
How to Use 6-way Busbar: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 6-way Busbar in Cirkit Designer
Design with 6-way Busbar in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A 6-way busbar is a conductive metal bar designed to distribute electrical power to multiple circuits or devices. It features six connection points, allowing for efficient and organized wiring in electrical systems. This component is commonly used in electrical panels, distribution boards, and other power management systems to simplify connections and ensure reliable power distribution.
Explore Projects Built with 6-way Busbar
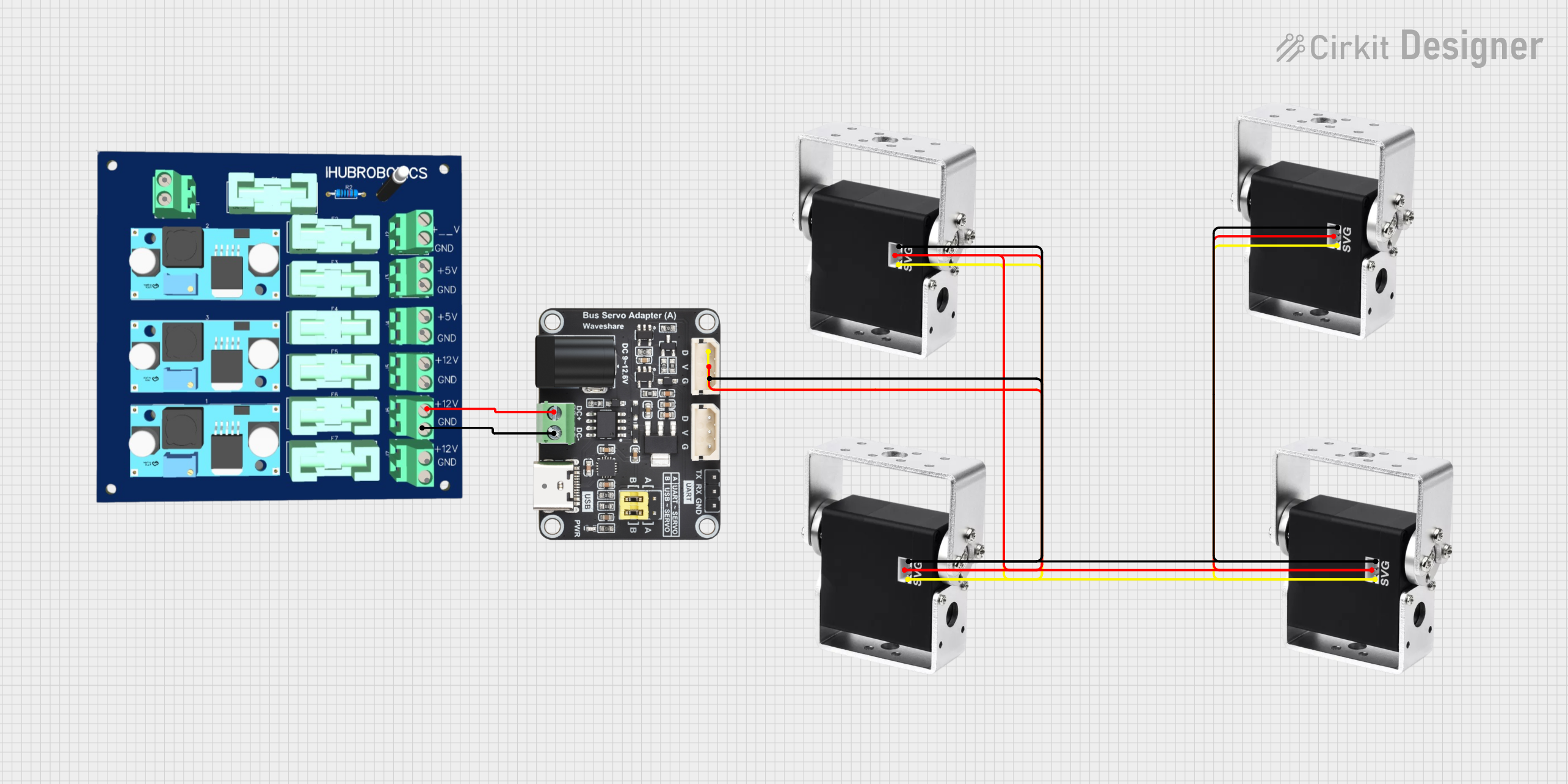
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer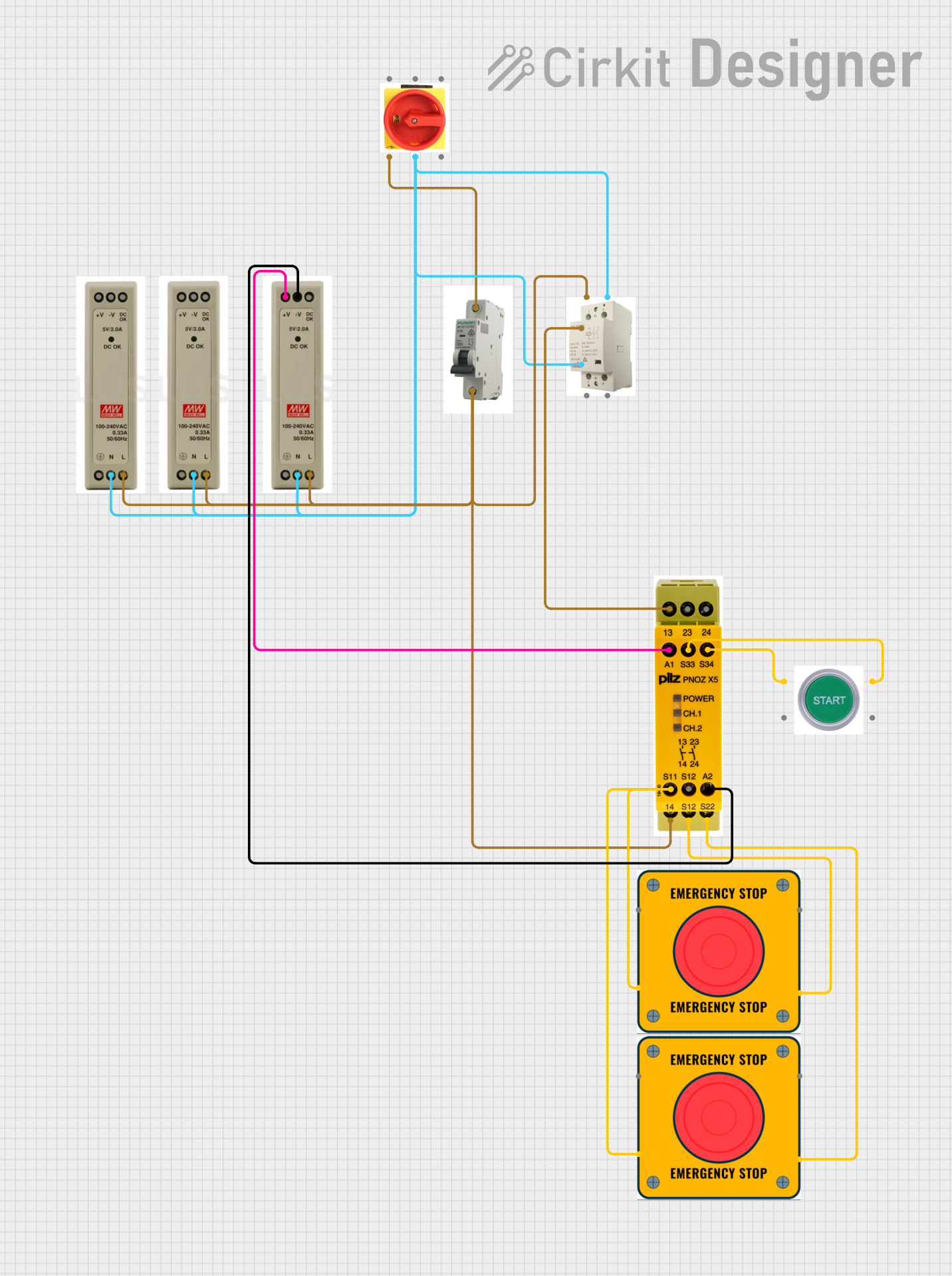
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 6-way Busbar

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Electrical panels for residential, commercial, and industrial applications
- Power distribution boards in renewable energy systems (e.g., solar panels)
- Automotive and marine electrical systems
- Circuit protection and grounding systems
- Simplifying wiring in complex electrical installations
Technical Specifications
The 6-way busbar is typically made of highly conductive materials such as copper or aluminum, ensuring minimal power loss and high current-carrying capacity. Below are the key technical details:
General Specifications
| Parameter | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| Material | Copper (tinned) or aluminum |
| Number of Connection Points | 6 |
| Maximum Current Rating | 100A to 250A (varies by model) |
| Voltage Rating | Up to 600V AC/DC |
| Mounting Type | Screw or bolt-mounted |
| Insulation | Optional plastic or ceramic base |
| Dimensions | Varies by model (e.g., 100mm x 20mm x 10mm) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The 6-way busbar does not have traditional "pins" like an IC but instead features connection points. Below is a description of the connection points:
| Connection Point | Description |
|---|---|
| 1-6 | Terminals for connecting wires or cables |
| Mounting Holes | Holes for securing the busbar to a panel or board |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the 6-Way Busbar in a Circuit
- Mounting the Busbar: Secure the busbar to a panel or distribution board using screws or bolts through the mounting holes. Ensure it is firmly attached to prevent movement.
- Connecting Wires:
- Strip the insulation from the wires to expose the conductive core.
- Insert the stripped wire ends into the connection points and secure them using screws or clamps (depending on the busbar design).
- Power Distribution:
- Connect the input power source (e.g., from a main breaker or battery) to one of the connection points.
- Distribute power to multiple circuits or devices by connecting their wires to the remaining connection points.
- Grounding (if applicable):
- If the busbar is used as a grounding bar, connect the ground wires from all circuits to the connection points.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Current Rating: Ensure the total current passing through the busbar does not exceed its maximum current rating.
- Wire Size: Use wires of appropriate gauge to handle the current without overheating.
- Insulation: If the busbar is not insulated, ensure it is mounted in a way that prevents accidental contact with other conductive surfaces.
- Tight Connections: Regularly check and tighten connections to prevent loose wires, which can cause overheating or arcing.
- Environmental Conditions: Use a corrosion-resistant busbar (e.g., tinned copper) in environments with high humidity or salt exposure.
Example: Connecting a 6-Way Busbar to an Arduino UNO
While a 6-way busbar is not directly connected to an Arduino UNO, it can be used to distribute power to multiple devices in an Arduino-based project. Below is an example of how to use a busbar to distribute 5V power from an Arduino to multiple sensors:
// Example: Distributing 5V power from Arduino UNO to multiple sensors
// Connect the Arduino's 5V pin to one connection point on the busbar.
// Connect the GND pin to another connection point for a common ground.
// Then, connect the sensors' power and ground wires to the busbar.
void setup() {
// Initialize sensors (example: 3 sensors connected to the busbar)
pinMode(2, INPUT); // Sensor 1 data pin
pinMode(3, INPUT); // Sensor 2 data pin
pinMode(4, INPUT); // Sensor 3 data pin
}
void loop() {
// Read sensor data
int sensor1 = digitalRead(2);
int sensor2 = digitalRead(3);
int sensor3 = digitalRead(4);
// Process sensor data (example: print to Serial Monitor)
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.print("Sensor 1: ");
Serial.println(sensor1);
Serial.print("Sensor 2: ");
Serial.println(sensor2);
Serial.print("Sensor 3: ");
Serial.println(sensor3);
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before reading again
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Overheating of the busbar | Exceeding current rating | Reduce the load or use a higher-rated busbar |
| Loose connections | Screws or clamps not tightened properly | Tighten all connections securely |
| Corrosion on the busbar | Exposure to moisture or salt | Use a tinned copper busbar or apply anti-corrosion coating |
| Short circuits | Accidental contact with other conductors | Ensure proper insulation and spacing |
FAQs
Can I use a 6-way busbar for DC and AC circuits?
- Yes, most busbars are designed to handle both DC and AC circuits. Check the voltage and current ratings to ensure compatibility.
What wire gauge should I use with a 6-way busbar?
- The wire gauge depends on the current being carried. Refer to a wire gauge chart to select the appropriate size for your application.
Can I use a 6-way busbar for grounding?
- Yes, a busbar can be used as a grounding bar. Ensure it is properly connected to the system's ground.
How do I prevent corrosion on the busbar?
- Use a tinned copper busbar or apply a protective coating. Regularly inspect and clean the busbar in harsh environments.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use a 6-way busbar in your electrical projects for safe and efficient power distribution.