
How to Use XL6019E1 DC-DC step-up/step-down: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with XL6019E1 DC-DC step-up/step-down in Cirkit Designer
Design with XL6019E1 DC-DC step-up/step-down in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The XL6019E1 is a versatile DC-DC converter capable of both step-up (boost) and step-down (buck) voltage regulation. This flexibility makes it ideal for applications requiring stable voltage output across varying input conditions. It is widely used in power supply systems, battery-powered devices, LED drivers, and industrial control systems. Its high efficiency and wide input voltage range make it a reliable choice for both hobbyist and professional projects.
Explore Projects Built with XL6019E1 DC-DC step-up/step-down

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer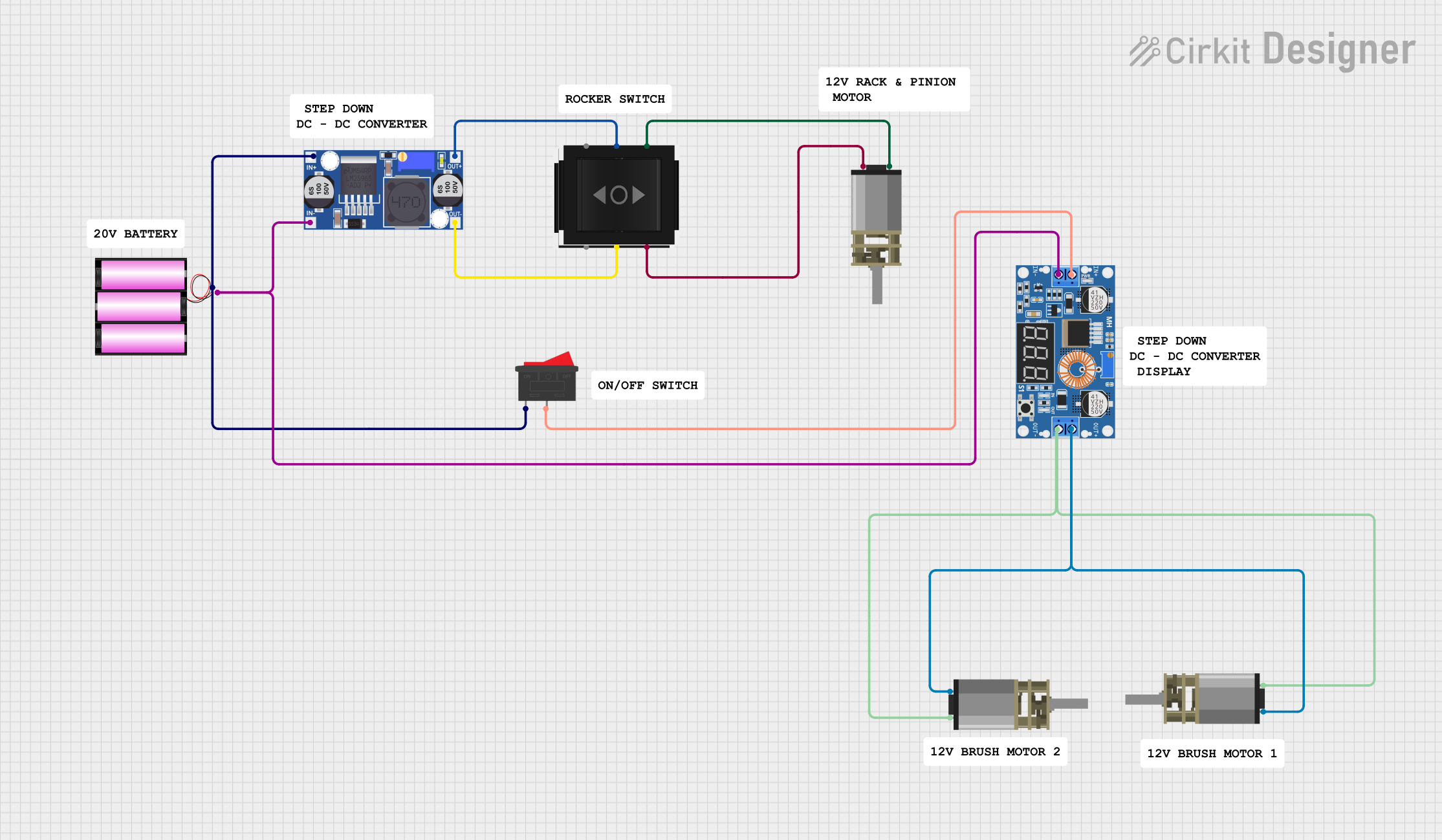
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with XL6019E1 DC-DC step-up/step-down

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Battery-powered devices requiring stable voltage output
- LED lighting systems
- Solar power systems
- Industrial control systems
- General-purpose power supply modules
Technical Specifications
The XL6019E1 is designed to handle a wide range of input and output voltages, making it suitable for diverse applications. Below are its key technical specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 5V to 32V |
| Output Voltage Range | 1.25V to 35V |
| Output Current | Up to 5A (with proper heat dissipation) |
| Switching Frequency | 180 kHz |
| Efficiency | Up to 96% (depending on load conditions) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Package Type | TO-263-5L |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The XL6019E1 has a 5-pin configuration. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VIN | Input voltage pin (5V to 32V). Connect to power source. |
| 2 | GND | Ground pin. Connect to circuit ground. |
| 3 | SW | Switching pin. Connect to the inductor and diode. |
| 4 | FB | Feedback pin. Used to set the output voltage via a resistor divider. |
| 5 | EN | Enable pin. High to enable the module, low to disable. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the XL6019E1 in a Circuit
- Input Voltage Connection: Connect the input voltage source (5V to 32V) to the
VINpin. Ensure the input voltage is within the specified range. - Output Voltage Adjustment: Use a resistor divider network connected to the
FBpin to set the desired output voltage. The formula for output voltage is: [ V_{OUT} = V_{REF} \times \left(1 + \frac{R1}{R2}\right) ] where ( V_{REF} ) is typically 1.25V. - Inductor and Diode Selection: Choose an appropriate inductor and Schottky diode based on the input/output voltage and current requirements. Refer to the datasheet for recommended values.
- Enable Pin: Connect the
ENpin to a high logic level (e.g., VIN) to enable the module. Pull it low to disable the module. - Heat Dissipation: For high-current applications, ensure proper heat dissipation using a heatsink or adequate PCB thermal design.
Example: Connecting XL6019E1 to an Arduino UNO
The XL6019E1 can be used to power an Arduino UNO by stepping down a higher voltage (e.g., 12V) to 5V. Below is an example circuit and Arduino code to monitor the output voltage.
Circuit Connections
- Connect a 12V power source to the
VINpin of the XL6019E1. - Set the output voltage to 5V using a resistor divider on the
FBpin. - Connect the
GNDpin of the XL6019E1 to the Arduino's GND. - Connect the output of the XL6019E1 to the Arduino's 5V pin.
Arduino Code
// This code reads the output voltage of the XL6019E1 using an analog pin
// and displays the value on the serial monitor.
const int voltagePin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the output voltage
const float referenceVoltage = 5.0; // Arduino reference voltage (5V)
const int adcResolution = 1024; // 10-bit ADC resolution
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
pinMode(voltagePin, INPUT); // Set the voltage pin as input
}
void loop() {
int adcValue = analogRead(voltagePin); // Read the ADC value
float outputVoltage = (adcValue * referenceVoltage) / adcResolution;
// Print the output voltage to the serial monitor
Serial.print("Output Voltage: ");
Serial.print(outputVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Important Considerations
- Input Voltage: Ensure the input voltage is always higher than the minimum required for proper operation.
- Output Current: Do not exceed the maximum output current of 5A. Use proper heat dissipation for high-current applications.
- Inductor Selection: Use an inductor with sufficient current rating to avoid saturation.
- Feedback Resistors: Use precision resistors for accurate output voltage regulation.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Voltage
- Cause: The
ENpin is not connected or is pulled low. - Solution: Ensure the
ENpin is connected to a high logic level (e.g., VIN).
- Cause: The
Output Voltage is Incorrect
- Cause: Incorrect resistor values in the feedback network.
- Solution: Verify the resistor values and recalculate using the output voltage formula.
Overheating
- Cause: Excessive current draw or insufficient heat dissipation.
- Solution: Use a heatsink or improve PCB thermal design. Ensure the load current does not exceed 5A.
High Output Ripple
- Cause: Poor capacitor selection or layout issues.
- Solution: Use low-ESR capacitors and ensure proper PCB layout.
FAQs
Can the XL6019E1 be used for both step-up and step-down applications?
- Yes, the XL6019E1 is designed for both boost and buck voltage regulation.
What is the maximum efficiency of the XL6019E1?
- The XL6019E1 can achieve up to 96% efficiency, depending on the load and input/output conditions.
Can I use the XL6019E1 with a 3.3V microcontroller?
- Yes, but ensure the output voltage is set to 3.3V and the input voltage is within the specified range.
What type of diode should I use with the XL6019E1?
- Use a high-speed Schottky diode with a current rating equal to or greater than the load current.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the XL6019E1 into your projects and troubleshoot common issues.