
How to Use S8550 2TY PNP SMD Transistor: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with S8550 2TY PNP SMD Transistor in Cirkit Designer
Design with S8550 2TY PNP SMD Transistor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The S8550 2TY is a PNP bipolar junction transistor (BJT) manufactured by Galaxy Electrical. It is designed for low-power switching and amplification applications. This transistor is housed in a compact SOT-23 surface-mount device (SMD) package, making it ideal for space-constrained circuit designs.
Explore Projects Built with S8550 2TY PNP SMD Transistor
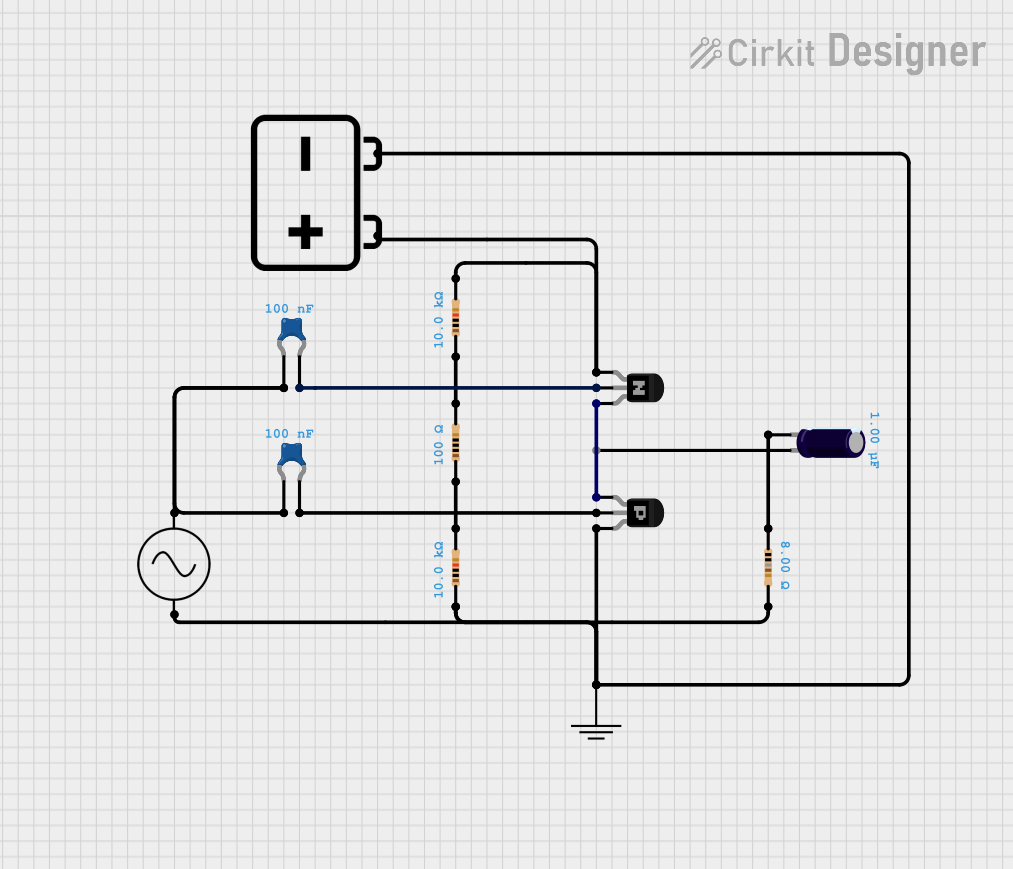
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer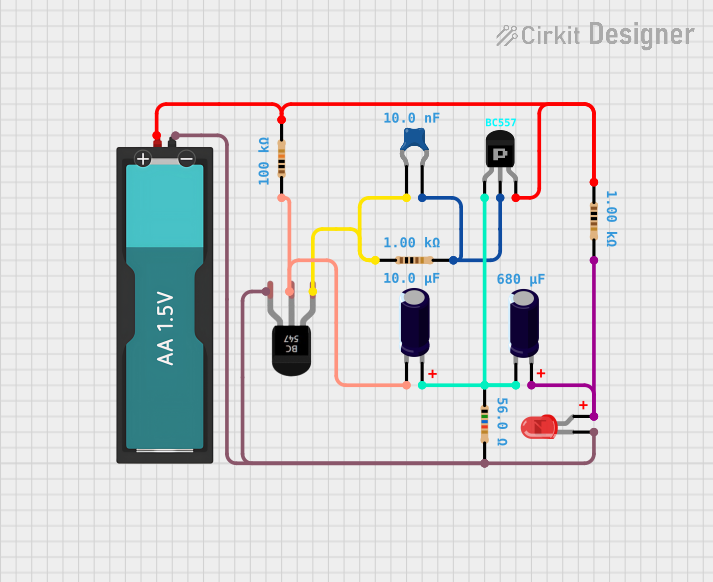
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer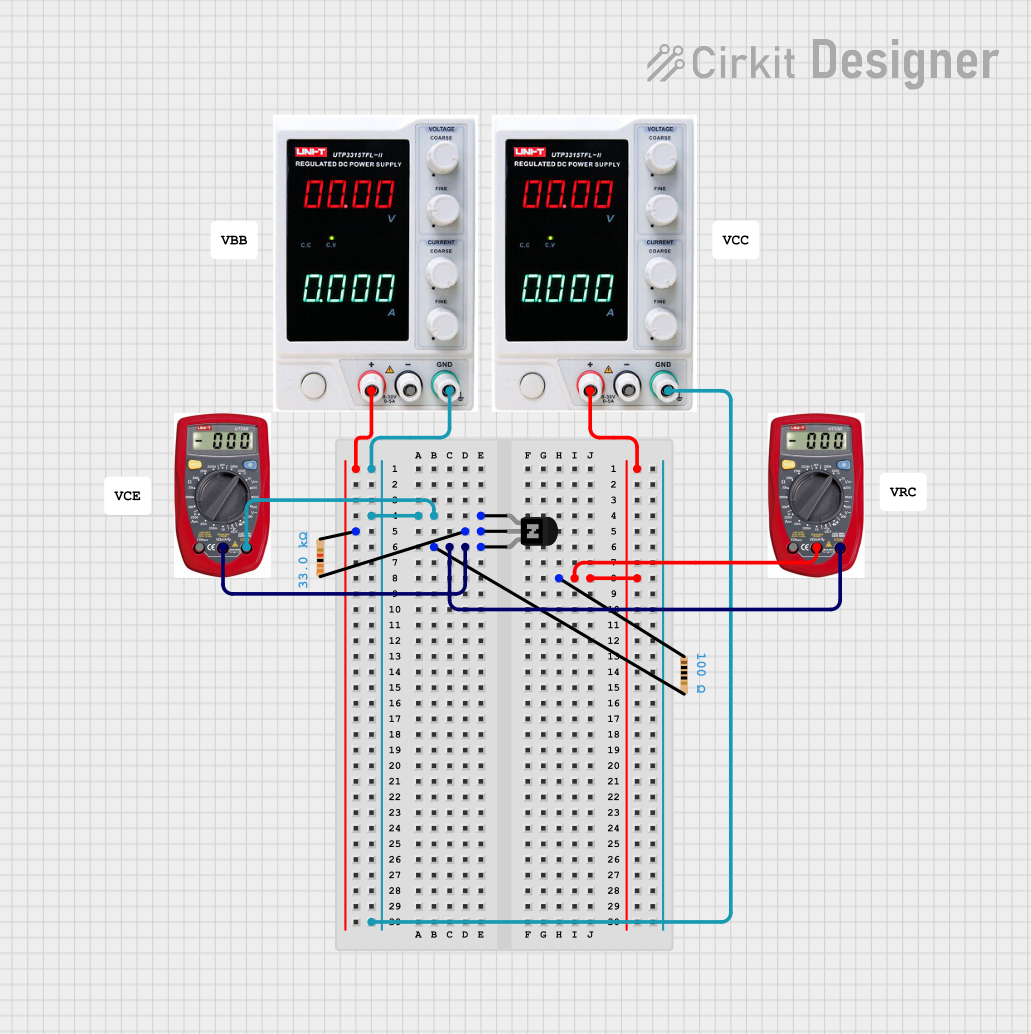
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer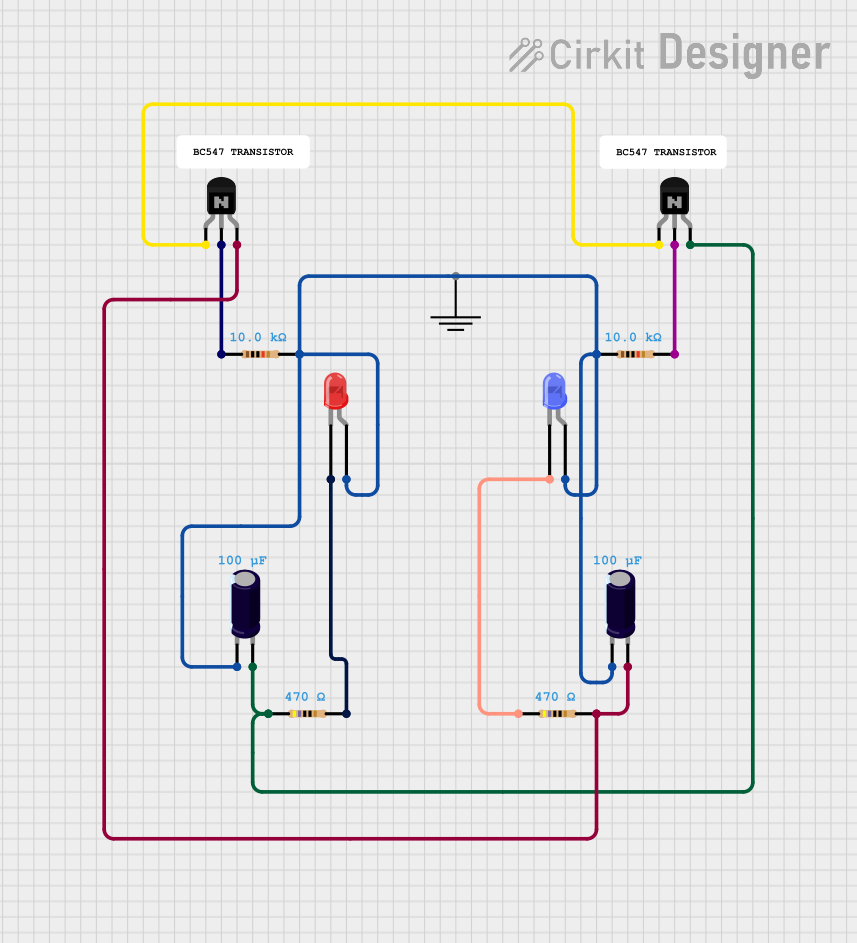
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with S8550 2TY PNP SMD Transistor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Signal amplification in low-power circuits
- Switching applications in small electronic devices
- General-purpose amplification in audio and RF circuits
- Used in battery-powered devices due to its low power consumption
Technical Specifications
Key Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Galaxy Electrical |
| Part Number | S8550 (SOT-23) |
| Transistor Type | PNP |
| Maximum Collector-Emitter Voltage (Vce) | -20V |
| Maximum Collector Current (Ic) | -1.5A |
| Maximum Power Dissipation (Pd) | 0.3W (300mW) |
| DC Current Gain (hFE) | 120 to 400 (at Ic = -0.1A) |
| Transition Frequency (fT) | 150 MHz |
| Operating Temperature Range | -55°C to +150°C |
| Package Type | SOT-23 |
Pin Configuration
The S8550 transistor has three pins, as shown below:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Emitter (E) | Current flows out of this terminal. |
| 2 | Base (B) | Controls the transistor's operation. |
| 3 | Collector (C) | Current flows into this terminal. |
Pinout Diagram
_______
| |
| SOT-23|
|_______|
| | |
E B C
Usage Instructions
How to Use the S8550 in a Circuit
Biasing the Transistor:
- The S8550 is a PNP transistor, so the base must be biased negatively relative to the emitter to turn it on.
- A resistor is typically connected to the base to limit the base current and protect the transistor.
Switching Applications:
- To use the S8550 as a switch, connect the emitter to the positive voltage supply and the collector to the load.
- Apply a small negative voltage to the base to turn the transistor on, allowing current to flow from the emitter to the collector.
Amplification Applications:
- In amplifier circuits, the S8550 can be used in common-emitter configuration for voltage or current amplification.
- Ensure proper biasing and coupling capacitors for stable operation.
Example Circuit with Arduino UNO
The S8550 can be used to control a small DC motor with an Arduino UNO. Below is an example circuit and code:
Circuit Description
- Connect the emitter (E) to the positive voltage supply (e.g., 5V).
- Connect the collector (C) to one terminal of the motor, and the other terminal of the motor to ground.
- Connect the base (B) to an Arduino digital pin through a 1kΩ resistor.
Arduino Code
// Example code to control a motor using the S8550 transistor
// Pin 9 is used to control the transistor
const int motorPin = 9; // Arduino pin connected to the base of S8550
void setup() {
pinMode(motorPin, OUTPUT); // Set motorPin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(motorPin, HIGH); // Turn the motor ON
delay(2000); // Keep the motor ON for 2 seconds
digitalWrite(motorPin, LOW); // Turn the motor OFF
delay(2000); // Keep the motor OFF for 2 seconds
}
Important Considerations
- Base Resistor: Always use a base resistor to limit the base current. A typical value is 1kΩ.
- Power Dissipation: Ensure the transistor does not exceed its maximum power dissipation of 300mW.
- Voltage Ratings: Do not exceed the maximum collector-emitter voltage of -20V.
- Heat Management: If the transistor operates near its maximum ratings, consider adding heat dissipation measures.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Transistor Not Switching Properly:
- Cause: Insufficient base current or incorrect biasing.
- Solution: Check the base resistor value and ensure the base voltage is negative relative to the emitter.
Overheating:
- Cause: Exceeding the maximum power dissipation or current rating.
- Solution: Reduce the load current or improve heat dissipation.
No Output Signal:
- Cause: Incorrect pin connections or damaged transistor.
- Solution: Verify the pin connections and replace the transistor if necessary.
FAQs
Q1: Can the S8550 be used for high-power applications?
A1: No, the S8550 is designed for low-power applications with a maximum power dissipation of 300mW.
Q2: What is the maximum current the S8550 can handle?
A2: The maximum collector current (Ic) is -1.5A.
Q3: Can the S8550 be used in audio amplifier circuits?
A3: Yes, the S8550 is suitable for low-power audio amplification applications.
Q4: Is the S8550 compatible with 3.3V logic?
A4: Yes, the S8550 can be used with 3.3V logic, but ensure proper biasing and base resistor selection.
Q5: How do I identify the pins on the SOT-23 package?
A5: Refer to the pinout diagram provided above. The pins are typically marked on the package, and the datasheet provides additional guidance.