment: Ensuring high-quality sound output without distortion.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Converting DC power from solar panels or batteries into AC power.
Technical Specifications
The technical specifications of a pure sine wave depend on the device or circuit generating it. Below are general parameters for a typical pure sine wave inverter or generator:
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value/Range | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Output Waveform | Pure Sine Wave | Smooth, periodic oscillation. |
| Output Voltage | 110V/220V AC (±5%) | Standard AC voltage for household devices. |
| Output Frequency | 50Hz or 60Hz | Matches regional power grid standards. |
| Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) | <3% | Ensures minimal distortion in the waveform. |
| Efficiency | 85%–95% | Conversion efficiency from DC to AC. |
| Power Rating | 100W–5000W (varies by model) | Maximum load capacity of the inverter. |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
For a pure sine wave inverter module, the pin configuration typically includes input and output terminals. Below is an example:
| Pin Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VIN+ | Input | Positive DC input terminal (e.g., battery +). |
| VIN- | Input | Negative DC input terminal (e.g., battery -). |
| AC OUT (L) | Output | Live AC output terminal. |
| AC OUT (N) | Output | Neutral AC output terminal. |
| GND | Ground | Ground connection for safety and stability. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Connect the DC Input:
- Attach the positive terminal of the DC power source (e.g., battery) to the
VIN+pin. - Connect the negative terminal of the DC power source to the
VIN-pin.
- Attach the positive terminal of the DC power source (e.g., battery) to the
- Connect the AC Output:
- Use the
AC OUT (L)andAC OUT (N)pins to connect the load (e.g., household appliances).
- Use the
- Power On:
- Turn on the DC power source. The inverter will convert the DC input into a pure sine wave AC output.
- Monitor the Output:
- Use an oscilloscope or multimeter to verify the output waveform and voltage.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Input Voltage: Ensure the DC input voltage matches the inverter's specifications to avoid damage.
- Load Capacity: Do not exceed the power rating of the inverter to prevent overheating or failure.
- Cooling: Provide adequate ventilation or cooling to maintain efficiency and prevent thermal shutdown.
- Grounding: Properly ground the system to ensure safety and reduce electrical noise.
- Sensitive Devices: Use pure sine wave inverters for devices like medical equipment, audio systems, and computers to avoid malfunctions caused by waveform distortion.
Example: Using a Pure Sine Wave Inverter with Arduino UNO
You can use an Arduino UNO to control a pure sine wave inverter module. Below is an example code snippet to toggle the inverter's power using a relay:
// Define the relay pin connected to the Arduino
const int relayPin = 7;
void setup() {
pinMode(relayPin, OUTPUT); // Set the relay pin as an output
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW); // Ensure the relay is off initially
}
void loop() {
// Turn on the inverter by activating the relay
digitalWrite(relayPin, HIGH);
delay(5000); // Keep the inverter on for 5 seconds
// Turn off the inverter by deactivating the relay
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW);
delay(5000); // Keep the inverter off for 5 seconds
}
Note: Ensure the relay module is rated for the inverter's input voltage and current.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| No AC output | Incorrect DC input connection | Verify the polarity and voltage of the input. |
| Overheating | Exceeding power rating or poor cooling | Reduce the load or improve ventilation. |
| Distorted waveform | Faulty inverter or excessive load | Check the inverter and reduce the load. |
| Device not powering on | Blown fuse or low battery voltage | Replace the fuse or recharge the battery. |
FAQs
Can I use a pure sine wave inverter with solar panels?
- Yes, as long as the inverter's input voltage matches the solar panel's output voltage.
Why is a pure sine wave better than a modified sine wave?
- A pure sine wave provides cleaner power with minimal harmonic distortion, ensuring compatibility with sensitive devices.
What happens if I exceed the inverter's power rating?
- The inverter may shut down, overheat, or become damaged. Always stay within the rated capacity.
How can I verify the output waveform?
- Use an oscilloscope to observe the waveform and ensure it is a smooth sine wave.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use and troubleshoot a pure sine wave inverter or generator in your projects.