
How to Use Digital Compass: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
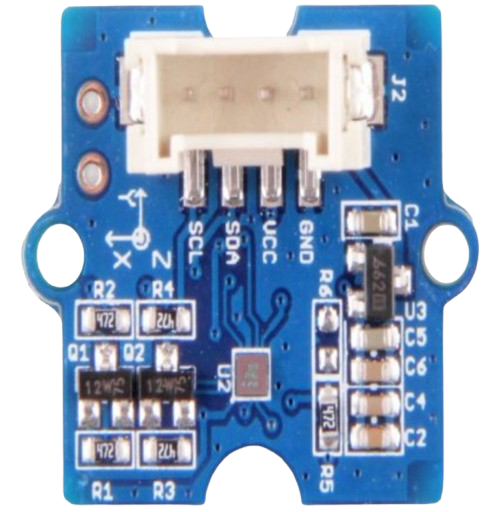
 Design with Digital Compass in Cirkit Designer
Design with Digital Compass in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Grove Digital Compass is an electronic device designed to determine direction relative to the Earth's magnetic field. It utilizes magnetic sensors to provide accurate heading information, making it an essential component for navigation, orientation, and robotics applications. This compact and reliable module is ideal for projects requiring precise directional data.
Explore Projects Built with Digital Compass

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer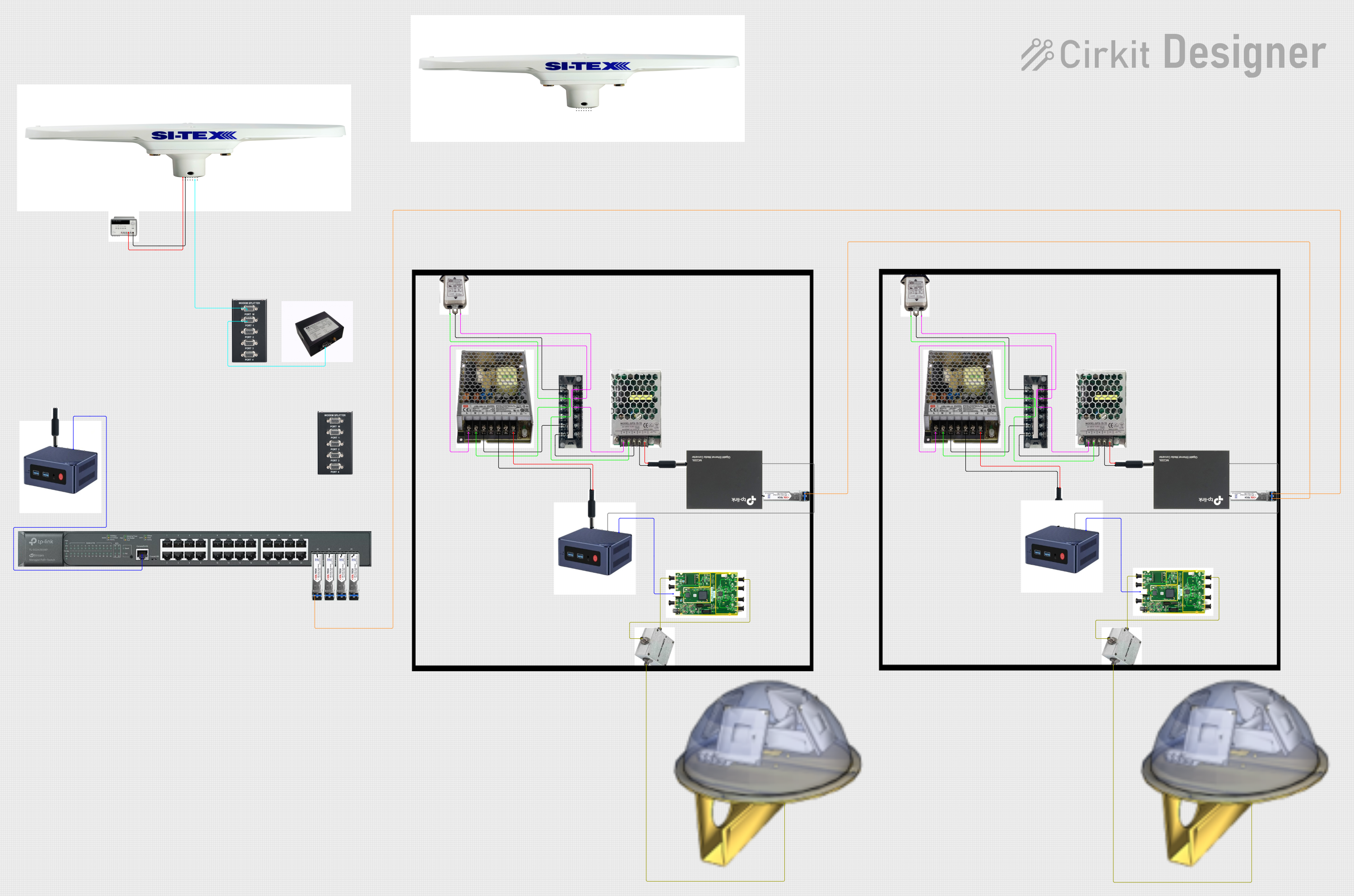
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer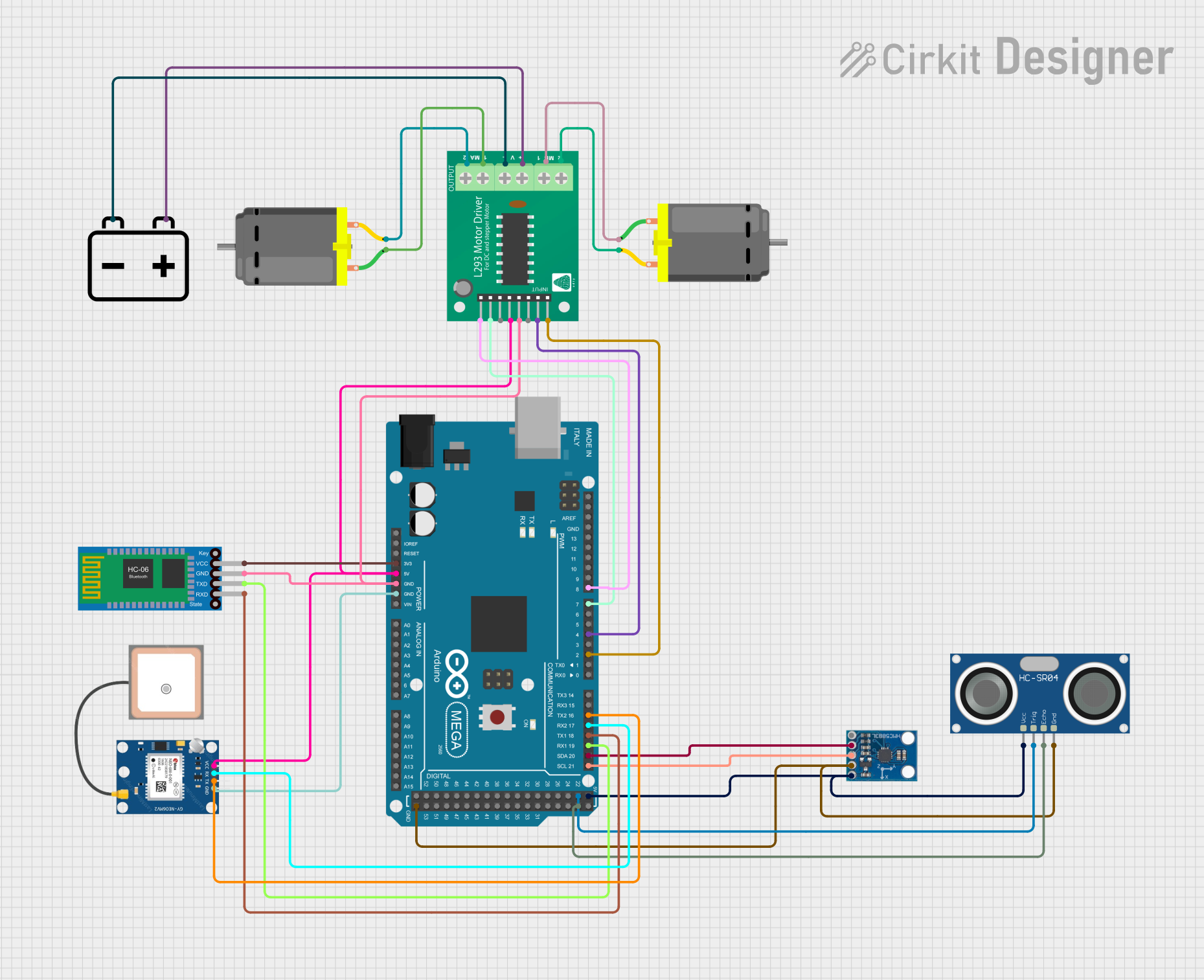
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer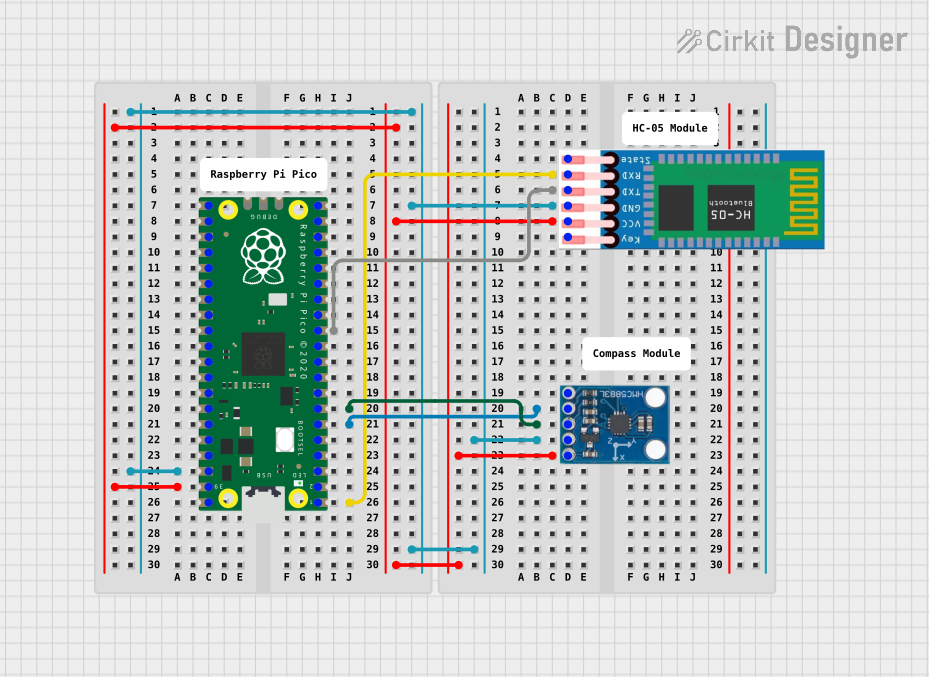
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Digital Compass

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Navigation systems for drones, robots, and vehicles
- Orientation tracking in wearable devices
- Geographic positioning and mapping
- Educational projects and prototyping with microcontrollers (e.g., Arduino)
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the Grove Digital Compass:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V to 5V |
| Operating Current | < 10mA |
| Communication Protocol | I2C |
| Measurement Range | 360° (full circle) |
| Accuracy | ±1° to ±2° |
| Dimensions | 20mm x 20mm |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to 85°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Grove Digital Compass features a 4-pin interface for easy connection. The pinout is as follows:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply input (3.3V to 5V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | SDA | I2C data line for communication |
| 4 | SCL | I2C clock line for communication |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Connect the Module: Use a Grove cable to connect the Digital Compass to an I2C port on a compatible microcontroller, such as an Arduino UNO.
- Power the Module: Ensure the module is powered with a voltage between 3.3V and 5V.
- Install Required Libraries: For Arduino, install the necessary I2C and compass libraries (e.g.,
Wire.handAdafruit_Sensor). - Write and Upload Code: Use the provided example code to read heading data from the compass.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid Magnetic Interference: Keep the module away from strong magnetic fields or ferromagnetic materials, as they can distort readings.
- Calibrate the Compass: Perform a calibration routine to ensure accurate measurements, especially in new environments.
- Use Proper Pull-Up Resistors: If not already included, add pull-up resistors (typically 4.7kΩ) on the SDA and SCL lines for stable I2C communication.
- Check I2C Address: The default I2C address of the module is typically
0x1E, but consult the datasheet to confirm.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example Arduino sketch to read heading data from the Grove Digital Compass:
#include <Wire.h> // Include the Wire library for I2C communication
#define COMPASS_ADDRESS 0x1E // Default I2C address of the compass
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
Wire.begin(); // Initialize I2C communication
initializeCompass(); // Call function to configure the compass
}
void loop() {
float heading = readHeading(); // Read the compass heading
Serial.print("Heading: ");
Serial.print(heading);
Serial.println("°"); // Print the heading in degrees
delay(500); // Wait for 500ms before the next reading
}
void initializeCompass() {
Wire.beginTransmission(COMPASS_ADDRESS); // Start communication with compass
Wire.write(0x00); // Select configuration register A
Wire.write(0x70); // Set measurement mode to normal
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.beginTransmission(COMPASS_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x02); // Select mode register
Wire.write(0x00); // Set continuous measurement mode
Wire.endTransmission();
}
float readHeading() {
Wire.beginTransmission(COMPASS_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x03); // Select data output register
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(COMPASS_ADDRESS, 6); // Request 6 bytes of data
if (Wire.available() == 6) {
int16_t x = (Wire.read() << 8) | Wire.read(); // Read X-axis data
int16_t z = (Wire.read() << 8) | Wire.read(); // Read Z-axis data
int16_t y = (Wire.read() << 8) | Wire.read(); // Read Y-axis data
// Calculate heading in degrees
float heading = atan2((float)y, (float)x) * 180 / PI;
if (heading < 0) heading += 360; // Ensure heading is positive
return heading;
}
return 0; // Return 0 if no data is available
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Data or Incorrect Readings
- Cause: Loose connections or incorrect wiring.
- Solution: Verify all connections, ensuring SDA and SCL are connected to the correct pins on the microcontroller.
Inconsistent or Fluctuating Readings
- Cause: Magnetic interference or lack of calibration.
- Solution: Move the module away from magnetic sources and perform a calibration routine.
I2C Communication Failure
- Cause: Incorrect I2C address or missing pull-up resistors.
- Solution: Check the module's I2C address and ensure pull-up resistors are in place.
FAQs
Q: Can I use this module with a Raspberry Pi?
- A: Yes, the Grove Digital Compass is compatible with Raspberry Pi via the I2C interface. Use libraries like
smbusfor Python.
- A: Yes, the Grove Digital Compass is compatible with Raspberry Pi via the I2C interface. Use libraries like
Q: How do I calibrate the compass?
- A: Rotate the module in all directions to map the magnetic field. Some libraries include built-in calibration functions.
Q: What is the maximum cable length for I2C communication?
- A: The maximum length depends on the pull-up resistor values and communication speed, but it is typically limited to 1 meter for reliable operation.
This documentation provides a comprehensive guide to using the Grove Digital Compass effectively in your projects.