
How to Use T-SIM7000G edited: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with T-SIM7000G edited in Cirkit Designer
Design with T-SIM7000G edited in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The T-SIM7000G is a versatile GSM/GPRS module manufactured by ESP32, designed for IoT (Internet of Things) applications. It supports multiple communication protocols, including LTE, and features low power consumption, making it ideal for battery-powered devices. Additionally, the module includes GPS functionality, enabling location tracking and navigation capabilities. The T-SIM7000G is widely used in applications such as smart metering, asset tracking, environmental monitoring, and remote data collection.
Explore Projects Built with T-SIM7000G edited

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer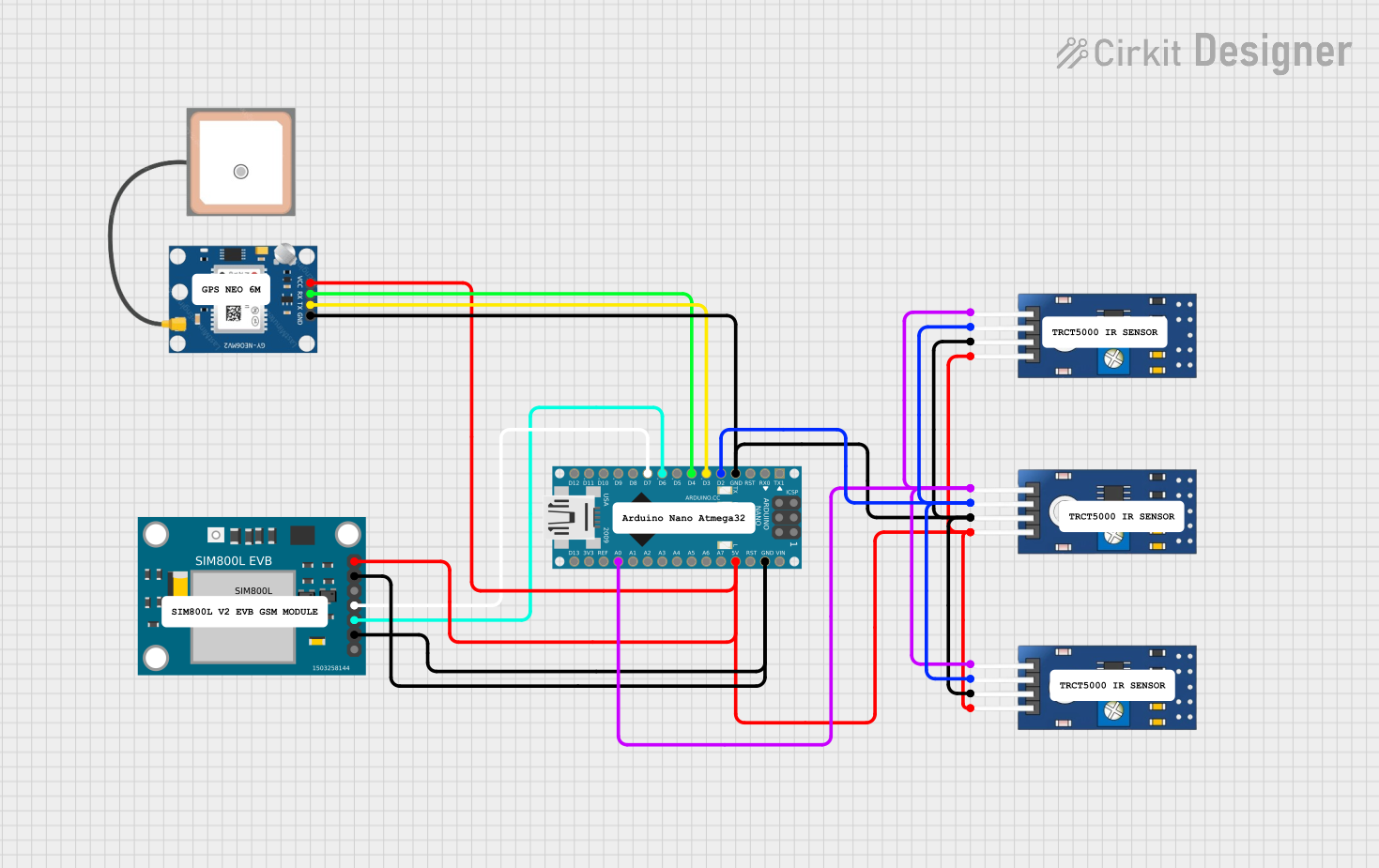
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with T-SIM7000G edited

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
The T-SIM7000G module is packed with features that make it suitable for a wide range of IoT applications. Below are its key technical specifications:
General Specifications
- Manufacturer: ESP32
- Communication Protocols: GSM, GPRS, LTE Cat-M1, NB-IoT
- GPS Support: Yes (GNSS functionality)
- Power Supply Voltage: 3.4V to 4.2V (typical 3.8V)
- Power Consumption:
- Idle: ~1.2mA (low power mode)
- Active: ~300mA (transmitting)
- Operating Temperature: -40°C to +85°C
- Dimensions: 24mm x 24mm
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The T-SIM7000G module has a variety of pins for power, communication, and control. Below is the pinout description:
| Pin Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VCC | Power Input | Main power supply (3.4V to 4.2V). |
| GND | Ground | Ground connection. |
| TXD | Digital Output | UART Transmit pin for serial communication. |
| RXD | Digital Input | UART Receive pin for serial communication. |
| PWRKEY | Digital Input | Power key to turn the module on/off. |
| NET_STATUS | Digital Output | Indicates network status (e.g., connected/disconnected). |
| GPS_TX | Digital Output | UART Transmit pin for GPS data. |
| GPS_RX | Digital Input | UART Receive pin for GPS data. |
| RESET | Digital Input | Resets the module when pulled low. |
| ADC | Analog Input | Analog-to-digital converter input. |
Usage Instructions
The T-SIM7000G module can be integrated into a circuit for IoT applications. Below are the steps and best practices for using the module:
Basic Setup
Power Supply:
- Connect the VCC pin to a stable 3.8V power source.
- Ensure the GND pin is connected to the ground of the circuit.
Serial Communication:
- Connect the TXD pin of the module to the RX pin of your microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO).
- Connect the RXD pin of the module to the TX pin of your microcontroller.
Powering On:
- Pull the PWRKEY pin low for at least 1 second to turn on the module.
Antenna Connection:
- Attach a compatible antenna to the module for GSM and GPS functionality.
Example: Using T-SIM7000G with Arduino UNO
Below is an example code to send an SMS using the T-SIM7000G module with an Arduino UNO:
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Define RX and TX pins for SoftwareSerial
SoftwareSerial sim7000(7, 8); // RX = 7, TX = 8
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication
Serial.begin(9600); // For debugging
sim7000.begin(9600); // For T-SIM7000G communication
Serial.println("Initializing T-SIM7000G...");
// Power on the module
pinMode(9, OUTPUT); // PWRKEY connected to pin 9
digitalWrite(9, LOW);
delay(1000); // Hold PWRKEY low for 1 second
digitalWrite(9, HIGH);
delay(5000); // Wait for the module to initialize
// Send AT command to check communication
sim7000.println("AT");
delay(1000);
while (sim7000.available()) {
Serial.write(sim7000.read());
}
// Send SMS
sim7000.println("AT+CMGF=1"); // Set SMS mode to text
delay(1000);
sim7000.println("AT+CMGS=\"+1234567890\""); // Replace with recipient's number
delay(1000);
sim7000.println("Hello from T-SIM7000G!"); // SMS content
sim7000.write(26); // Send Ctrl+Z to send the SMS
delay(5000);
}
void loop() {
// Nothing to do here
}
Best Practices
- Use a stable power supply to avoid unexpected resets or malfunctions.
- Ensure proper antenna placement for optimal GSM and GPS signal reception.
- Use level shifters if interfacing with a 5V microcontroller, as the module operates at 3.3V logic levels.
- Avoid placing the module near high-frequency noise sources to prevent interference.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Module Not Powering On:
- Ensure the PWRKEY pin is pulled low for at least 1 second during startup.
- Verify the power supply voltage is within the specified range (3.4V to 4.2V).
No Network Connection:
- Check the antenna connection and ensure it is securely attached.
- Verify that the SIM card is properly inserted and activated.
- Use the
AT+CSQcommand to check signal strength.
GPS Not Working:
- Ensure the GPS antenna is connected and placed in an open area with a clear view of the sky.
- Use the
AT+CGNSPWR=1command to enable GPS functionality.
Serial Communication Issues:
- Confirm the baud rate of the module matches the microcontroller's settings.
- Check the wiring of the TX and RX pins.
FAQs
Q: Can the T-SIM7000G operate on 5V logic levels?
A: No, the module operates at 3.3V logic levels. Use level shifters if interfacing with a 5V microcontroller.Q: How do I check the module's firmware version?
A: Use theAT+CGMRcommand to retrieve the firmware version.Q: What is the maximum data rate supported by the module?
A: The T-SIM7000G supports a maximum data rate of 375kbps for LTE Cat-M1 and 32kbps for NB-IoT.Q: Can I use the module for voice calls?
A: Yes, the T-SIM7000G supports voice calls in addition to SMS and data communication.
By following this documentation, users can effectively integrate and utilize the T-SIM7000G module in their IoT projects.