
Cirkit Designer
Your all-in-one circuit design IDE
Home /
Component Documentation
How to Use MCB 2POLE AC: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with MCB 2POLE AC in Cirkit Designer
Design with MCB 2POLE AC in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The MCB 2POLE AC is a Miniature Circuit Breaker designed for alternating current (AC) applications. It features two poles, making it suitable for protecting electrical circuits from overcurrent and short circuits. This component is essential in residential, commercial, and industrial electrical systems to ensure safety and prevent damage to electrical equipment.
Explore Projects Built with MCB 2POLE AC
Flush Switch Controlled Lamp Circuit with AC Power Supply and MCB Protection

This circuit is designed to control a lamp using a flush switch and is protected by two MCBs (Miniature Circuit Breakers). The AC supply is connected to the input of the first MCB, whose output is connected to the flush switch. The flush switch then controls the power to the lamp, with the second MCB placed in the neutral line for additional safety.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerSolar-Powered Home Energy System with Automatic Transfer Switch and Battery Backup
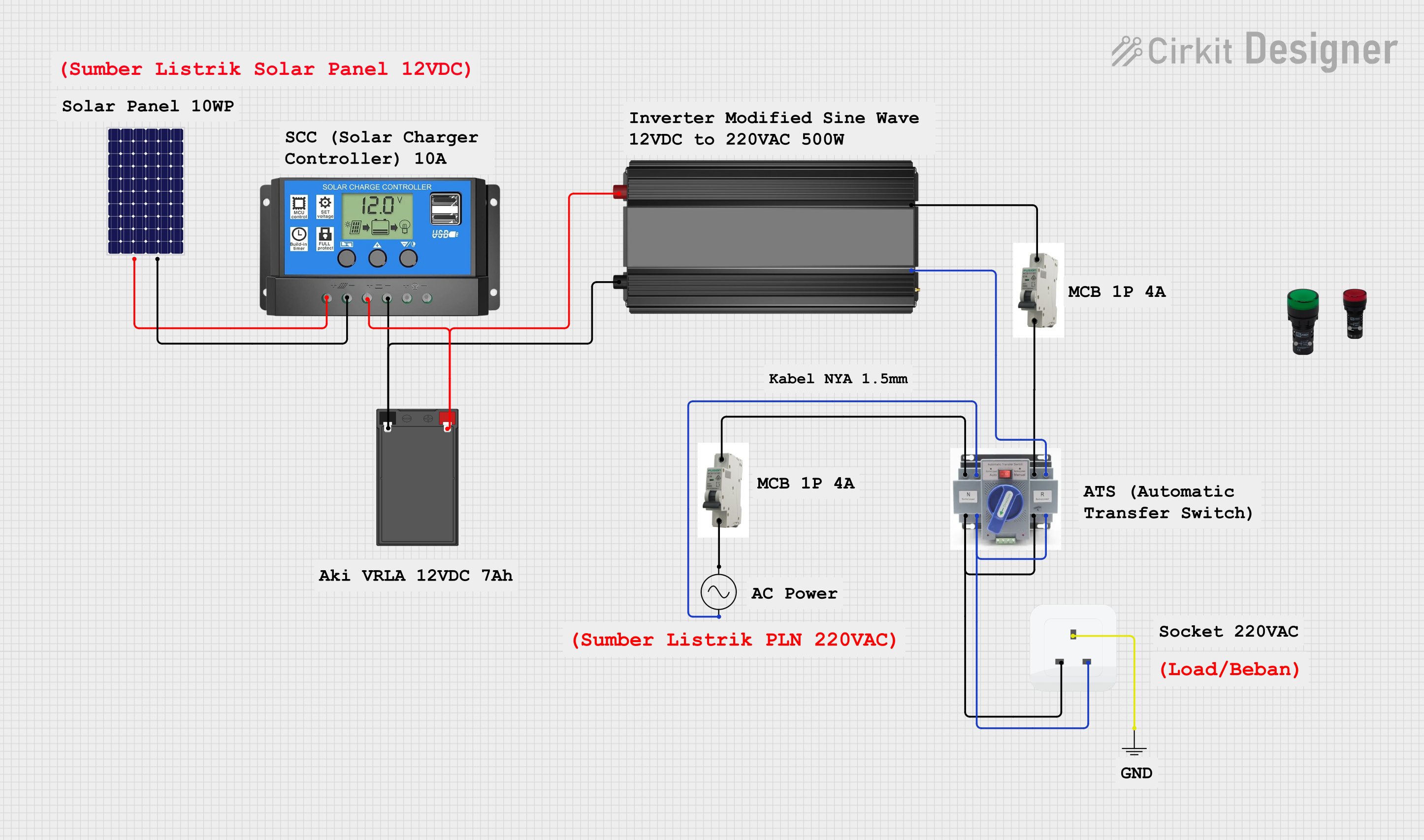
This circuit is a solar power system with an automatic transfer switch (ATS) that manages power from both a solar panel and an AC supply. The solar panel charges a battery through a solar charge controller, and the power inverter converts the stored DC power to AC, which is then distributed through an MCB to a socket. The ATS ensures seamless switching between solar and AC power sources.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerSolar-Powered Battery Charging System with DC-DC Converter
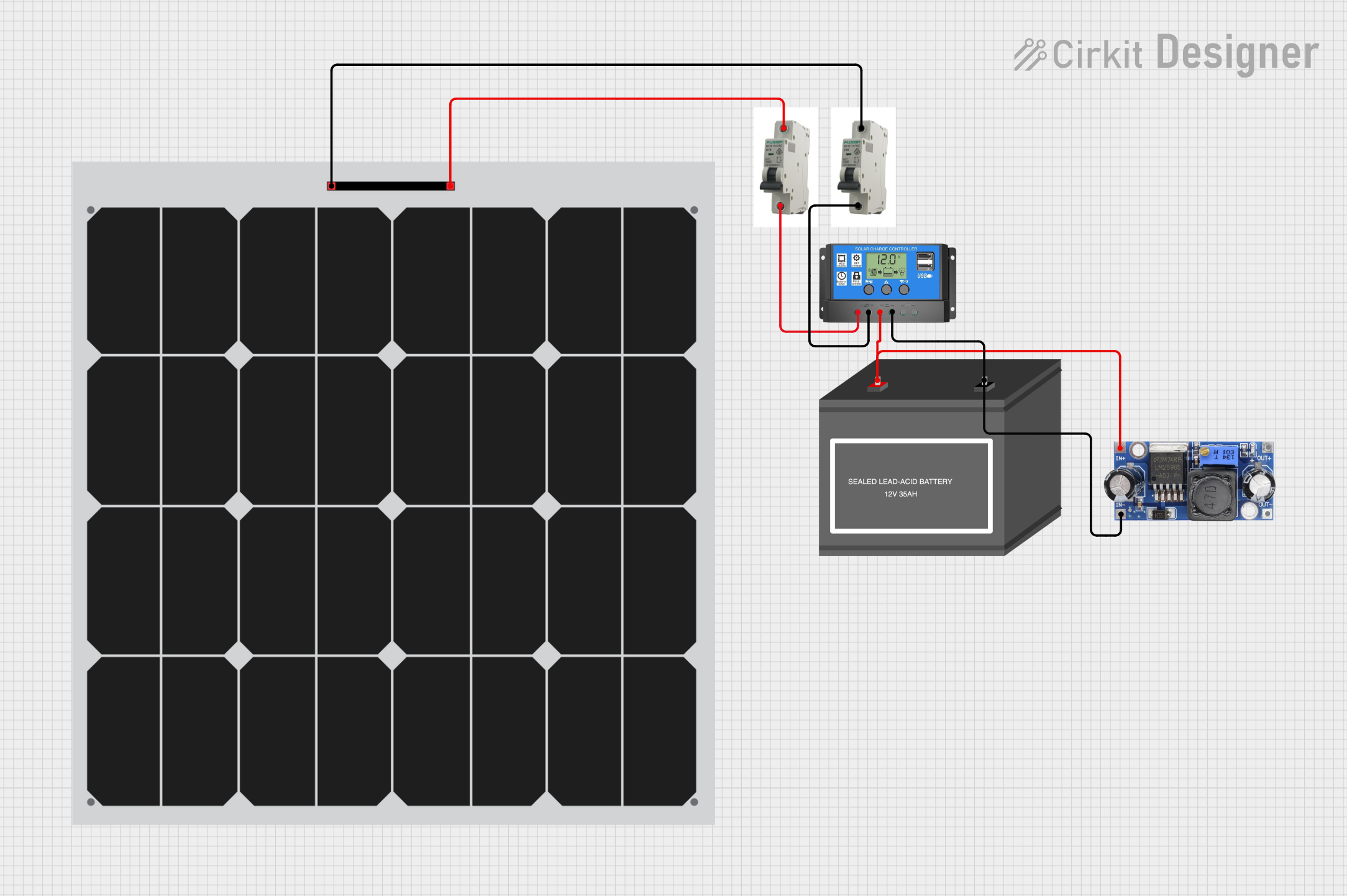
This circuit is a solar power system that uses two solar panels connected through MCBs to a solar charge controller. The charge controller manages the charging of a 12V battery and powers a DC-DC converter, which provides a regulated output voltage.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerAC Bulb Control Circuit with Flush Switch and MCB Protection

This circuit is designed to control an AC bulb using a flush switch. The AC power supply is connected through an MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) for protection, and the flush switch acts as an on/off control for the bulb. There is no microcontroller or embedded code involved in this simple power control circuit.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with MCB 2POLE AC

Flush Switch Controlled Lamp Circuit with AC Power Supply and MCB Protection
This circuit is designed to control a lamp using a flush switch and is protected by two MCBs (Miniature Circuit Breakers). The AC supply is connected to the input of the first MCB, whose output is connected to the flush switch. The flush switch then controls the power to the lamp, with the second MCB placed in the neutral line for additional safety.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Solar-Powered Home Energy System with Automatic Transfer Switch and Battery Backup
This circuit is a solar power system with an automatic transfer switch (ATS) that manages power from both a solar panel and an AC supply. The solar panel charges a battery through a solar charge controller, and the power inverter converts the stored DC power to AC, which is then distributed through an MCB to a socket. The ATS ensures seamless switching between solar and AC power sources.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Solar-Powered Battery Charging System with DC-DC Converter
This circuit is a solar power system that uses two solar panels connected through MCBs to a solar charge controller. The charge controller manages the charging of a 12V battery and powers a DC-DC converter, which provides a regulated output voltage.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
AC Bulb Control Circuit with Flush Switch and MCB Protection
This circuit is designed to control an AC bulb using a flush switch. The AC power supply is connected through an MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) for protection, and the flush switch acts as an on/off control for the bulb. There is no microcontroller or embedded code involved in this simple power control circuit.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Residential Electrical Panels: Protects household circuits from overloads and short circuits.
- Commercial Buildings: Ensures the safety of electrical installations in offices and retail spaces.
- Industrial Settings: Safeguards machinery and equipment from electrical faults.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Used in solar and wind power installations to protect inverters and other components.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Rated Voltage | 240/415V AC |
| Rated Current | 6A, 10A, 16A, 20A, 25A, 32A |
| Breaking Capacity | 6kA |
| Number of Poles | 2 |
| Frequency | 50/60 Hz |
| Tripping Curve | B, C, D |
| Operating Temperature | -5°C to +40°C |
| Mounting | DIN Rail |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Line Input (Pole 1) |
| 2 | Line Output (Pole 1) |
| 3 | Line Input (Pole 2) |
| 4 | Line Output (Pole 2) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Mounting the MCB:
- Secure the MCB onto a DIN rail in your electrical panel.
- Ensure it is firmly attached to prevent any movement.
Wiring the MCB:
- Connect the incoming AC supply to the Line Input terminals (Pin 1 and Pin 3).
- Connect the outgoing load to the Line Output terminals (Pin 2 and Pin 4).
- Ensure all connections are tight and secure to prevent loose contacts.
Testing the MCB:
- After installation, switch on the MCB.
- Verify that the connected load operates correctly without tripping the MCB.
- Test the tripping mechanism by creating a controlled overload condition.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Correct Rating: Ensure the MCB rating matches the load requirements to avoid nuisance tripping or insufficient protection.
- Regular Inspection: Periodically check the MCB for signs of wear or damage.
- Proper Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation around the MCB to prevent overheating.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the rated current of the MCB to maintain its protective function.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
MCB Tripping Frequently:
- Cause: Overloaded circuit or short circuit.
- Solution: Reduce the load or check for short circuits in the wiring.
MCB Not Tripping During Fault:
- Cause: Faulty MCB or incorrect rating.
- Solution: Replace the MCB or verify the rating matches the circuit requirements.
Loose Connections:
- Cause: Improper tightening of terminals.
- Solution: Ensure all terminal screws are securely tightened.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Check Load: Verify that the connected load does not exceed the MCB's rated current.
- Inspect Wiring: Look for any signs of damaged or frayed wires that could cause short circuits.
- Test MCB: Use a multimeter to check the continuity and proper functioning of the MCB.
- Replace if Necessary: If the MCB is found to be faulty, replace it with a new one of the same rating and specifications.
By following this documentation, users can effectively utilize the MCB 2POLE AC in their electrical systems, ensuring safety and reliability.