
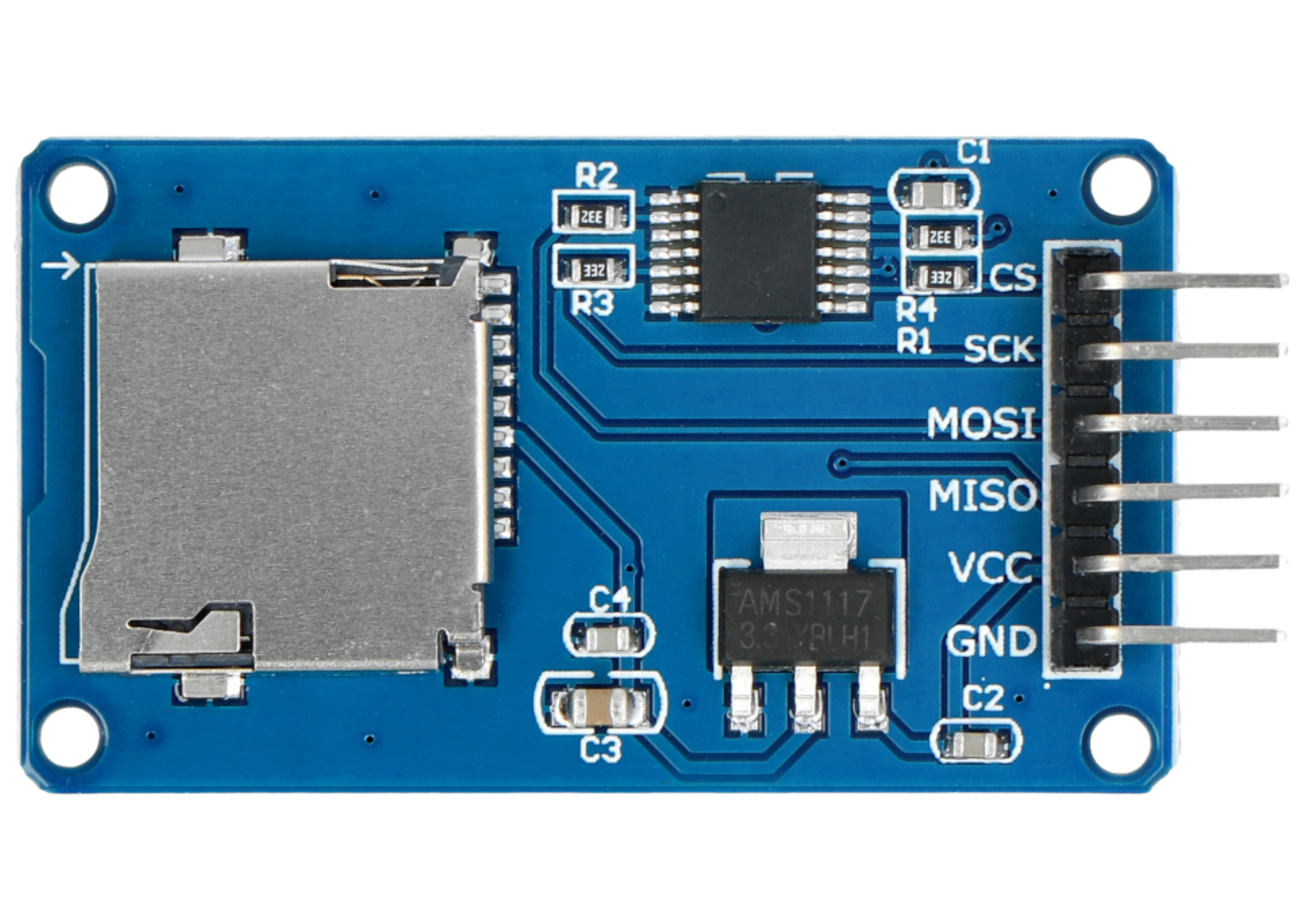
How to Use sd card module: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with sd card module in Cirkit Designer
Design with sd card module in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The SD Card Module is a compact and versatile component designed to interface SD (Secure Digital) cards with microcontrollers. It enables the storage and retrieval of data, making it an essential tool for projects requiring large amounts of non-volatile memory. This module is widely used in applications such as data logging, file storage, multimedia playback, and portable devices.
Common applications and use cases:
- Data logging for sensors in IoT projects
- Storing configuration files or firmware updates
- Multimedia storage for audio, video, or images
- File transfer and storage in embedded systems
Explore Projects Built with sd card module
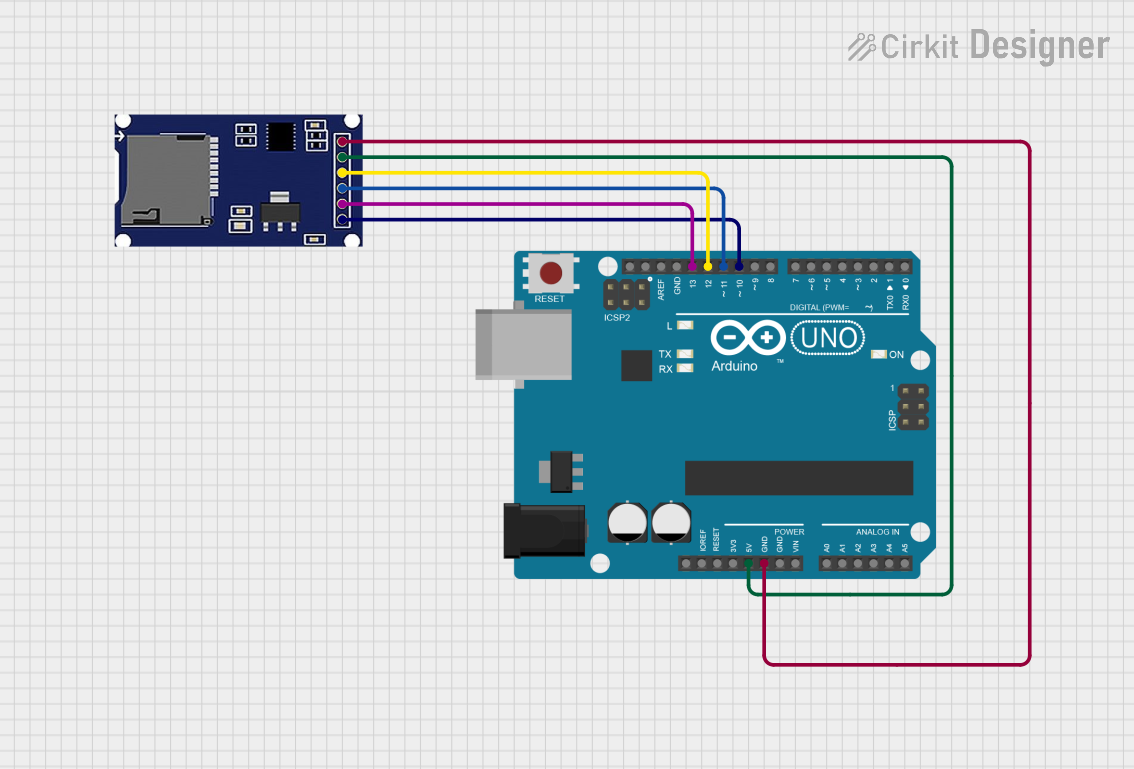
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer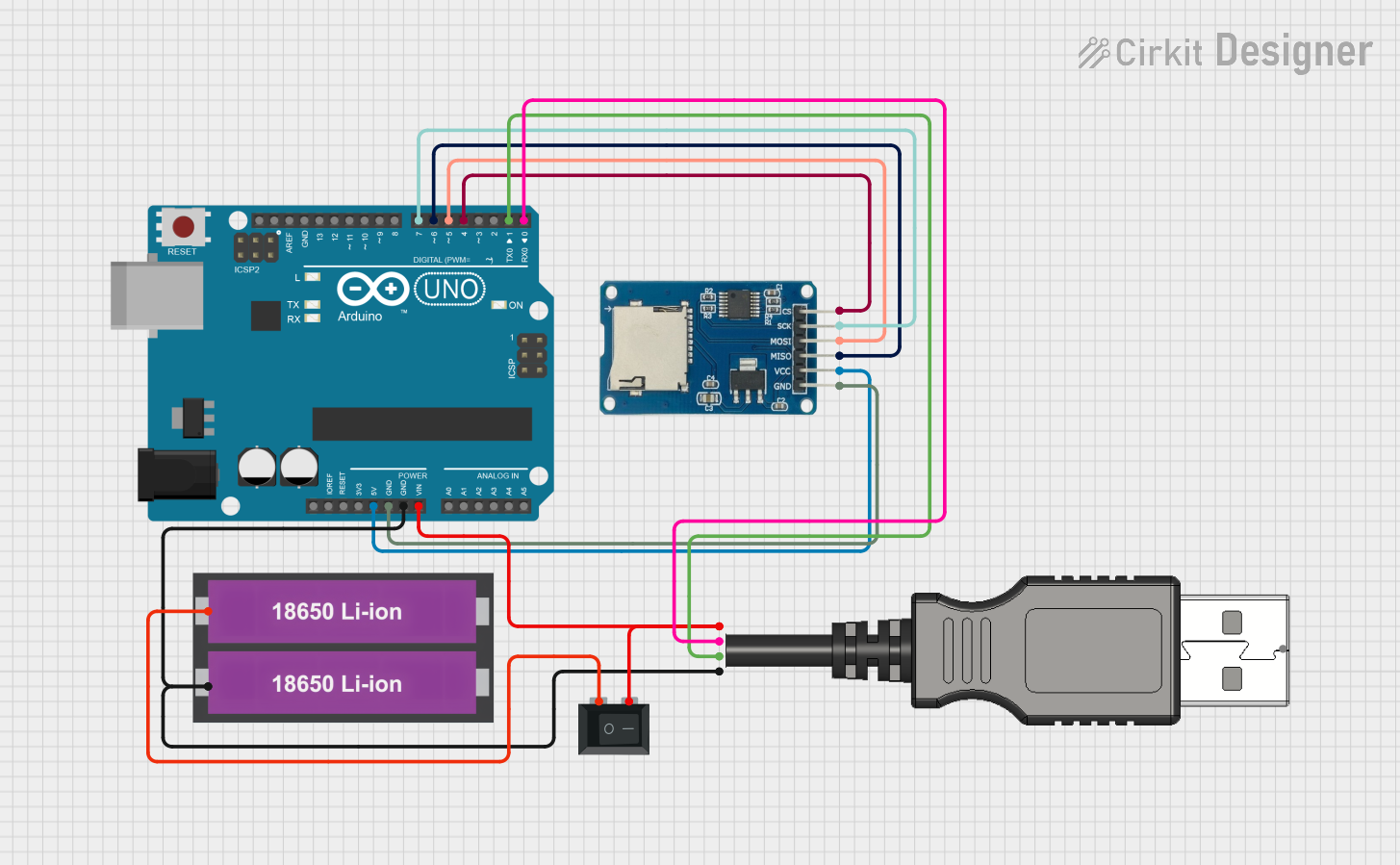
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer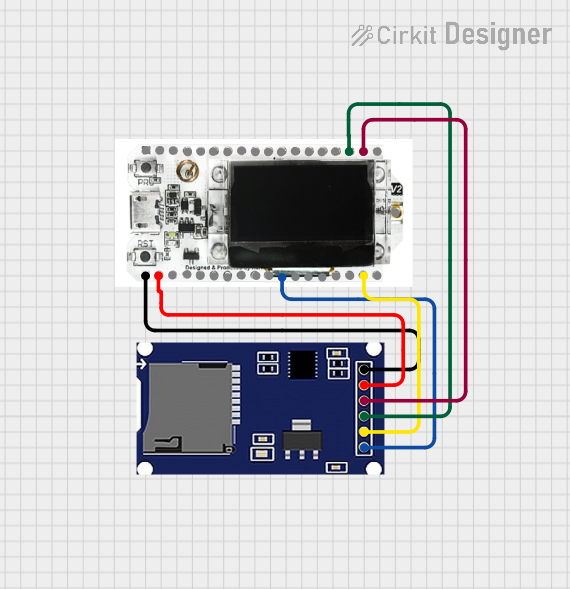
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer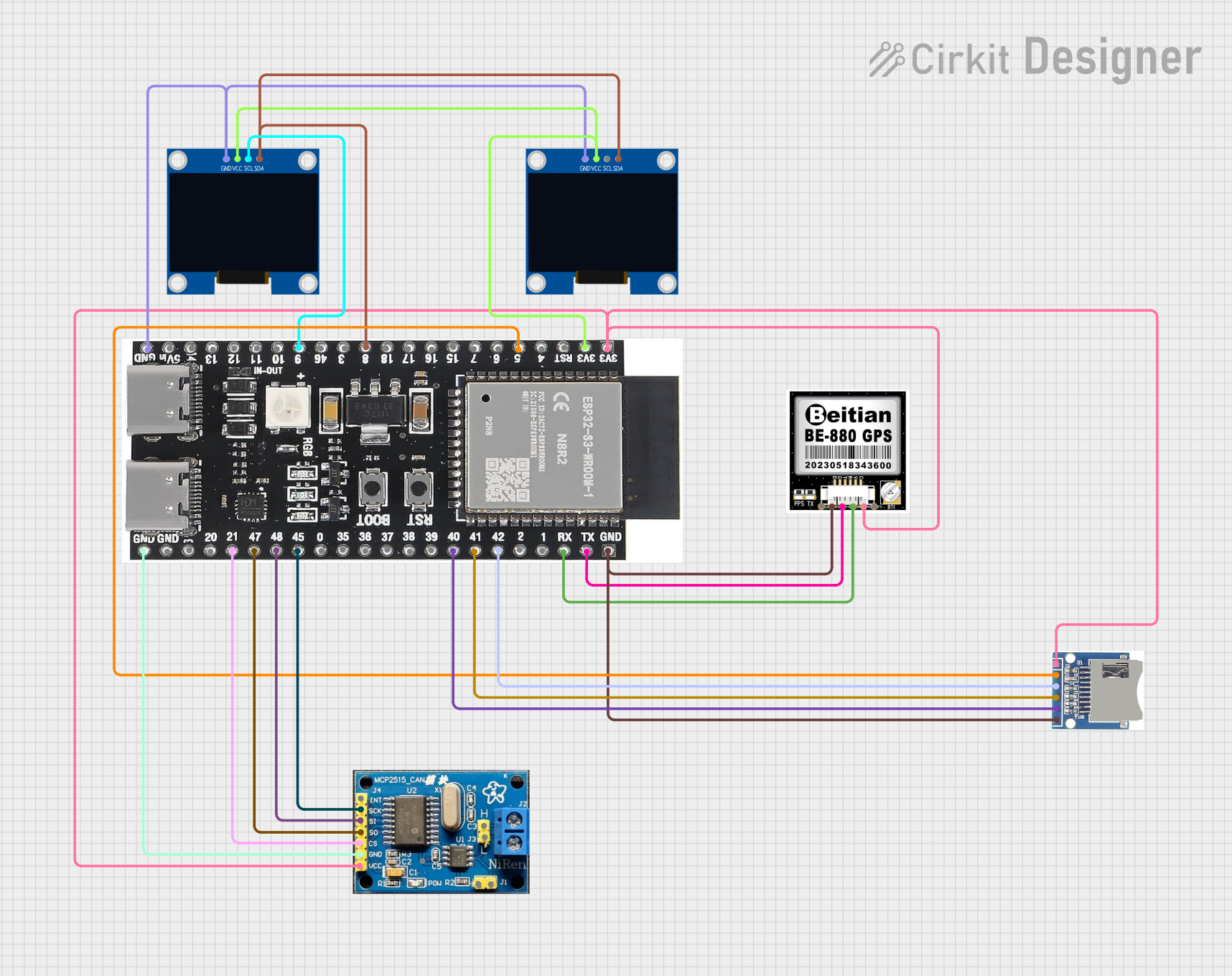
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with sd card module

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V (logic level) with onboard voltage regulator for 5V compatibility
- Current Consumption: Typically 50mA (varies with SD card usage)
- Supported SD Card Types: Standard SD and microSD cards (FAT16/FAT32 file systems)
- Communication Protocol: SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface)
- Dimensions: Typically 42mm x 24mm x 12mm (varies by manufacturer)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
VCC |
Power input (3.3V or 5V, depending on the module's onboard regulator). |
GND |
Ground connection. |
MISO |
Master In Slave Out - SPI data output from the SD card to the microcontroller. |
MOSI |
Master Out Slave In - SPI data input from the microcontroller to the SD card. |
SCK |
Serial Clock - SPI clock signal. |
CS |
Chip Select - Used to select the SD card module for communication. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the SD Card Module in a Circuit
- Power the Module: Connect the
VCCpin to a 3.3V or 5V power source (depending on the module's regulator) and theGNDpin to ground. - Connect SPI Pins: Connect the
MISO,MOSI,SCK, andCSpins to the corresponding SPI pins on your microcontroller. - Insert SD Card: Ensure the SD card is formatted to FAT16 or FAT32 before inserting it into the module.
- Initialize the Module: Use an appropriate library (e.g., the Arduino SD library) to initialize the module and verify the SD card is detected.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Levels: Ensure the module is compatible with your microcontroller's logic levels (3.3V or 5V). Most modules include a voltage regulator and level shifters for 5V compatibility.
- File System: Format the SD card to FAT16 or FAT32 for compatibility with most libraries.
- SPI Speed: Use a suitable SPI clock speed to ensure reliable communication. Start with a lower speed if issues arise.
- Pull-Up Resistors: Some modules may require external pull-up resistors on the SPI lines for stable operation.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the SD Card Module with an Arduino UNO to read and write data to a file.
#include <SPI.h>
#include <SD.h>
// Define the chip select pin for the SD card module
const int chipSelect = 10;
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial) {
; // Wait for the serial port to connect (for native USB boards)
}
Serial.println("Initializing SD card...");
// Check if the SD card is present and can be initialized
if (!SD.begin(chipSelect)) {
Serial.println("Card failed, or not present");
// Don't proceed if the SD card initialization fails
while (1);
}
Serial.println("Card initialized successfully!");
// Create or open a file on the SD card
File dataFile = SD.open("example.txt", FILE_WRITE);
// Check if the file opened successfully
if (dataFile) {
dataFile.println("Hello, SD card!"); // Write data to the file
dataFile.close(); // Close the file to save changes
Serial.println("Data written to file.");
} else {
Serial.println("Error opening file.");
}
}
void loop() {
// Nothing to do here
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
SD Card Not Detected:
- Ensure the SD card is properly inserted into the module.
- Verify the SD card is formatted to FAT16 or FAT32.
- Check the wiring between the module and the microcontroller, especially the
CSpin.
File Read/Write Errors:
- Ensure the file name follows the 8.3 filename convention (e.g.,
example.txt). - Verify the SD card is not write-protected or corrupted.
- Ensure the file name follows the 8.3 filename convention (e.g.,
Unstable Operation:
- Use shorter wires for SPI connections to reduce noise.
- Add pull-up resistors to the SPI lines if necessary.
Power Issues:
- Ensure the power supply can provide sufficient current for the module and SD card.
- Check if the onboard voltage regulator is functioning correctly.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a microSD card with this module?
A: Yes, most SD card modules support both standard SD and microSD cards using an adapter.
Q: What is the maximum storage size supported?
A: This depends on the library and microcontroller used. Most libraries support up to 32GB (FAT32).
Q: Can I use multiple SD card modules on the same SPI bus?
A: Yes, but each module must have a unique CS pin to avoid conflicts.
Q: Why is my SD card module overheating?
A: Check for incorrect wiring or voltage levels. Ensure the module is not exposed to excessive current.