
Cirkit Designer
Your all-in-one circuit design IDE
Home /
Component Documentation
How to Use INA226: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
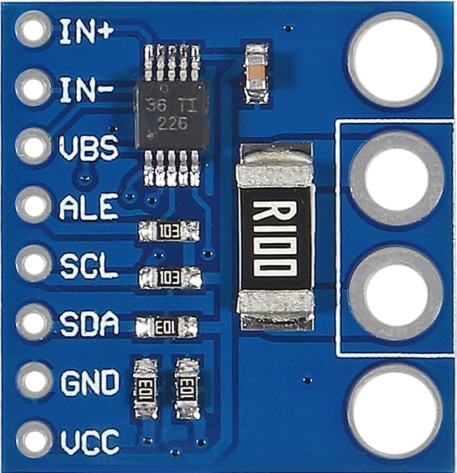
 Design with INA226 in Cirkit Designer
Design with INA226 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The INA226, manufactured by Sensor (Part ID: Volt/Current), is a high-side current shunt monitor with an integrated I2C interface. It is designed to measure voltage, current, and power in a wide range of applications. The device features a precision analog-to-digital converter (ADC) and operates with a supply voltage of 2.7V to 5.5V, making it ideal for battery-powered devices and energy monitoring systems.
Explore Projects Built with INA226
Battery-Powered Load Cell Amplifier with INA125 and LM324
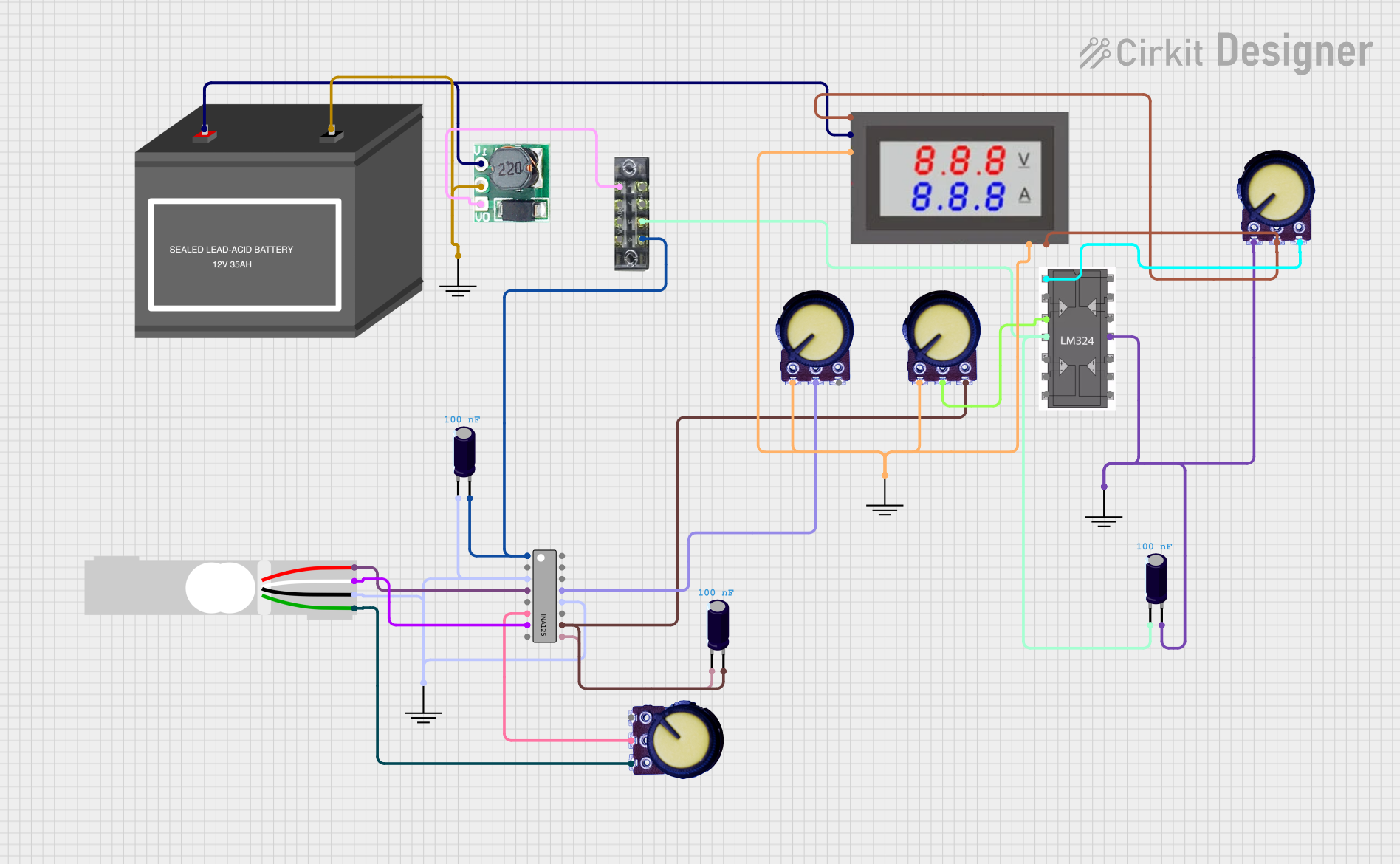
This circuit is a load cell signal conditioning and amplification system. It uses an INA125 instrumentation amplifier to amplify the differential signal from a load cell, with additional filtering and gain control provided by potentiometers and capacitors. The amplified signal is then monitored by a digital voltmeter, and the entire system is powered by a 12V battery with a step-up boost converter to provide stable voltage.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerESP32-Based Motor Control System with INA219 Current Sensor and ST7735S Display
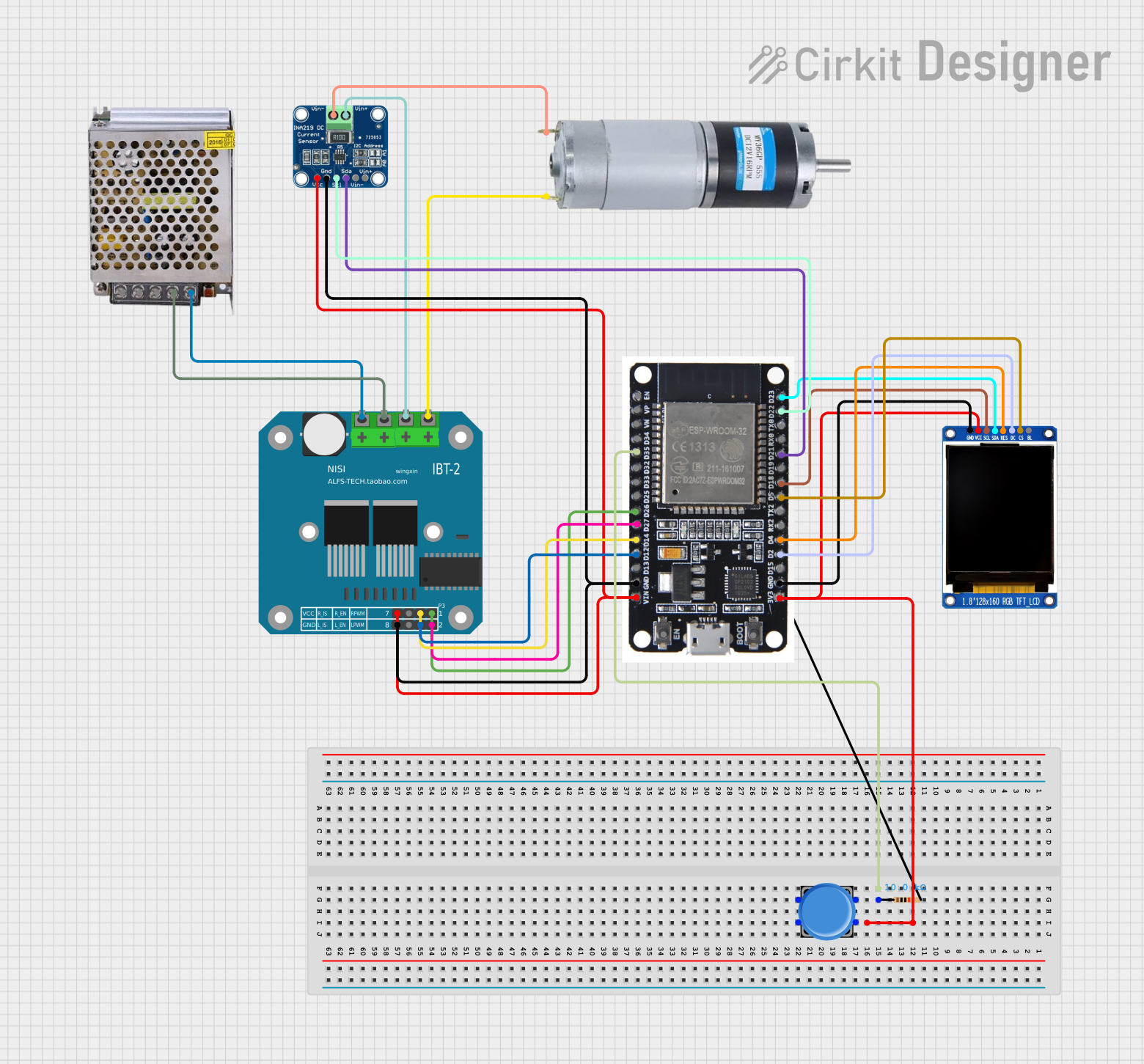
This circuit is a motor control system using an ESP32 microcontroller, an INA219 current sensor, and a BTS7960 motor driver. The ESP32 reads current data from the INA219 and controls the motor driver, while a display module shows relevant information. A pushbutton is included for user interaction.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerSolar-Powered Environmental Monitoring System with ESP32-C3 and MPPT Charge Control
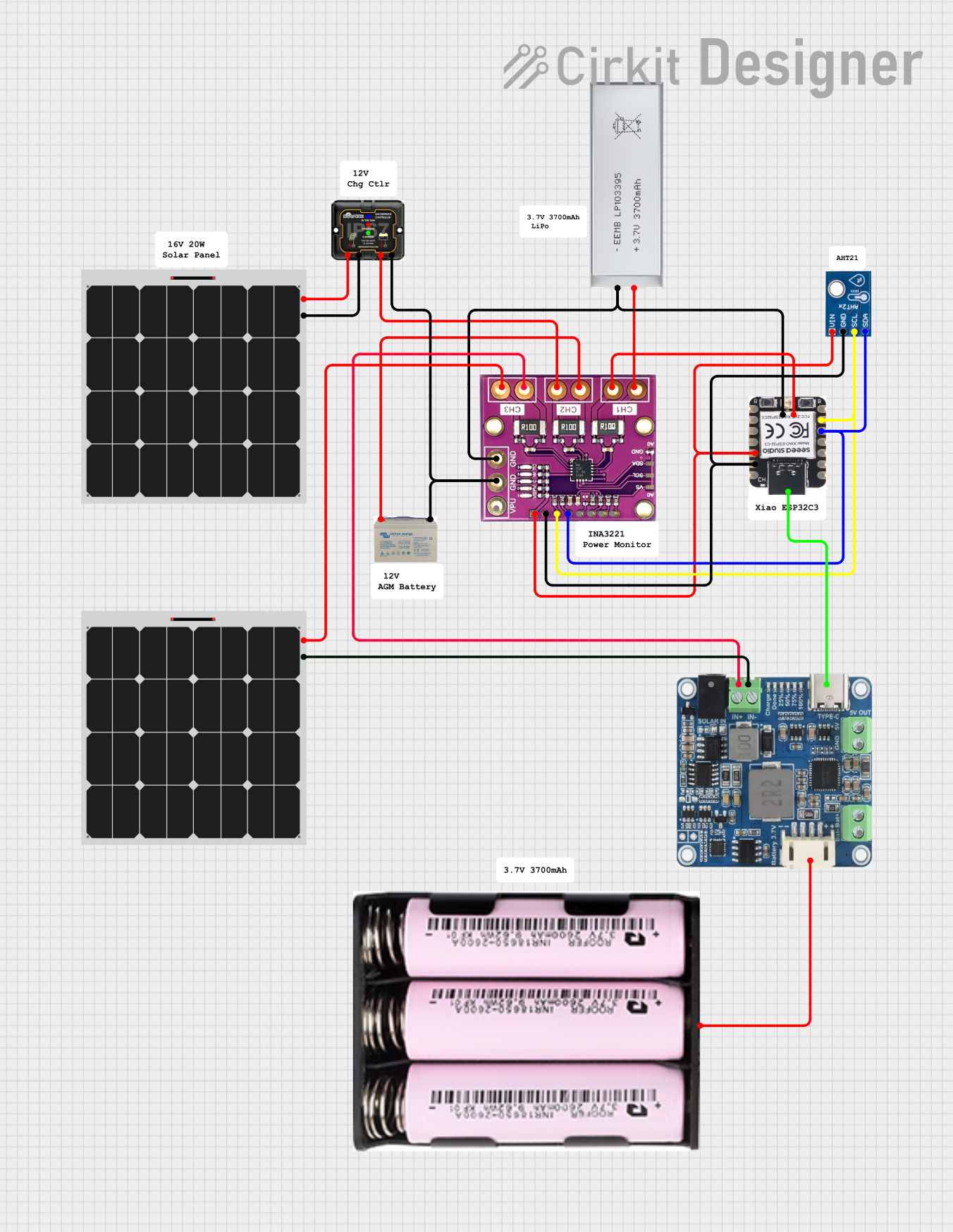
This circuit is designed for solar energy management and monitoring. It includes a 12V AGM battery charged by solar panels through an MPPT charge controller, with voltage monitoring provided by an INA3221 sensor. Additionally, a 3.7V battery is connected to an ESP32-C3 microcontroller and an AHT21 sensor for environmental data collection, with power management handled by a Waveshare Solar Manager.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerBattery-Powered Emergency Alert System with NUCLEO-F072RB, SIM800L, and GPS NEO 6M

This circuit is an emergency alert system that uses a NUCLEO-F072RB microcontroller to send SMS alerts and make calls via a SIM800L GSM module, while obtaining location data from a GPS NEO 6M module. The system is powered by a Li-ion battery and includes a TP4056 module for battery charging and protection, with a rocker switch to control power to the microcontroller.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with INA226

Battery-Powered Load Cell Amplifier with INA125 and LM324
This circuit is a load cell signal conditioning and amplification system. It uses an INA125 instrumentation amplifier to amplify the differential signal from a load cell, with additional filtering and gain control provided by potentiometers and capacitors. The amplified signal is then monitored by a digital voltmeter, and the entire system is powered by a 12V battery with a step-up boost converter to provide stable voltage.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
ESP32-Based Motor Control System with INA219 Current Sensor and ST7735S Display
This circuit is a motor control system using an ESP32 microcontroller, an INA219 current sensor, and a BTS7960 motor driver. The ESP32 reads current data from the INA219 and controls the motor driver, while a display module shows relevant information. A pushbutton is included for user interaction.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Solar-Powered Environmental Monitoring System with ESP32-C3 and MPPT Charge Control
This circuit is designed for solar energy management and monitoring. It includes a 12V AGM battery charged by solar panels through an MPPT charge controller, with voltage monitoring provided by an INA3221 sensor. Additionally, a 3.7V battery is connected to an ESP32-C3 microcontroller and an AHT21 sensor for environmental data collection, with power management handled by a Waveshare Solar Manager.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Battery-Powered Emergency Alert System with NUCLEO-F072RB, SIM800L, and GPS NEO 6M
This circuit is an emergency alert system that uses a NUCLEO-F072RB microcontroller to send SMS alerts and make calls via a SIM800L GSM module, while obtaining location data from a GPS NEO 6M module. The system is powered by a Li-ion battery and includes a TP4056 module for battery charging and protection, with a rocker switch to control power to the microcontroller.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Battery management systems
- Power supply monitoring
- Solar inverters
- Industrial automation
- IoT devices requiring energy consumption tracking
Technical Specifications
Key Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Supply Voltage (Vcc) | 2.7V to 5.5V |
| Input Voltage Range | 0V to 36V |
| Current Measurement Range | Determined by external shunt |
| ADC Resolution | 16-bit |
| Communication Interface | I2C (up to 1 MHz) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +125°C |
| Power Consumption | 330 µA (typical) |
Pin Configuration
The INA226 is available in a small 10-pin VSSOP package. Below is the pinout description:
| Pin No. | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VBUS | Voltage input to measure bus voltage |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | SCL | I2C clock input |
| 4 | SDA | I2C data input/output |
| 5 | ALERT | Alert output for programmable threshold violations |
| 6 | ADDR | I2C address selection pin |
| 7 | VSHUNT | Voltage input to measure across the external shunt resistor |
| 8 | VCC | Power supply input |
| 9, 10 | NC | No connection (leave floating or connect to ground for stability) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the INA226 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a 2.7V to 5.5V power source and the GND pin to the ground.
- Shunt Resistor: Place a precision shunt resistor between the load and ground. Connect the VSHUNT pin to the positive side of the shunt resistor and the GND pin to the negative side.
- Voltage Measurement: Connect the VBUS pin to the voltage source you want to monitor.
- I2C Communication: Connect the SCL and SDA pins to the corresponding I2C lines of your microcontroller. Use pull-up resistors (typically 4.7kΩ) on these lines.
- Address Configuration: Use the ADDR pin to set the I2C address. This allows multiple INA226 devices to share the same I2C bus.
- Alert Pin: Optionally, connect the ALERT pin to a microcontroller GPIO to monitor threshold violations.
Important Considerations
- Shunt Resistor Selection: Choose a shunt resistor with a low resistance value to minimize power loss but high enough to generate a measurable voltage drop.
- I2C Pull-Up Resistors: Ensure proper pull-up resistors are used on the I2C lines for reliable communication.
- Bypass Capacitor: Place a 0.1µF ceramic capacitor close to the VCC pin to stabilize the power supply.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to interface the INA226 with an Arduino UNO to measure voltage and current:
#include <Wire.h>
// INA226 I2C address (default is 0x40, adjust if ADDR pin is configured differently)
#define INA226_ADDRESS 0x40
// Register addresses
#define REG_BUS_VOLTAGE 0x02
#define REG_SHUNT_VOLTAGE 0x01
void setup() {
Wire.begin(); // Initialize I2C communication
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication for debugging
// Configure INA226 (e.g., calibration, averaging, etc.)
configureINA226();
}
void loop() {
float busVoltage = readBusVoltage(); // Read bus voltage
float shuntVoltage = readShuntVoltage(); // Read shunt voltage
float current = shuntVoltage / 0.01; // Calculate current (assuming 0.01Ω shunt resistor)
// Print results to the serial monitor
Serial.print("Bus Voltage: ");
Serial.print(busVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
Serial.print("Current: ");
Serial.print(current);
Serial.println(" A");
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before the next reading
}
void configureINA226() {
Wire.beginTransmission(INA226_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x00); // Configuration register
Wire.write(0x45); // High byte of configuration
Wire.write(0x27); // Low byte of configuration
Wire.endTransmission();
}
float readBusVoltage() {
Wire.beginTransmission(INA226_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(REG_BUS_VOLTAGE); // Bus voltage register
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(INA226_ADDRESS, 2);
uint16_t rawData = (Wire.read() << 8) | Wire.read();
return rawData * 0.00125; // Convert to volts (1.25mV per LSB)
}
float readShuntVoltage() {
Wire.beginTransmission(INA226_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(REG_SHUNT_VOLTAGE); // Shunt voltage register
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(INA226_ADDRESS, 2);
uint16_t rawData = (Wire.read() << 8) | Wire.read();
return rawData * 0.0000025; // Convert to volts (2.5µV per LSB)
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
No I2C Communication:
- Ensure the SCL and SDA lines have proper pull-up resistors (typically 4.7kΩ).
- Verify the I2C address matches the configuration of the ADDR pin.
- Check for loose or incorrect wiring.
Incorrect Voltage or Current Readings:
- Verify the shunt resistor value and connections.
- Ensure the VBUS and VSHUNT pins are connected to the correct points in the circuit.
- Check the calibration settings in the INA226 configuration.
Alert Pin Not Functioning:
- Confirm the alert threshold is correctly programmed.
- Ensure the ALERT pin is connected to a microcontroller GPIO or an external pull-up resistor.
Tips for Troubleshooting
- Use an oscilloscope or logic analyzer to monitor the I2C lines for proper communication.
- Double-check all connections and component values in the circuit.
- Refer to the INA226 datasheet for detailed configuration and troubleshooting guidance.