
How to Use MOSFET: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with MOSFET in Cirkit Designer
Design with MOSFET in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET) is a type of transistor used for switching and amplifying electronic signals. It is a voltage-controlled device with three terminals: Gate (G), Drain (D), and Source (S). MOSFETs are widely used in power electronics, digital circuits, and analog signal processing due to their high efficiency, fast switching capabilities, and low power consumption.
Explore Projects Built with MOSFET
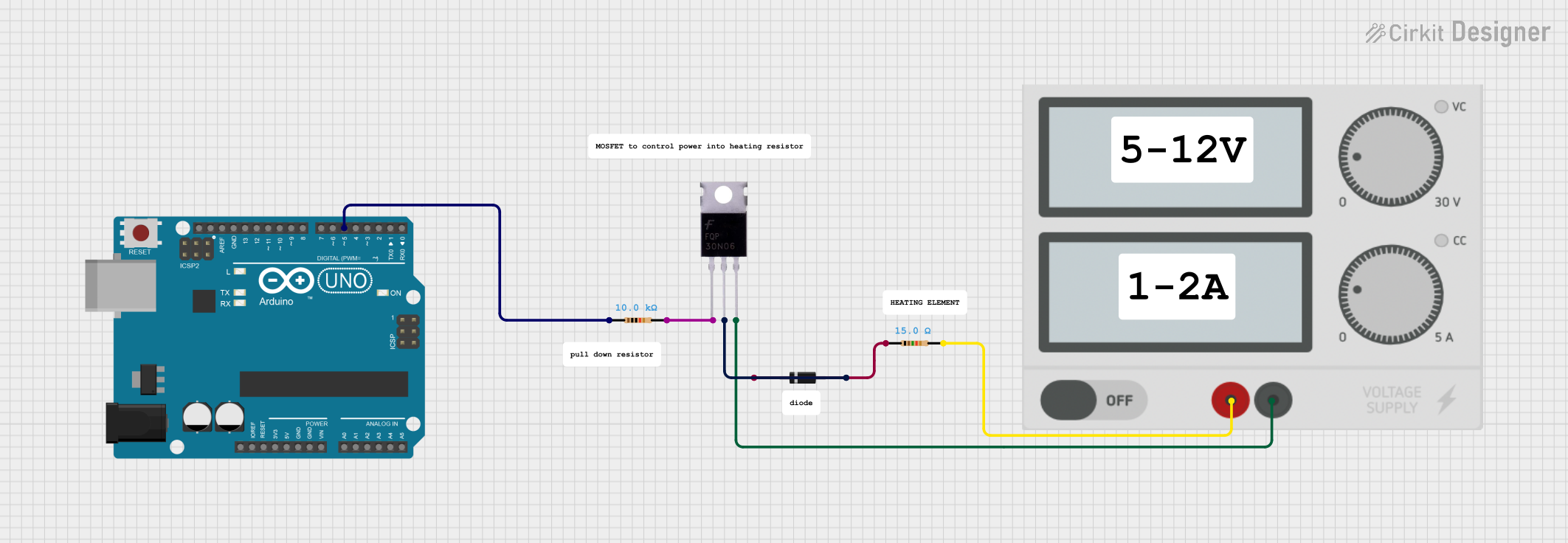
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer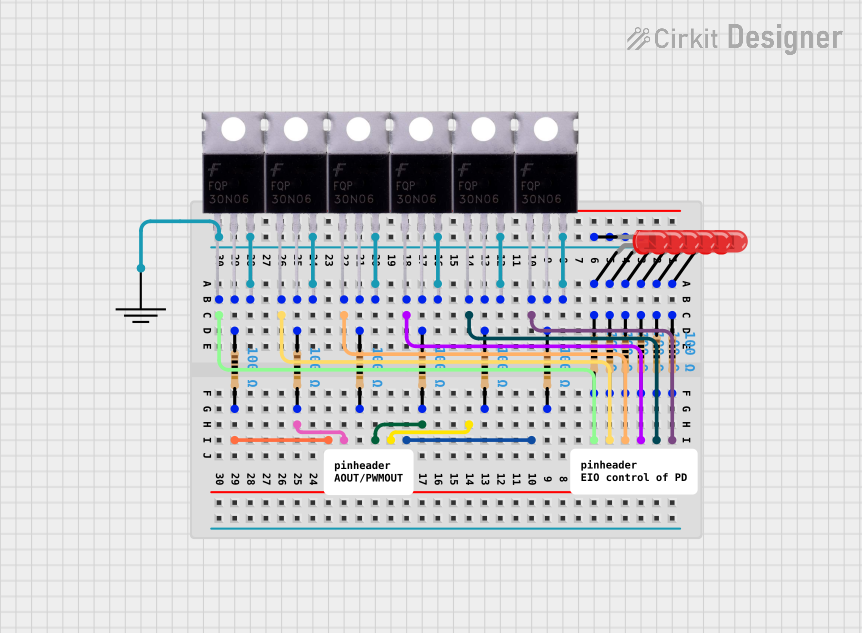
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer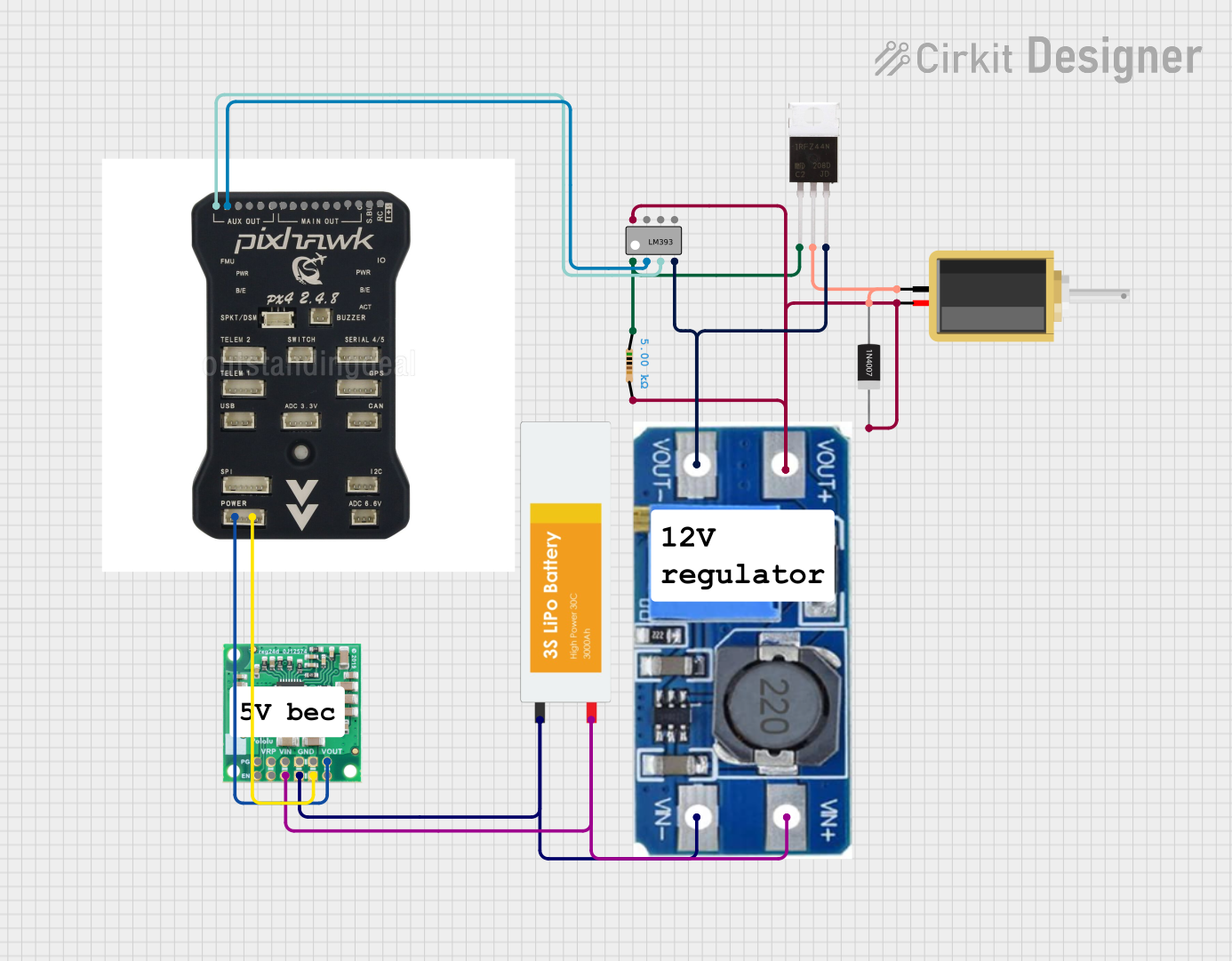
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer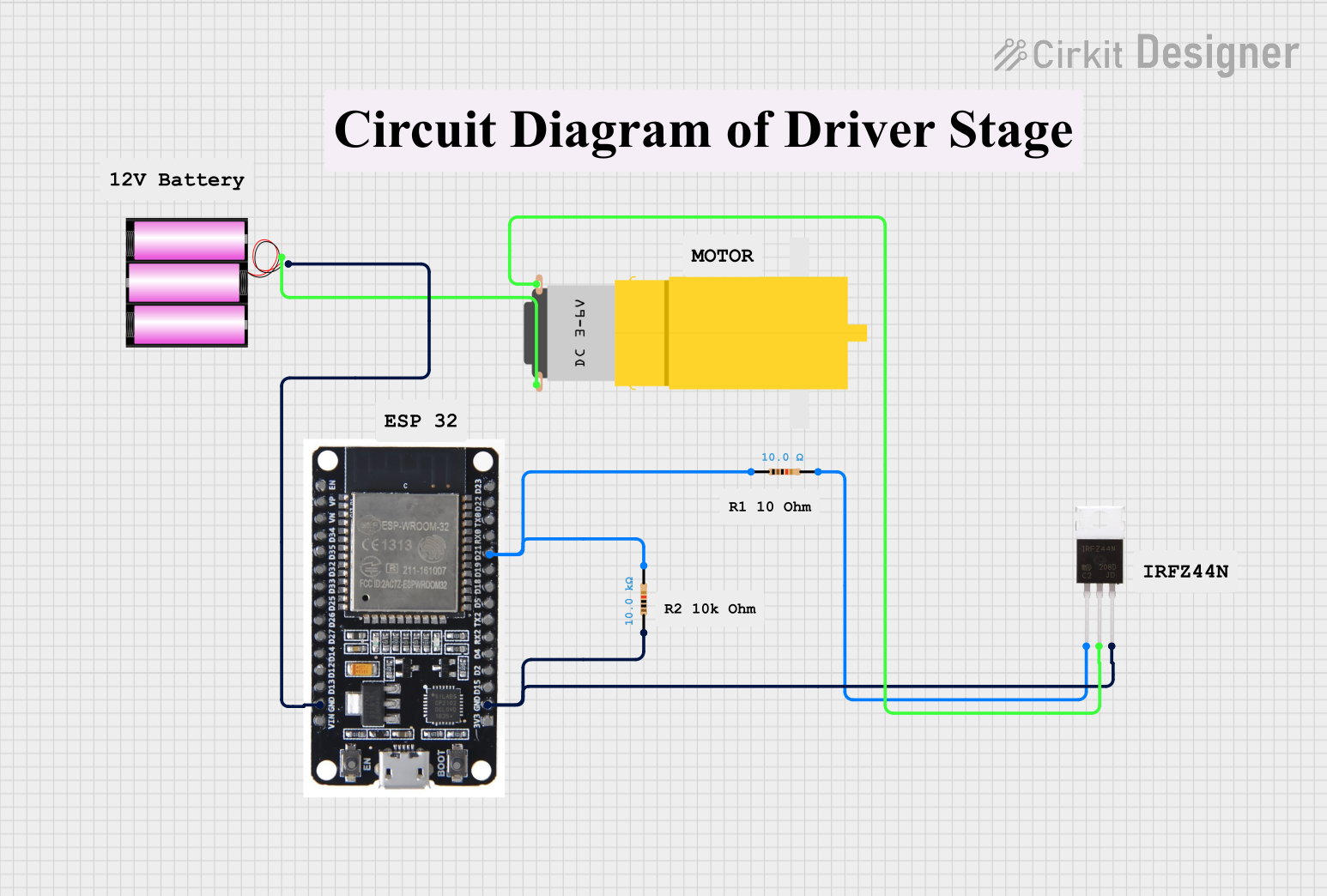
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with MOSFET

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Power supply circuits (e.g., DC-DC converters, inverters)
- Motor control and speed regulation
- Audio amplifiers
- Switching regulators
- Digital logic circuits
- LED dimming and control
Technical Specifications
MOSFETs come in various types and ratings. Below are the general technical specifications for a typical N-channel MOSFET (e.g., IRF540N):
Key Technical Details
- Type: N-channel or P-channel
- Voltage Rating (VDS): Up to 1000V (varies by model)
- Current Rating (ID): Up to 100A (varies by model)
- Gate Threshold Voltage (VGS(th)): 2V to 4V
- RDS(on) (On-Resistance): As low as 0.001Ω
- Switching Speed: Nanoseconds to microseconds
- Power Dissipation: Up to 300W (varies by model)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The MOSFET typically has three pins: Gate (G), Drain (D), and Source (S). Below is the pinout for a standard TO-220 package:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gate (G) | Controls the flow of current between |
| Drain and Source. A voltage applied here | ||
| turns the MOSFET on or off. | ||
| 2 | Drain (D) | Current flows from Drain to Source when |
| the MOSFET is on. | ||
| 3 | Source (S) | The return path for current. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the MOSFET in a Circuit
- Determine the Type: Identify whether the MOSFET is N-channel or P-channel. N-channel MOSFETs are more common and require a positive voltage at the Gate to turn on.
- Connect the Terminals:
- Connect the Source to the ground (for N-channel) or positive supply (for P-channel).
- Connect the Drain to the load.
- Apply a control voltage to the Gate to switch the MOSFET on or off.
- Gate Resistor: Use a resistor (typically 10Ω to 1kΩ) between the Gate and the control signal to limit inrush current and prevent damage.
- Flyback Diode: When driving inductive loads (e.g., motors, relays), add a flyback diode across the load to protect the MOSFET from voltage spikes.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Gate Drive Voltage: Ensure the Gate voltage is within the specified range (e.g., 10V for many power MOSFETs).
- Heat Dissipation: Use a heatsink or active cooling for high-power applications to prevent overheating.
- Static Sensitivity: MOSFETs are sensitive to static electricity. Handle with care and use anti-static precautions.
- Switching Speed: Use a proper Gate driver circuit for high-speed switching to avoid slow transitions and excessive heat.
Example: Controlling an LED with an N-Channel MOSFET and Arduino UNO
Below is an example of using an N-channel MOSFET to control an LED with an Arduino UNO:
Circuit Connections
- Source (S): Connect to ground.
- Drain (D): Connect to the negative terminal of the LED. The positive terminal of the LED connects to a 12V power supply through a current-limiting resistor.
- Gate (G): Connect to an Arduino digital pin (e.g., D9) through a 220Ω resistor.
Arduino Code
// MOSFET LED Control Example
// This code turns an LED on and off using an N-channel MOSFET
// connected to an Arduino UNO.
const int mosfetGatePin = 9; // Pin connected to the MOSFET Gate
void setup() {
pinMode(mosfetGatePin, OUTPUT); // Set the Gate pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(mosfetGatePin, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(mosfetGatePin, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
MOSFET Not Turning On:
- Ensure the Gate voltage is high enough to exceed the threshold voltage (VGS(th)).
- Check for proper connections and verify the control signal.
Excessive Heat:
- Verify that the MOSFET is operating within its current and voltage ratings.
- Use a heatsink or improve cooling if necessary.
MOSFET Always On or Off:
- Check for a short circuit between the Gate and Source or Drain.
- Ensure the Gate resistor is properly connected.
Voltage Spikes Damaging the MOSFET:
- Add a flyback diode across inductive loads to suppress voltage spikes.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a MOSFET without a Gate resistor?
A: While it is possible, it is not recommended. A Gate resistor limits inrush current and prevents damage to the MOSFET and the control circuit.
Q: How do I choose between an N-channel and P-channel MOSFET?
A: N-channel MOSFETs are generally more efficient and have lower RDS(on). Use N-channel MOSFETs for low-side switching and P-channel MOSFETs for high-side switching.
Q: Why is my MOSFET heating up even with no load?
A: This could be due to improper Gate drive voltage or slow switching, causing the MOSFET to operate in the linear region instead of fully on or off.
Q: Can I use a MOSFET for AC signals?
A: Yes, but you will need additional circuitry (e.g., an H-bridge) to handle bidirectional current flow.