
How to Use YL-69: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with YL-69 in Cirkit Designer
Design with YL-69 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The YL-69 is a soil moisture sensor designed to measure the moisture content in the soil. It is widely used in gardening and agricultural applications to automate watering systems, ensuring that plants receive the right amount of water. The sensor consists of two parts: the soil probe (YL-69) and the control board (YL-38). The soil probe measures the moisture level, while the control board processes the signal and provides an output that can be read by a microcontroller, such as an Arduino.
Explore Projects Built with YL-69
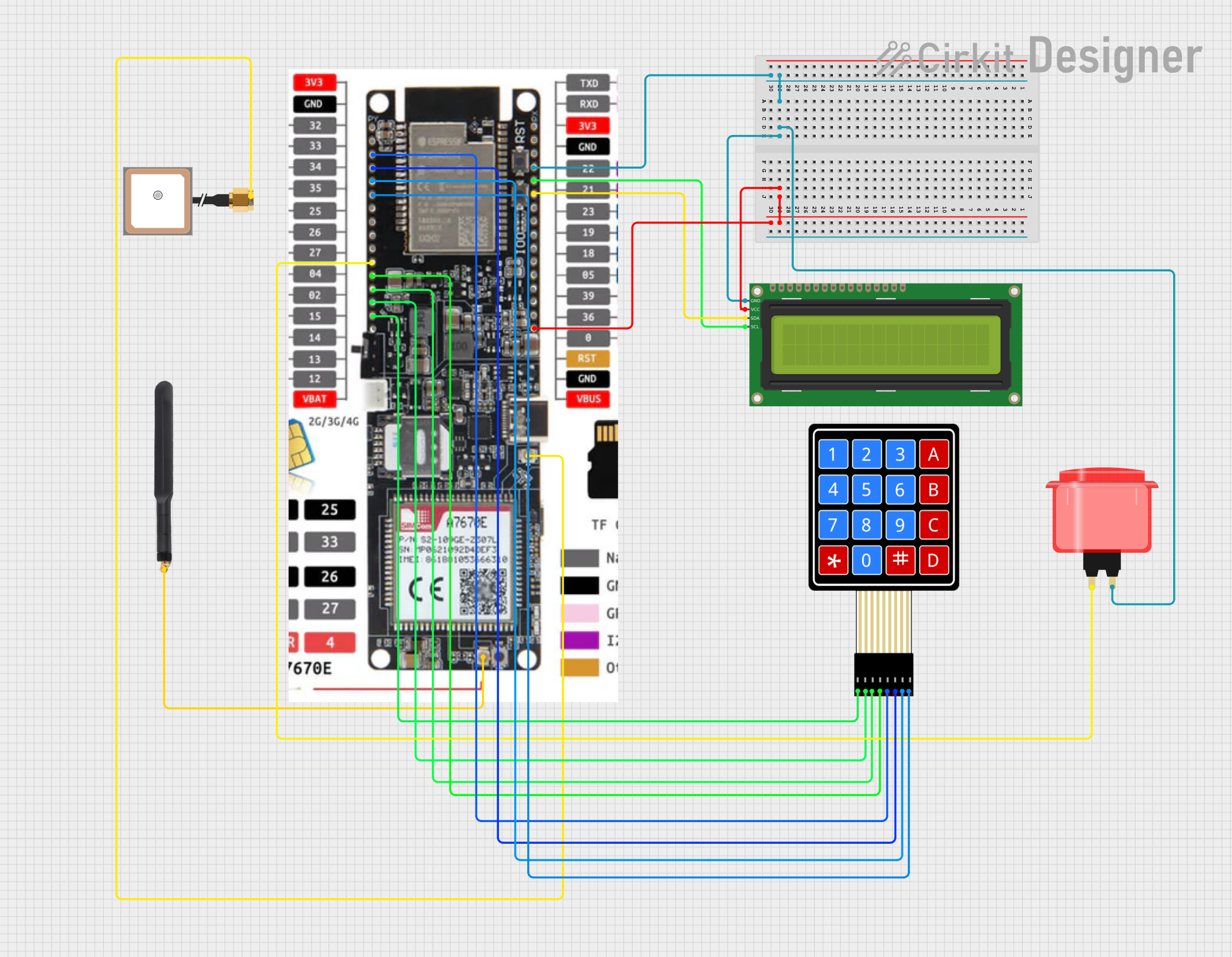
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer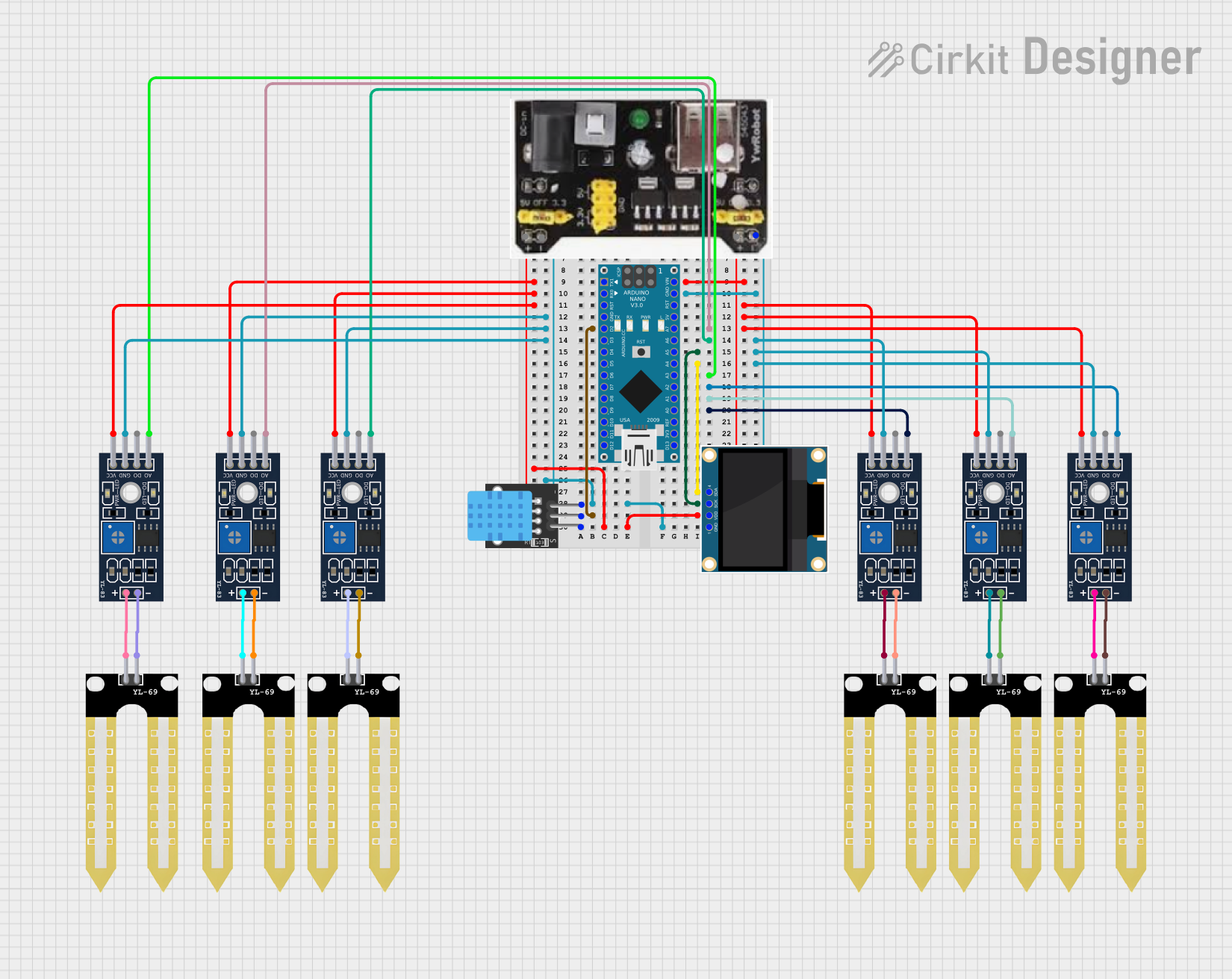
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with YL-69

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V - 5V |
| Output Voltage | 0V - 4.2V (Analog) |
| Current | < 20mA |
| Interface | Analog and Digital |
| Dimensions | Probe: 60mm x 20mm |
| Control Board: 30mm x 15mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
YL-69 Soil Probe
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | VCC (Power Supply) |
| 2 | GND (Ground) |
YL-38 Control Board
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power Supply (3.3V-5V) |
| GND | Ground |
| A0 | Analog Output |
| D0 | Digital Output |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connect the Soil Probe to the Control Board:
- Connect the VCC pin of the soil probe to the VCC pin of the control board.
- Connect the GND pin of the soil probe to the GND pin of the control board.
Connect the Control Board to the Arduino:
- Connect the VCC pin of the control board to the 5V pin on the Arduino.
- Connect the GND pin of the control board to the GND pin on the Arduino.
- Connect the A0 pin of the control board to an analog input pin (e.g., A0) on the Arduino.
- Optionally, connect the D0 pin of the control board to a digital input pin on the Arduino if you want to use the digital output.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Calibration: The sensor may need calibration to provide accurate readings. You can calibrate it by adjusting the potentiometer on the control board.
- Placement: Ensure the soil probe is placed at the root level of the plants for accurate moisture measurement.
- Power Supply: Use a stable power supply to avoid fluctuations in sensor readings.
- Corrosion: The soil probe may corrode over time. Regularly check and replace the probe if necessary.
Example Code for Arduino
// YL-69 Soil Moisture Sensor Example Code
// This code reads the analog value from the YL-69 sensor and prints it to the
// Serial Monitor.
const int sensorPin = A0; // Analog input pin that the sensor is attached to
int sensorValue = 0; // Variable to store the value coming from the sensor
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 bits per second
}
void loop() {
// Read the analog value from the sensor
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
// Print the sensor value to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Soil Moisture Level: ");
Serial.println(sensorValue);
// Wait for 1 second before taking another reading
delay(1000);
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
Inaccurate Readings:
- Solution: Calibrate the sensor by adjusting the potentiometer on the control board. Ensure the probe is placed correctly in the soil.
No Output:
- Solution: Check all connections and ensure the sensor is powered correctly. Verify that the sensor is connected to the correct pins on the Arduino.
Corroded Probe:
- Solution: Regularly inspect the soil probe for corrosion. Replace the probe if necessary.
FAQs
Q: How do I know if the sensor is working correctly? A: You can test the sensor by placing it in dry and wet soil and observing the changes in the analog output value. Dry soil should give a higher value, while wet soil should give a lower value.
Q: Can I use the YL-69 sensor with other microcontrollers? A: Yes, the YL-69 sensor can be used with other microcontrollers that have analog input pins, such as the ESP8266, ESP32, and Raspberry Pi.
Q: How often should I replace the soil probe? A: The frequency of replacement depends on the soil conditions and usage. Regularly inspect the probe for signs of corrosion and replace it as needed.
This documentation provides a comprehensive guide to using the YL-69 soil moisture sensor. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced user, following these instructions will help you effectively integrate the sensor into your projects.