
How to Use RGB LED: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with RGB LED in Cirkit Designer
Design with RGB LED in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
An RGB LED is a versatile electronic component that combines red, green, and blue light-emitting diodes to produce a wide spectrum of colors. By adjusting the intensity of each individual color, it can create various hues and shades, making it popular in decorative lighting, signal indicators, and display panels. RGB LEDs are commonly used in electronics projects, including those involving microcontrollers like the Arduino UNO.
Explore Projects Built with RGB LED
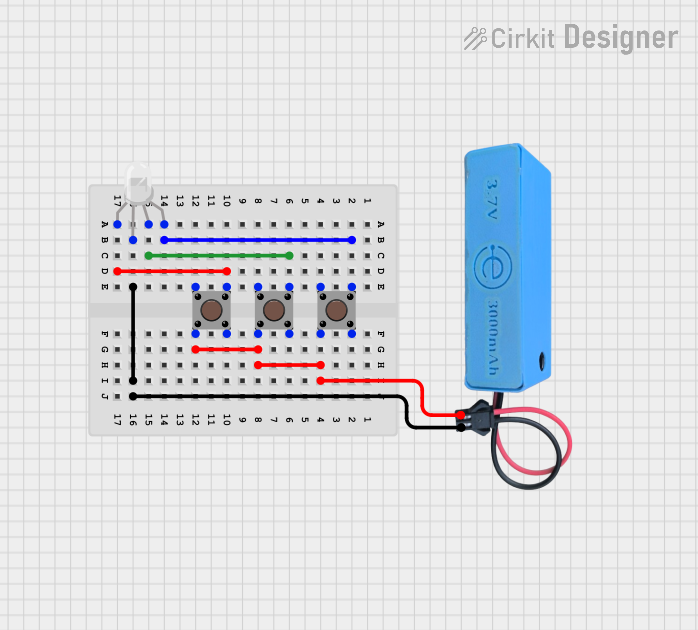
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer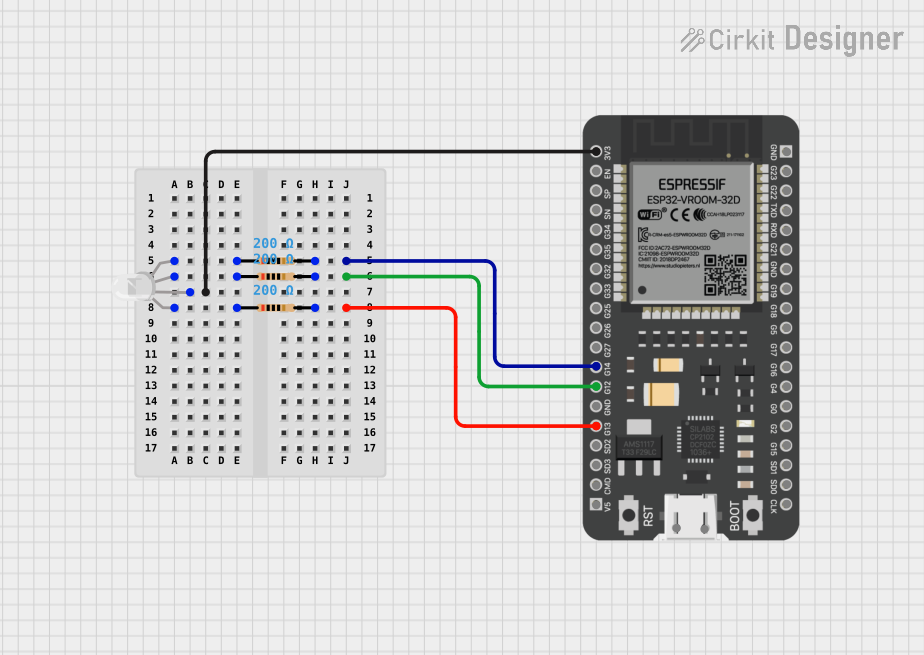
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer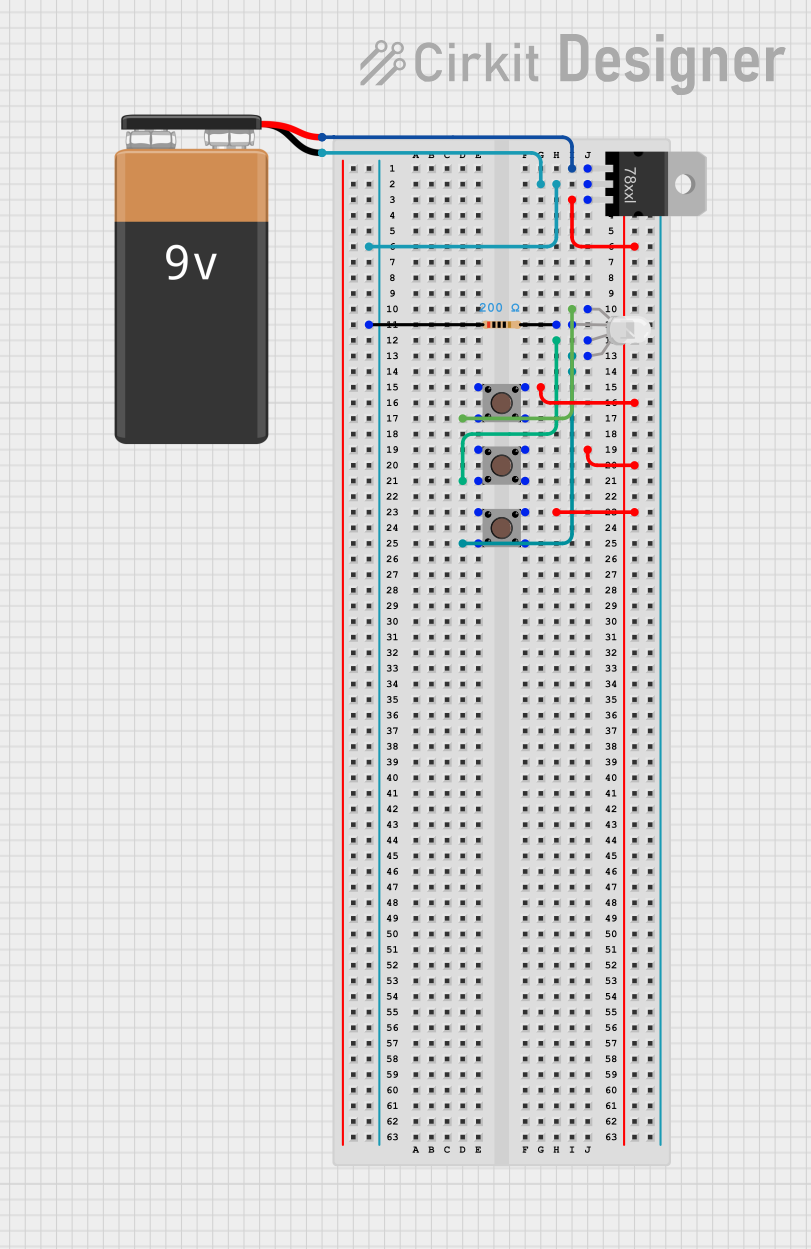
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer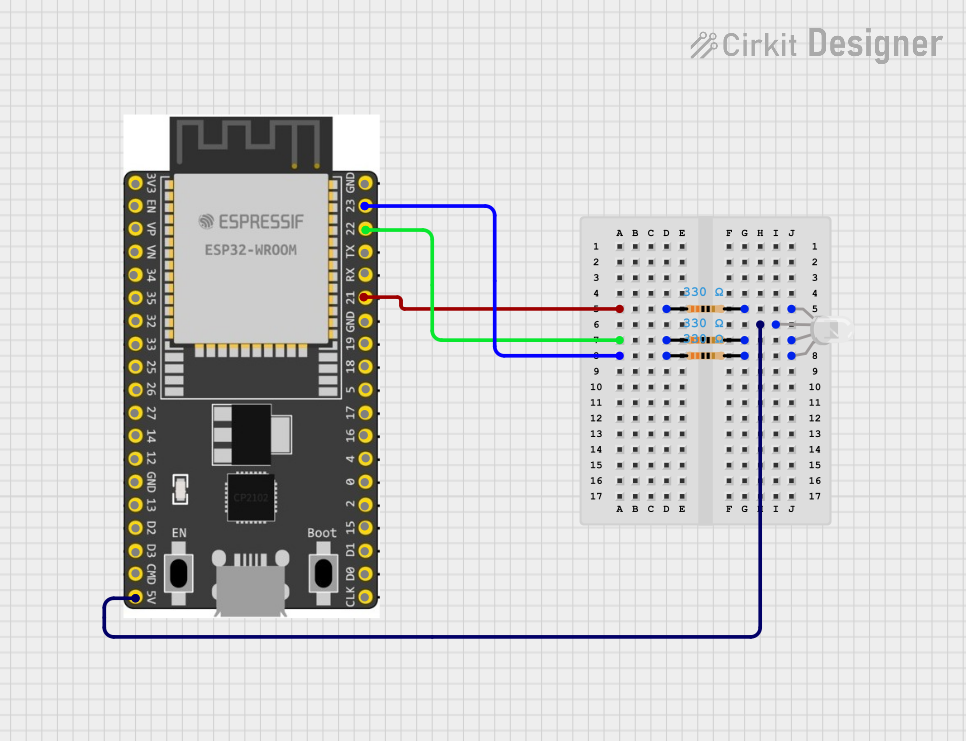
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with RGB LED

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Forward Voltage (Typical): Red: 2.0-2.2V, Green: 3.0-3.2V, Blue: 3.0-3.2V
- Forward Current: 20mA (per channel)
- Luminous Intensity: Varies by color and manufacturer
- Viewing Angle: Typically 120 degrees
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description | Common Type |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Red Anode/Cathode | Anode/Cathode |
| 2 | Green Anode/Cathode | Anode/Cathode |
| 3 | Blue Anode/Cathode | Anode/Cathode |
| 4 | Common Cathode/Anode | Cathode/Anode |
Note: The common pin is either the common anode or common cathode, depending on the type of RGB LED.
Usage Instructions
Connecting to a Circuit
- Identify the Type: Determine if your RGB LED is common anode or common cathode.
- Current Limiting Resistors: Connect a current-limiting resistor in series with each anode/cathode of the red, green, and blue LEDs. Calculate the resistor value using Ohm's law:
R = (V_supply - V_LED) / I_LED. - Wiring to Arduino: Connect the common pin to either GND (common cathode) or 5V (common anode). Connect the other pins to PWM-capable digital pins on the Arduino.
Best Practices
- Use pulse-width modulation (PWM) to control the brightness of each color.
- Avoid exceeding the maximum forward current to prevent damage.
- Use resistors to prevent excessive current through the LEDs.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
// Define the RGB LED pins
const int RED_PIN = 9; // Red pin connected to digital pin 9
const int GREEN_PIN = 10; // Green pin connected to digital pin 10
const int BLUE_PIN = 11; // Blue pin connected to digital pin 11
void setup() {
// Set the RGB LED pins as output
pinMode(RED_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(GREEN_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(BLUE_PIN, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Set the color to purple (Red + Blue)
analogWrite(RED_PIN, 255); // Red at full intensity
analogWrite(GREEN_PIN, 0); // Green off
analogWrite(BLUE_PIN, 255); // Blue at full intensity
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
// Set the color to aqua (Green + Blue)
analogWrite(RED_PIN, 0); // Red off
analogWrite(GREEN_PIN, 255); // Green at full intensity
analogWrite(BLUE_PIN, 255); // Blue at full intensity
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Note: The above code assumes a common anode RGB LED. For a common cathode, set the pins to LOW to turn on the LED.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- LED Not Lighting Up: Ensure the common pin is correctly connected to 5V (common anode) or GND (common cathode). Check the polarity of the individual LED pins.
- Incorrect Colors: Verify that the correct pins are connected to the corresponding color channels on the Arduino.
- Dim LED: Confirm that the current-limiting resistors are of the correct value and that the Arduino's PWM function is working properly.
Solutions and Tips
- Double-check wiring and pin assignments.
- Use a multimeter to verify the voltage across the LED pins.
- Ensure that the PWM values in the code match the desired color mix.
FAQs
Q: Can I connect an RGB LED directly to an Arduino without resistors? A: No, you should always use current-limiting resistors to prevent damaging the LED and the Arduino.
Q: How do I produce white light with an RGB LED? A: Set the PWM values for red, green, and blue to full brightness to mix the colors into white.
Q: What is PWM and how does it control the LED brightness? A: PWM stands for Pulse-Width Modulation. It controls the brightness by varying the duty cycle of the power supplied to the LED.