
How to Use LM393: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
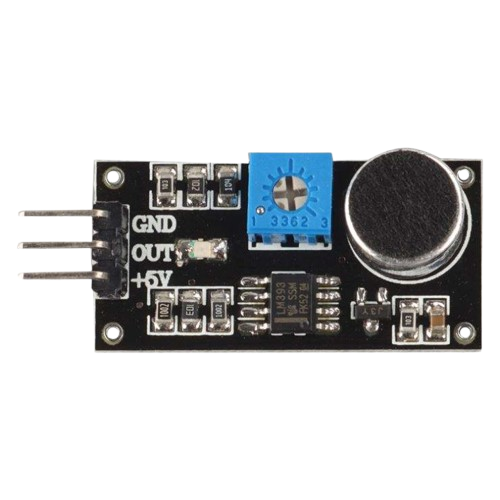
 Design with LM393 in Cirkit Designer
Design with LM393 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The LM393 is a dual comparator integrated circuit (IC) designed to compare two input voltages and output a digital signal based on the comparison. It features two independent voltage comparators in a single package, making it versatile and efficient for a wide range of applications. The LM393 operates with a wide range of supply voltages and is known for its low power consumption.
Explore Projects Built with LM393
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer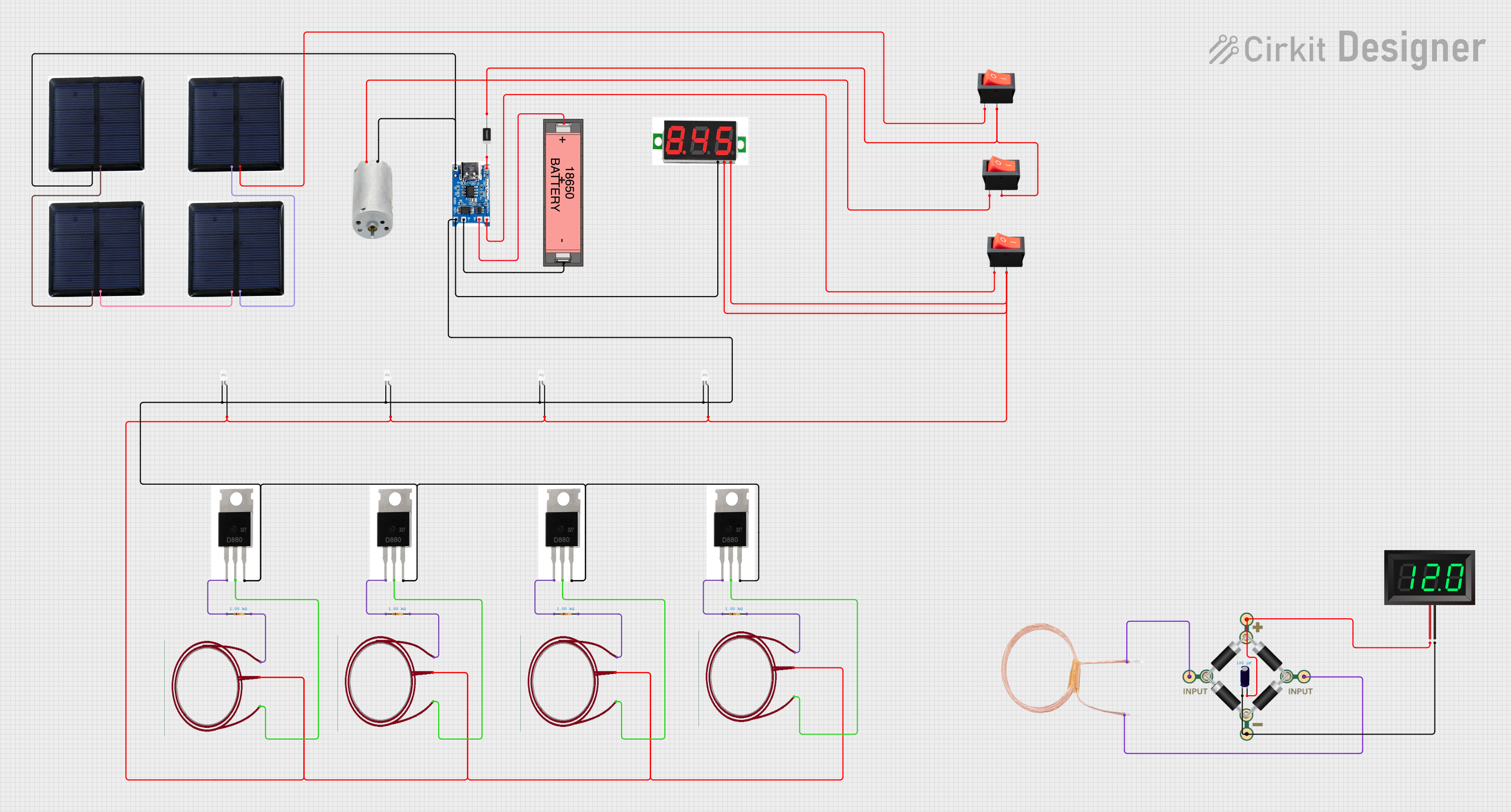
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with LM393

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Voltage level detection
- Signal conditioning
- Zero-crossing detectors
- Pulse-width modulation (PWM) circuits
- Analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) circuits
- Control systems and automation
Technical Specifications
The LM393 is a robust and reliable IC with the following key specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Supply Voltage (Vcc) | 2V to 36V |
| Input Offset Voltage | ±5mV (typical) |
| Input Common-Mode Voltage | 0V to Vcc - 1.5V |
| Output Voltage (Low) | 0.2V (typical) at 4mA sink current |
| Output Sink Current | Up to 16mA |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Package Types | DIP-8, SOIC-8, TSSOP-8 |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The LM393 is typically available in an 8-pin Dual In-line Package (DIP) or similar formats. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Output 1 | Output of comparator 1 |
| 2 | Inverting Input 1 | Inverting input of comparator 1 |
| 3 | Non-Inverting Input 1 | Non-inverting input of comparator 1 |
| 4 | GND | Ground (0V reference) |
| 5 | Non-Inverting Input 2 | Non-inverting input of comparator 2 |
| 6 | Inverting Input 2 | Inverting input of comparator 2 |
| 7 | Output 2 | Output of comparator 2 |
| 8 | Vcc | Positive power supply (2V to 36V) |
Usage Instructions
The LM393 is straightforward to use in a variety of circuits. Below are the steps and considerations for using the component effectively:
Basic Circuit Setup
- Power Supply: Connect the Vcc pin (Pin 8) to a positive voltage source (2V to 36V) and the GND pin (Pin 4) to ground.
- Inputs: Provide the two voltages to be compared to the inverting and non-inverting input pins of the comparator.
- For Comparator 1: Use Pins 2 (inverting) and 3 (non-inverting).
- For Comparator 2: Use Pins 6 (inverting) and 5 (non-inverting).
- Output: The output pins (Pins 1 and 7) will provide a digital signal based on the comparison:
- If the voltage at the non-inverting input is greater than the inverting input, the output will be high (open collector).
- Otherwise, the output will be low.
Important Considerations
- Pull-Up Resistor: The LM393 has an open-collector output, so a pull-up resistor is required to ensure proper operation. Connect a resistor (e.g., 10kΩ) between the output pin and the positive supply voltage.
- Input Voltage Range: Ensure that the input voltages remain within the common-mode voltage range (0V to Vcc - 1.5V).
- Bypass Capacitor: Add a decoupling capacitor (e.g., 0.1µF) near the Vcc pin to reduce noise and improve stability.
Example: Using LM393 with Arduino UNO
The LM393 can be used with an Arduino UNO to detect voltage levels. Below is an example circuit and code:
Circuit Description
- Connect the LM393's Vcc to the Arduino's 5V pin and GND to the Arduino's GND.
- Connect the non-inverting input (Pin 3) to a voltage divider or sensor output.
- Connect the inverting input (Pin 2) to a reference voltage (e.g., 2.5V).
- Use a pull-up resistor (10kΩ) on the output pin (Pin 1) and connect it to an Arduino digital input pin (e.g., D2).
Arduino Code
// LM393 Comparator Example with Arduino UNO
// This code reads the output of the LM393 and turns on an LED if the input
// voltage exceeds the reference voltage.
const int lm393OutputPin = 2; // LM393 output connected to digital pin 2
const int ledPin = 13; // Onboard LED pin
void setup() {
pinMode(lm393OutputPin, INPUT); // Set LM393 output pin as input
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set LED pin as output
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn off LED initially
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int comparatorState = digitalRead(lm393OutputPin); // Read LM393 output
if (comparatorState == HIGH) {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn on LED if input voltage > reference
Serial.println("Input voltage is HIGH");
} else {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn off LED if input voltage <= reference
Serial.println("Input voltage is LOW");
}
delay(500); // Wait for 500ms before next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
No Output Signal:
- Ensure the pull-up resistor is connected to the output pin.
- Verify that the input voltages are within the specified range.
- Check the power supply connections.
Unstable Output:
- Add a bypass capacitor (e.g., 0.1µF) near the Vcc pin to reduce noise.
- Ensure the input signals are not noisy or fluctuating.
Incorrect Output:
- Verify the polarity of the input connections (inverting vs. non-inverting).
- Check the reference voltage and ensure it is set correctly.
FAQs
Q: Can the LM393 be used for high-speed applications?
A: The LM393 is suitable for moderate-speed applications, with a typical response time of a few microseconds. For high-speed requirements, consider using a high-speed comparator IC.
Q: What is the purpose of the pull-up resistor?
A: The LM393 has an open-collector output, which requires a pull-up resistor to define the output voltage level when the output transistor is off.
Q: Can the LM393 handle negative input voltages?
A: No, the LM393 is not designed for negative input voltages. Ensure all input voltages are within the range of 0V to Vcc - 1.5V.
By following this documentation, users can effectively integrate the LM393 into their projects and troubleshoot common issues with ease.