
How to Use ESP32 - CAM: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with ESP32 - CAM in Cirkit Designer
Design with ESP32 - CAM in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
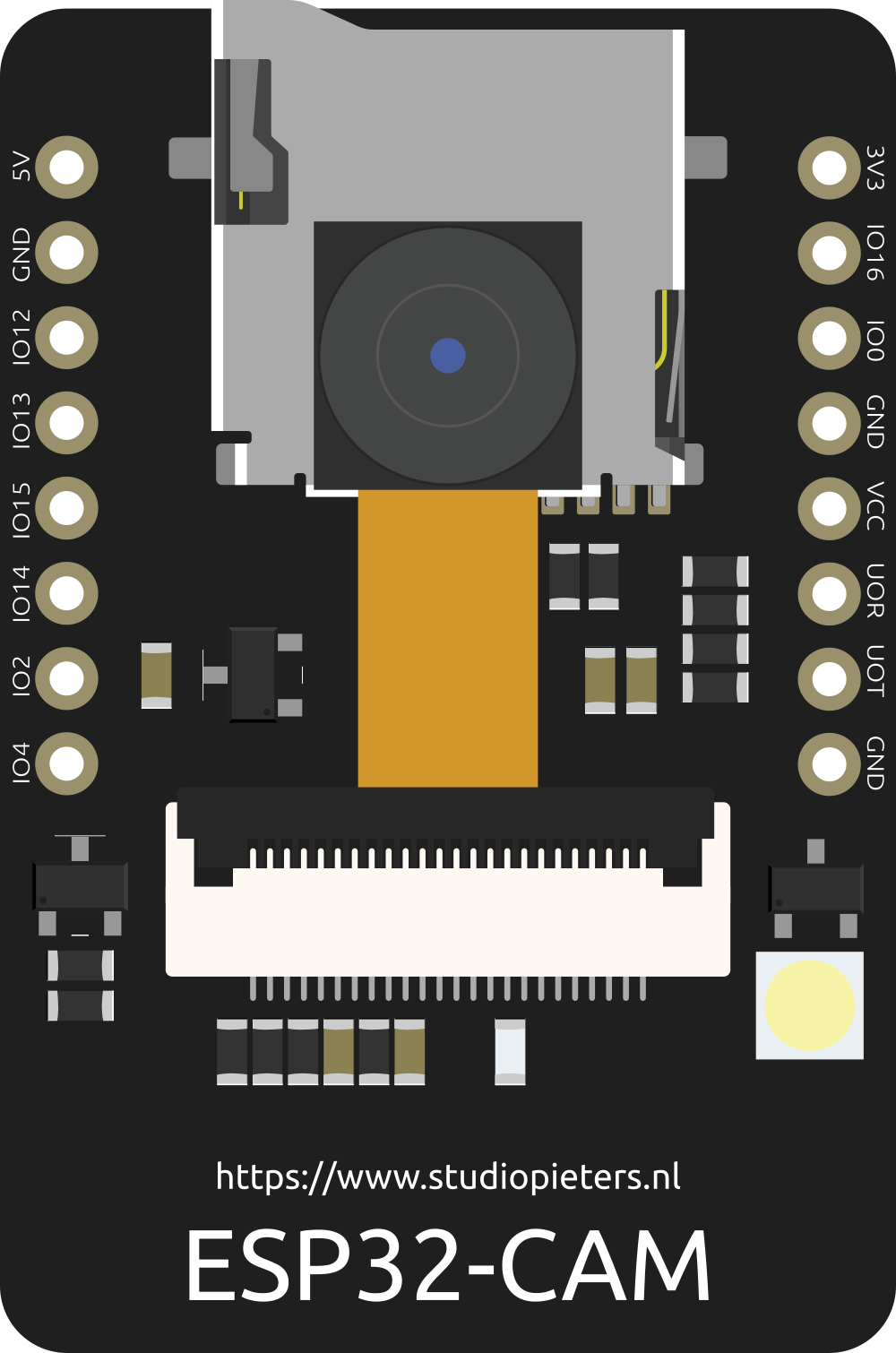
The ESP32-CAM is a low-cost development board that combines the powerful ESP32 microcontroller with integrated Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities, along with a camera module. This compact and versatile board is ideal for IoT applications, enabling image capture, video streaming, and wireless communication. Its small form factor and rich feature set make it a popular choice for projects such as home automation, surveillance systems, and AI-powered image recognition.
Explore Projects Built with ESP32 - CAM
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer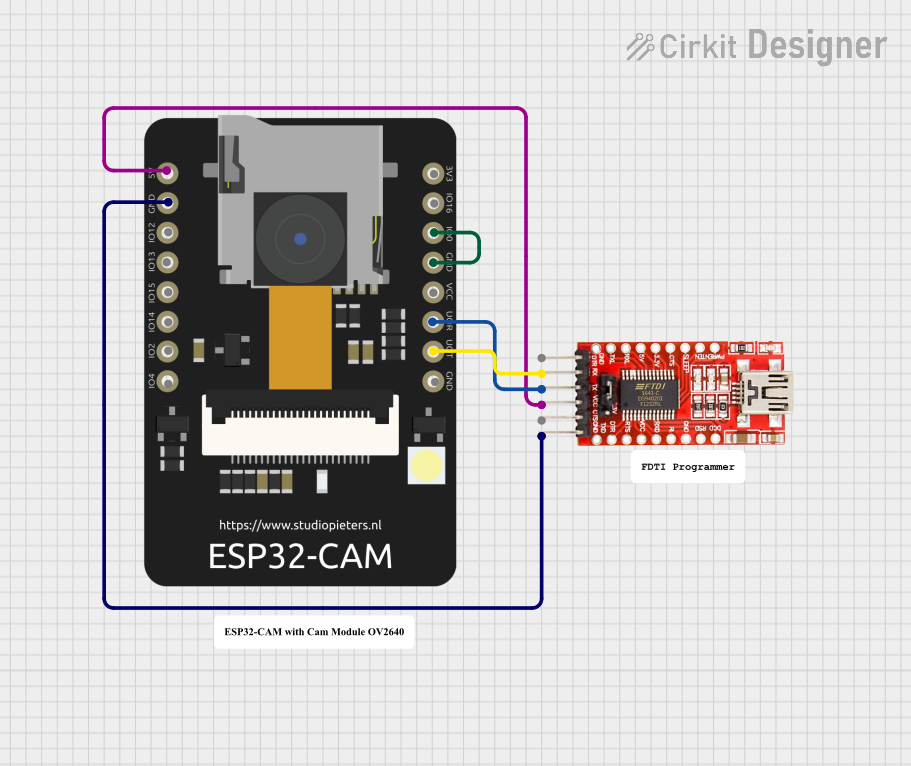
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer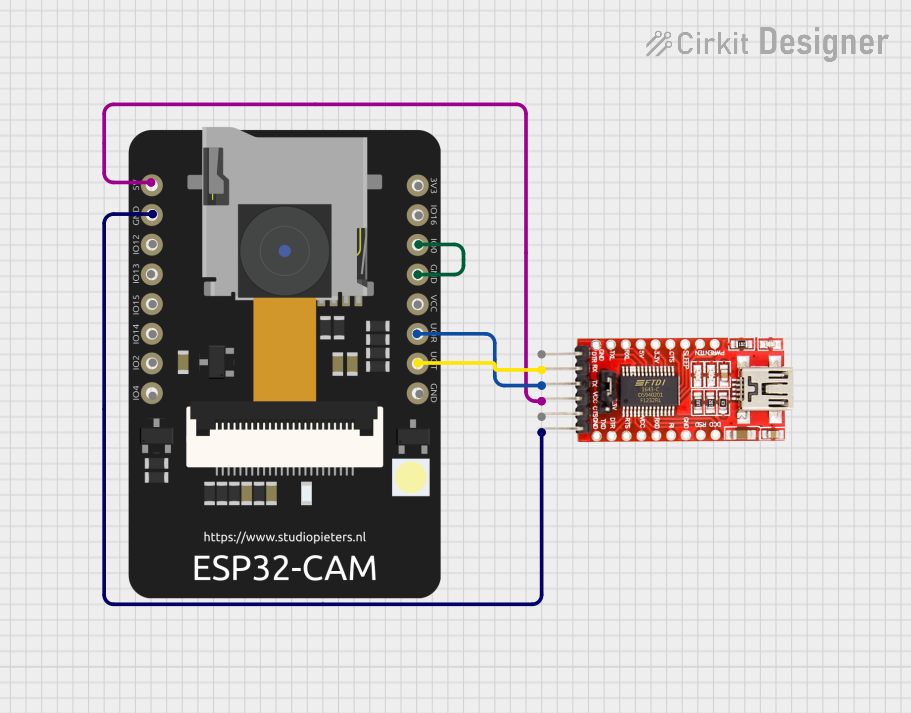
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with ESP32 - CAM

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Wireless video streaming and surveillance systems
- Smart home automation with image recognition
- IoT devices requiring camera functionality
- AI-based object detection and tracking
- Remote monitoring and control systems
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Microcontroller: ESP32-D0WDQ6
- Wireless Connectivity: Wi-Fi 802.11 b/g/n and Bluetooth 4.2
- Camera Module: OV2640 (2MP resolution)
- Flash Memory: 4 MB (PSRAM)
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V
- Input Voltage Range: 5V (via micro-USB or 5V pin)
- GPIO Pins: 9 available for user applications
- Image Output Formats: JPEG, BMP, GRAYSCALE
- Power Consumption: ~160 mA in active mode
- Dimensions: 27 x 40.5 mm
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The ESP32-CAM has a total of 16 pins. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground connection |
| 2 | 5V | Power input (5V) |
| 3 | 3.3V | Power output (3.3V) |
| 4 | GPIO0 | General-purpose I/O pin; used for boot mode selection |
| 5 | GPIO1 (U0TXD) | UART0 TX pin; used for serial communication |
| 6 | GPIO3 (U0RXD) | UART0 RX pin; used for serial communication |
| 7 | GPIO16 | General-purpose I/O pin |
| 8 | GPIO17 | General-purpose I/O pin |
| 9 | GPIO12 | General-purpose I/O pin; connected to the microSD card interface (DATA2) |
| 10 | GPIO13 | General-purpose I/O pin; connected to the microSD card interface (DATA3) |
| 11 | GPIO14 | General-purpose I/O pin; connected to the microSD card interface (CLK) |
| 12 | GPIO15 | General-purpose I/O pin; connected to the microSD card interface (CMD) |
| 13 | GPIO2 | General-purpose I/O pin; connected to the onboard LED |
| 14 | GPIO4 | General-purpose I/O pin; connected to the camera module |
| 15 | GPIO5 | General-purpose I/O pin; connected to the camera module |
| 16 | RESET | Reset pin; used to restart the ESP32-CAM |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the ESP32-CAM in a Circuit
Powering the Board:
- Supply 5V to the
5Vpin or via the micro-USB port. Ensure the power source can provide at least 500 mA. - Connect the
GNDpin to the ground of your circuit.
- Supply 5V to the
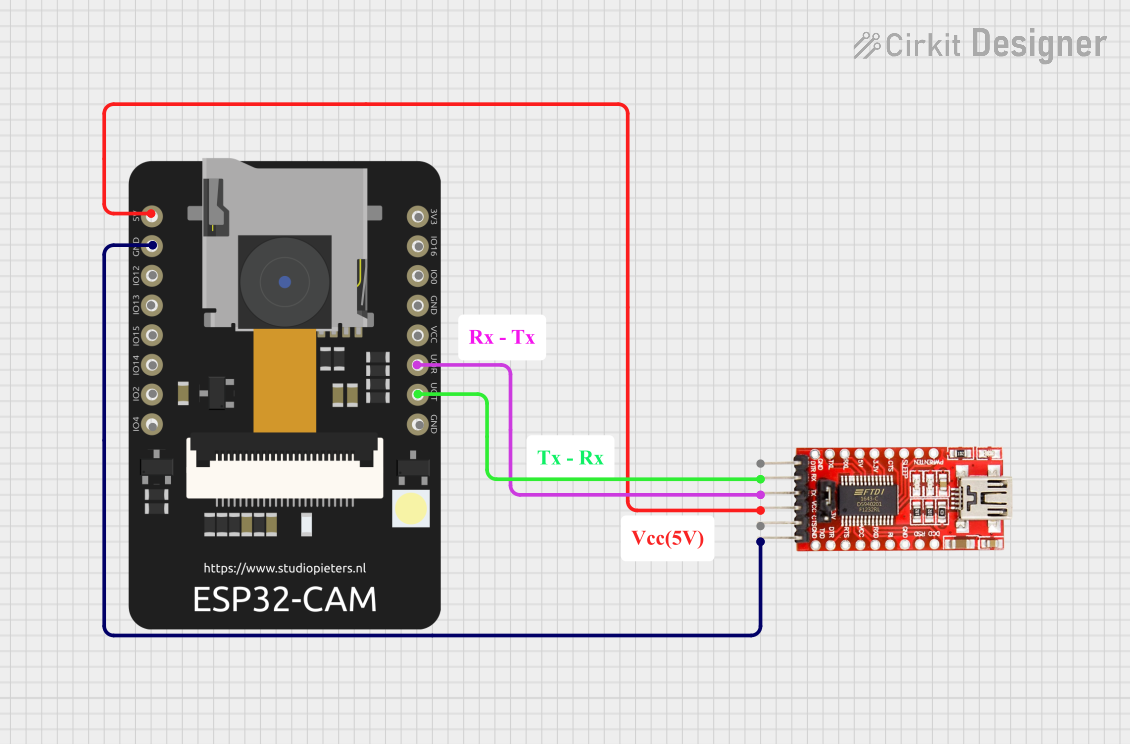
Programming the ESP32-CAM:
- The ESP32-CAM does not have a built-in USB-to-serial converter. Use an external FTDI programmer or USB-to-serial adapter.
- Connect the FTDI adapter as follows:
- FTDI
TX→ ESP32-CAMU0RXD(GPIO3) - FTDI
RX→ ESP32-CAMU0TXD(GPIO1) - FTDI
GND→ ESP32-CAMGND - FTDI
5V→ ESP32-CAM5V
- FTDI
- Set the FTDI adapter to 5V mode.
- To enter programming mode, connect GPIO0 to GND and press the reset button.
Uploading Code:
- Use the Arduino IDE or ESP-IDF to upload code. Select "AI-Thinker ESP32-CAM" as the board in the Arduino IDE.
Connecting Peripherals:
- Use the GPIO pins to connect sensors, actuators, or other peripherals. Be mindful of the 3.3V logic level.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Ensure a stable 5V power supply to avoid unexpected resets or malfunctions.
- Heat Management: The ESP32-CAM can get warm during operation. Consider adding a heatsink for prolonged use.
- Antenna Selection: The board has an onboard PCB antenna and a connector for an external antenna. Use a jumper to select the desired antenna.
- Boot Mode: Always disconnect GPIO0 from GND after uploading code to boot the ESP32-CAM normally.
Example Code for Arduino UNO Integration
Below is an example of how to use the ESP32-CAM to capture and stream video:
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <esp_camera.h>
// Replace with your network credentials
const char* ssid = "Your_SSID";
const char* password = "Your_PASSWORD";
// Camera configuration
#define PWDN_GPIO_NUM -1
#define RESET_GPIO_NUM -1
#define XCLK_GPIO_NUM 0
#define SIOD_GPIO_NUM 26
#define SIOC_GPIO_NUM 27
#define Y9_GPIO_NUM 35
#define Y8_GPIO_NUM 34
#define Y7_GPIO_NUM 39
#define Y6_GPIO_NUM 36
#define Y5_GPIO_NUM 21
#define Y4_GPIO_NUM 19
#define Y3_GPIO_NUM 18
#define Y2_GPIO_NUM 5
#define VSYNC_GPIO_NUM 25
#define HREF_GPIO_NUM 23
#define PCLK_GPIO_NUM 22
void startCameraServer();
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
// Wait for Wi-Fi connection
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("\nWiFi connected");
// Camera initialization
camera_config_t config;
config.ledc_channel = LEDC_CHANNEL_0;
config.ledc_timer = LEDC_TIMER_0;
config.pin_d0 = Y2_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_d1 = Y3_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_d2 = Y4_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_d3 = Y5_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_d4 = Y6_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_d5 = Y7_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_d6 = Y8_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_d7 = Y9_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_xclk = XCLK_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_pclk = PCLK_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_vsync = VSYNC_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_href = HREF_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_sscb_sda = SIOD_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_sscb_scl = SIOC_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_pwdn = PWDN_GPIO_NUM;
config.pin_reset = RESET_GPIO_NUM;
config.xclk_freq_hz = 20000000;
config.pixel_format = PIXFORMAT_JPEG;
if (!esp_camera_init(&config)) {
Serial.println("Camera initialized successfully");
} else {
Serial.println("Camera initialization failed");
return;
}
startCameraServer();
}
void loop() {
// Main loop does nothing; camera server handles requests
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
ESP32-CAM Not Detected by the Computer:
- Ensure the FTDI adapter is connected correctly.
- Check that GPIO0 is connected to GND during programming.
Frequent Resets or Instability:
- Use a stable 5V power supply with sufficient current (at least 500 mA).
- Avoid powering the ESP32-CAM through the FTDI adapter for extended periods.
Camera Initialization Failed:
- Verify the camera module is securely connected to the ESP32-CAM board.
- Ensure the correct camera model (e.g., OV2640) is selected in the code.
Wi-Fi Connection Issues:
- Double-check the SSID and password in the code.
- Ensure the Wi-Fi network is within range and not overloaded.
FAQs
Can I use the ESP32-CAM without a camera module?
Yes, the ESP32-CAM can function as a standard ESP32 development board without the camera.What is the maximum resolution supported by the camera?
The OV2640 camera module supports up to 1600x1200 (UXGA) resolution.Can I use an external antenna?
Yes, you can connect an