
How to Use 12.8V 30000mAh 3C 4S5P LiFePO4 Battery Pack: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 12.8V 30000mAh 3C 4S5P LiFePO4 Battery Pack in Cirkit Designer
Design with 12.8V 30000mAh 3C 4S5P LiFePO4 Battery Pack in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 12.8V 30000mAh 3C 4S5P LiFePO4 Battery Pack (Manufacturer Part ID: IFR 32650) by Pro-Range is a high-performance rechargeable lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) battery pack. It features a nominal voltage of 12.8V, a capacity of 30,000mAh, and a discharge rate of 3C. The pack is constructed using 4 cells in series (4S) and 5 cells in parallel (5P), ensuring high energy density, long cycle life, and enhanced safety.
Explore Projects Built with 12.8V 30000mAh 3C 4S5P LiFePO4 Battery Pack

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer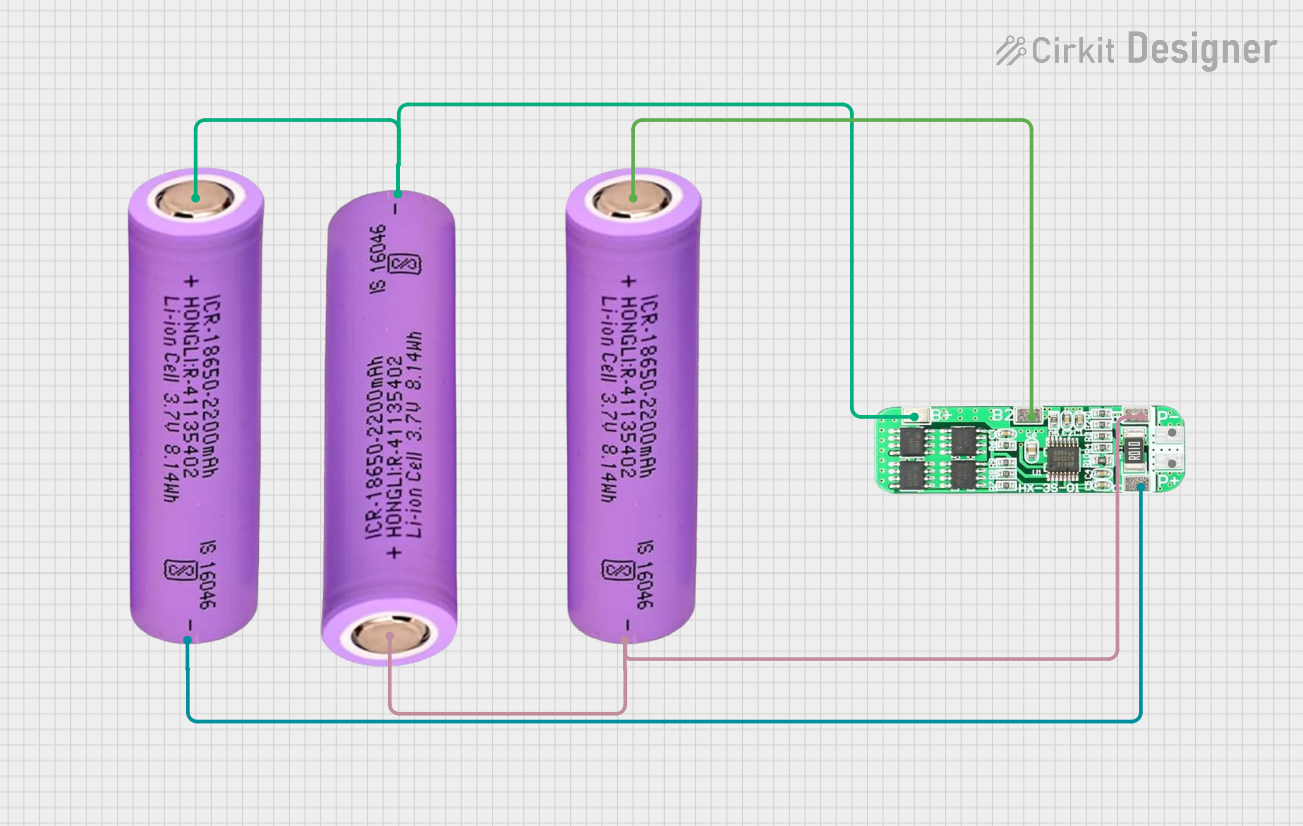
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer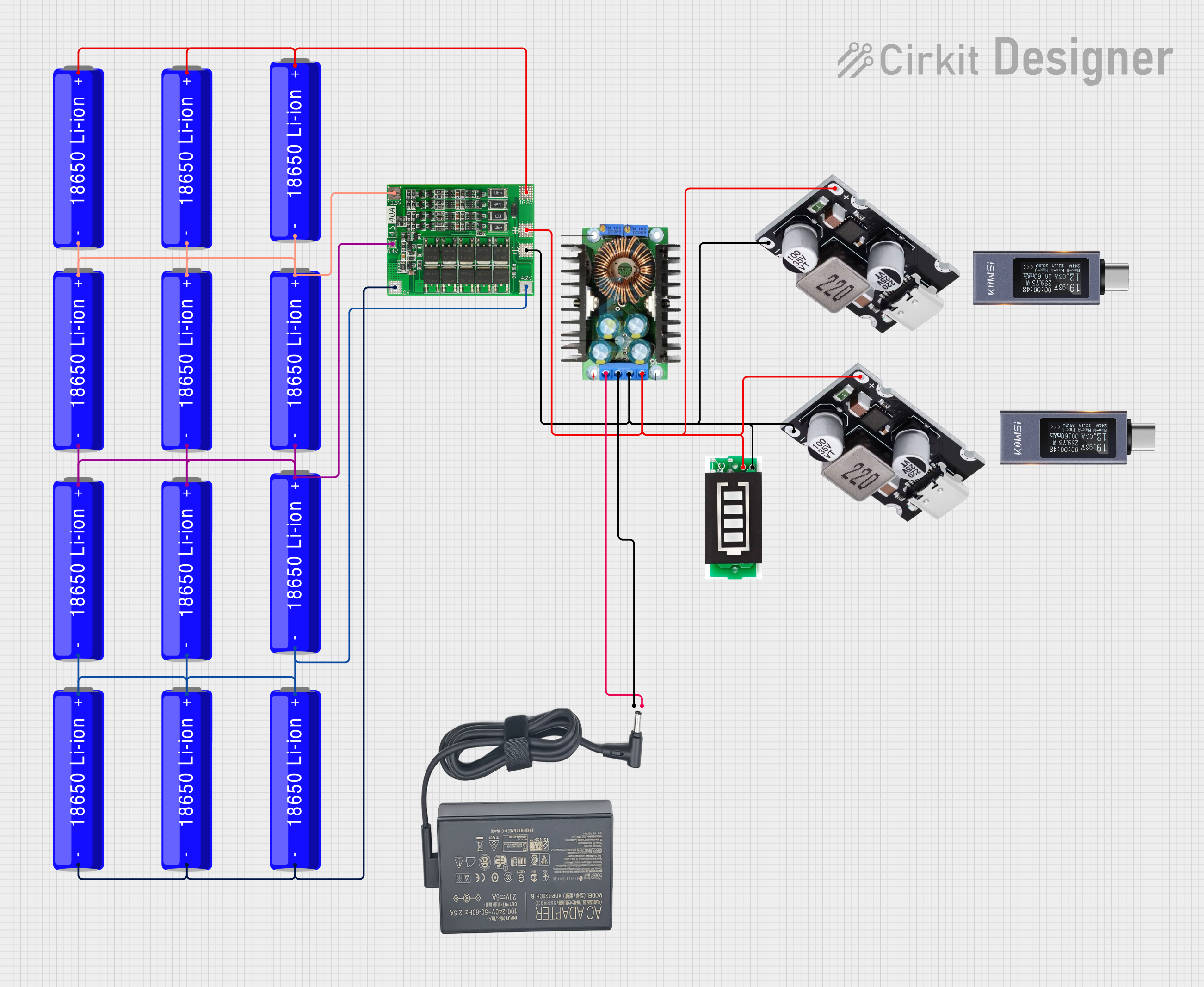
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer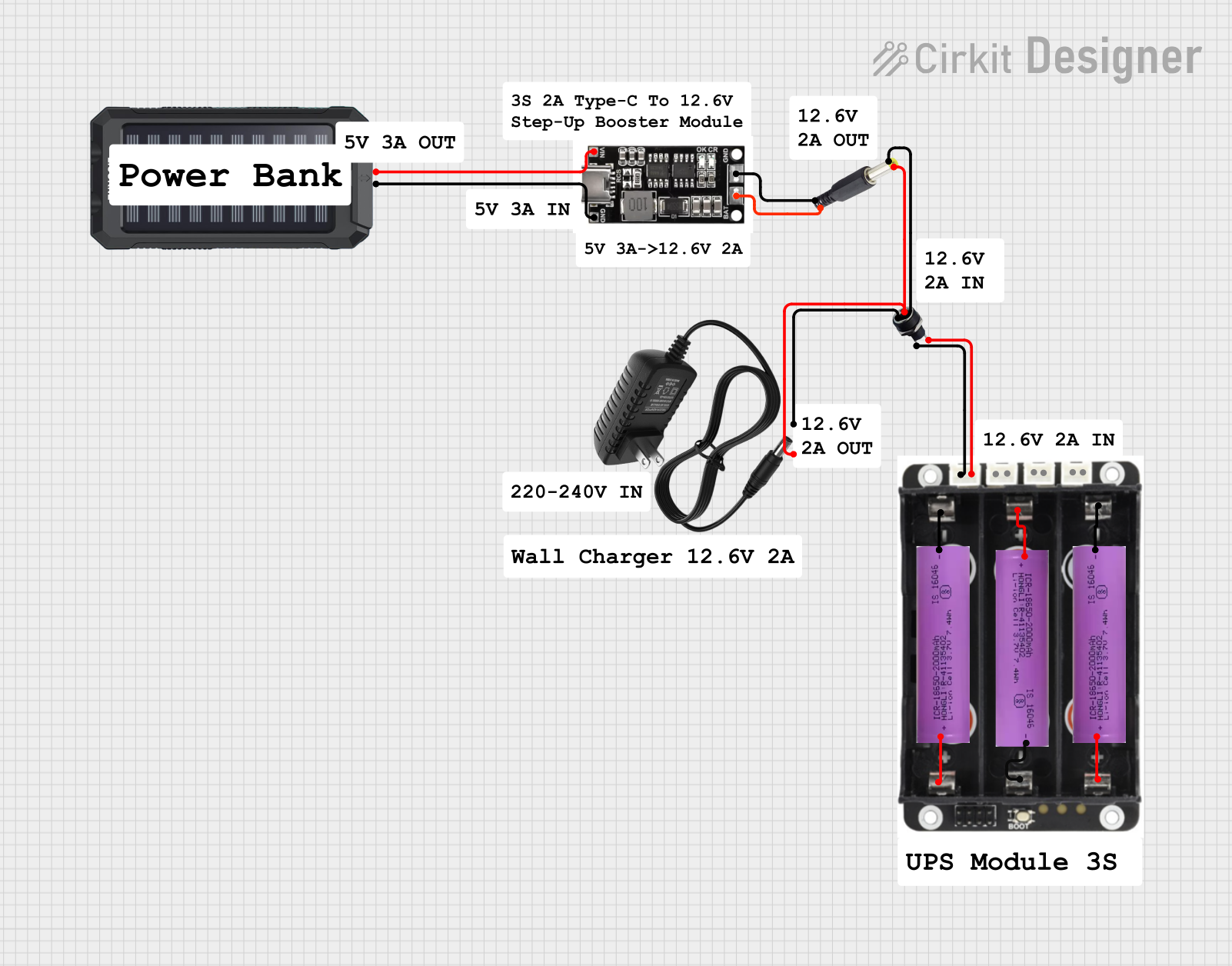
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 12.8V 30000mAh 3C 4S5P LiFePO4 Battery Pack

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Solar energy storage systems
- Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS)
- Electric vehicles (EVs) and e-bikes
- Portable power stations
- Robotics and industrial equipment
- Marine and RV power systems
Technical Specifications
Key Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Nominal Voltage | 12.8V |
| Capacity | 30,000mAh (30Ah) |
| Discharge Rate (C-Rate) | 3C (90A maximum continuous) |
| Charge Voltage | 14.6V (maximum) |
| Cut-off Voltage | 10.0V |
| Cell Configuration | 4S5P |
| Chemistry | Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) |
| Cycle Life | >2000 cycles (at 80% DOD) |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to 60°C (discharge) |
| Storage Temperature | -10°C to 45°C |
| Dimensions | Varies by manufacturer |
| Weight | Approx. 4.5kg (varies) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The battery pack typically includes a Battery Management System (BMS) with the following connections:
| Pin/Terminal | Description |
|---|---|
| Positive (+) | Main positive terminal for load/charging |
| Negative (-) | Main negative terminal for load/charging |
| BMS Ports | Balance leads for cell monitoring |
| Temperature | Optional temperature sensor connection |
Note: The exact pinout may vary depending on the specific BMS used in the battery pack. Refer to the manufacturer's datasheet for detailed wiring diagrams.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Battery Pack in a Circuit
Connection to Load:
- Connect the positive terminal of the battery pack to the positive input of your load.
- Connect the negative terminal of the battery pack to the negative input of your load.
- Ensure the load does not exceed the maximum continuous discharge current (90A).
Charging the Battery:
- Use a LiFePO4-compatible charger with a maximum charge voltage of 14.6V.
- Ensure the charger’s current rating does not exceed the recommended charge current (typically 0.5C or 15A for this pack).
Battery Management System (BMS):
- The integrated BMS protects the battery from overcharge, over-discharge, overcurrent, and short circuits.
- Ensure all balance leads are properly connected if using an external BMS.
Wiring Example: Below is a simple wiring example for connecting the battery pack to a load and charger:
+-------------------+ +-------------------+ | LiFePO4 Pack | | Load | | + - |-------| + - | +-------------------+ +-------------------+ | | | | +--------------------------+ Charger
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid Overdischarge: Do not allow the battery voltage to drop below 10.0V to prevent damage.
- Use Proper Chargers: Always use a charger specifically designed for LiFePO4 batteries.
- Temperature Monitoring: Avoid charging or discharging the battery outside the recommended temperature range.
- Storage: Store the battery at 50% charge in a cool, dry place if not in use for extended periods.
- Safety Precautions: Do not puncture, crush, or expose the battery to fire or water.
Arduino UNO Example
If you are using this battery pack to power an Arduino UNO, ensure the voltage is regulated to 5V using a DC-DC step-down converter. Below is an example of Arduino code to monitor the battery voltage using an analog input:
// Arduino code to monitor battery voltage
const int batteryPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to battery voltage divider
const float voltageDividerRatio = 5.7; // Adjust based on resistor values
const float referenceVoltage = 5.0; // Arduino reference voltage (5V)
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int rawValue = analogRead(batteryPin); // Read analog value
float batteryVoltage = (rawValue / 1023.0) * referenceVoltage * voltageDividerRatio;
// Print the battery voltage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.print(batteryVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before next reading
}
Note: Use a voltage divider circuit to step down the battery voltage to a safe range for the Arduino analog input (0-5V).
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Battery does not charge | Charger not compatible with LiFePO4 | Use a LiFePO4-specific charger |
| Battery voltage drops quickly | Overdischarge or aging cells | Avoid deep discharges; replace if needed |
| BMS triggers protection frequently | Overcurrent or short circuit detected | Check load current and wiring |
| Battery overheats during use | Exceeding discharge current limit | Reduce load or use a higher-capacity pack |
FAQs
Can I connect multiple packs in series or parallel?
- Yes, but ensure the BMS supports such configurations and balance the packs before connecting.
How do I know when the battery is fully charged?
- The charger will typically indicate full charge when the voltage reaches 14.6V and the current drops to near zero.
What is the expected lifespan of this battery pack?
- The pack can last over 2000 cycles at 80% Depth of Discharge (DOD) under proper usage conditions.
Can I use this battery pack for starting a car engine?
- No, this pack is not designed for high instantaneous current required for engine cranking.
By following the guidelines and best practices outlined in this documentation, you can ensure safe and efficient use of the 12.8V 30000mAh 3C 4S5P LiFePO4 Battery Pack.