
How to Use Relay Module 30 A / 250 VAC: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Relay Module 30 A / 250 VAC in Cirkit Designer
Design with Relay Module 30 A / 250 VAC in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
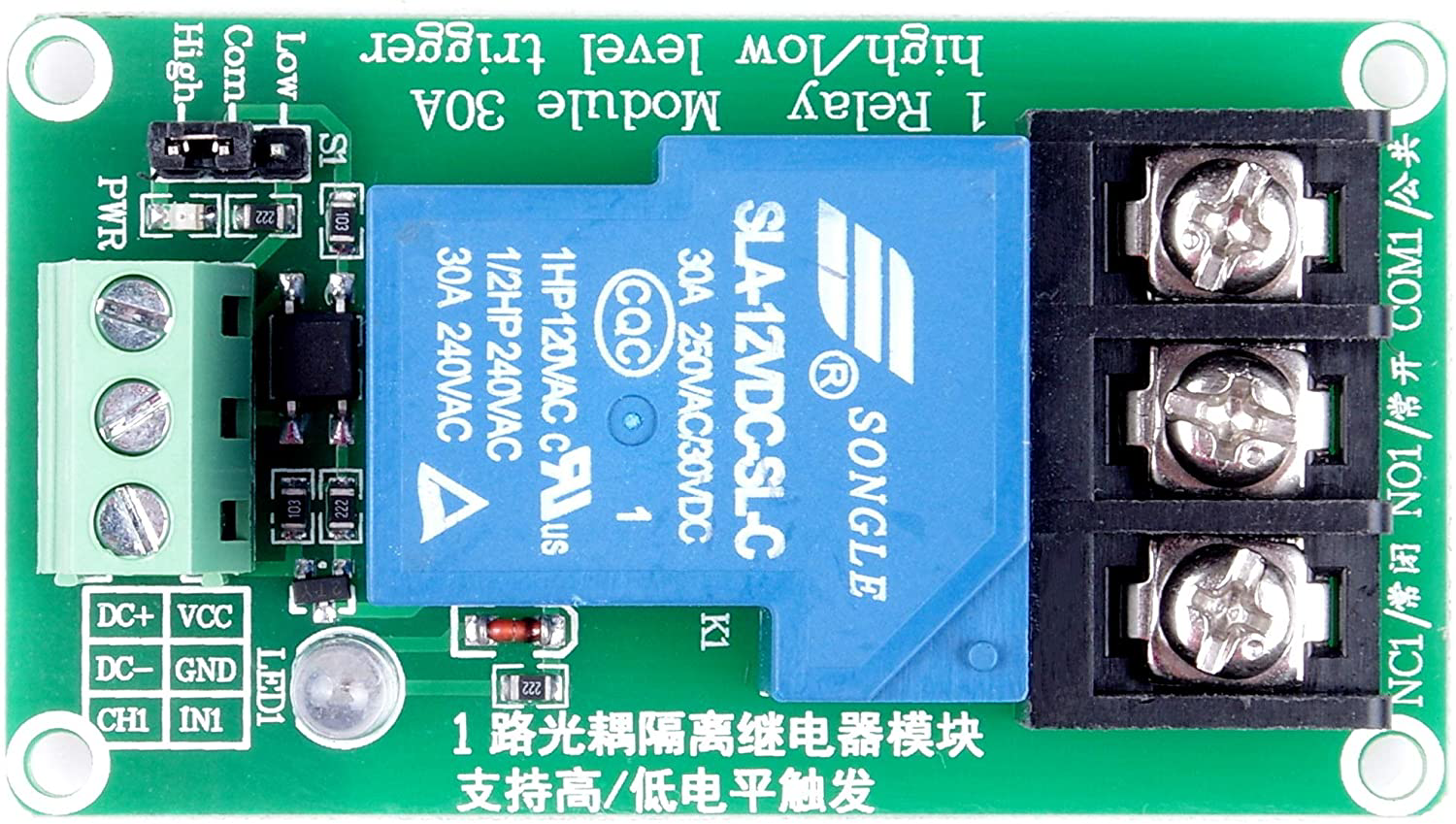
The Relay Module 30 A / 250 VAC is an electromechanical switching device designed to control high-power loads using low-power control signals. It is capable of switching loads up to 30 Amperes at 250 Volts AC, making it ideal for applications requiring the control of high-power devices such as motors, heaters, and lighting systems. The module typically includes an optocoupler for electrical isolation, ensuring safe operation when interfacing with microcontrollers or other low-voltage control systems.
Explore Projects Built with Relay Module 30 A / 250 VAC
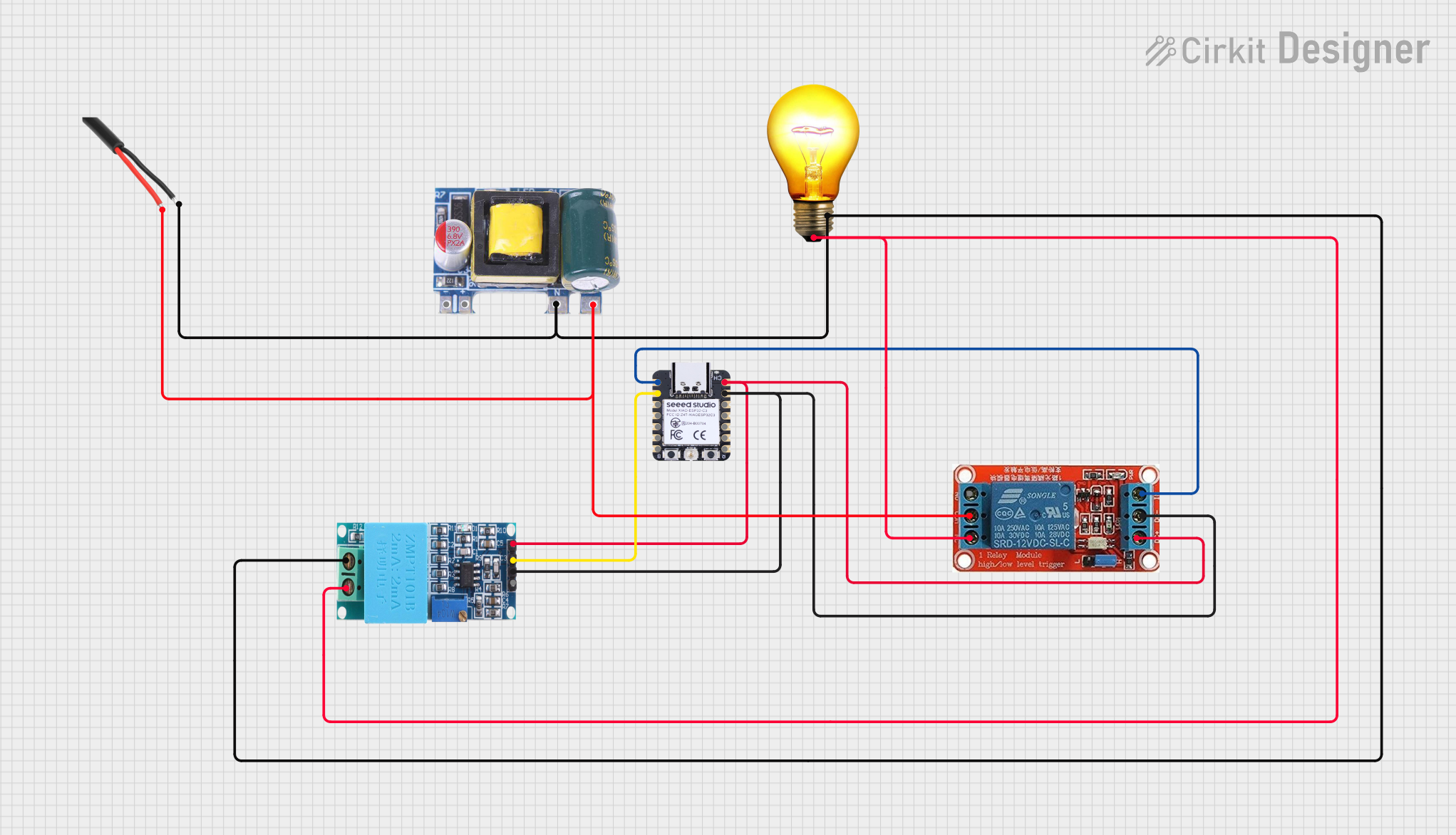
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer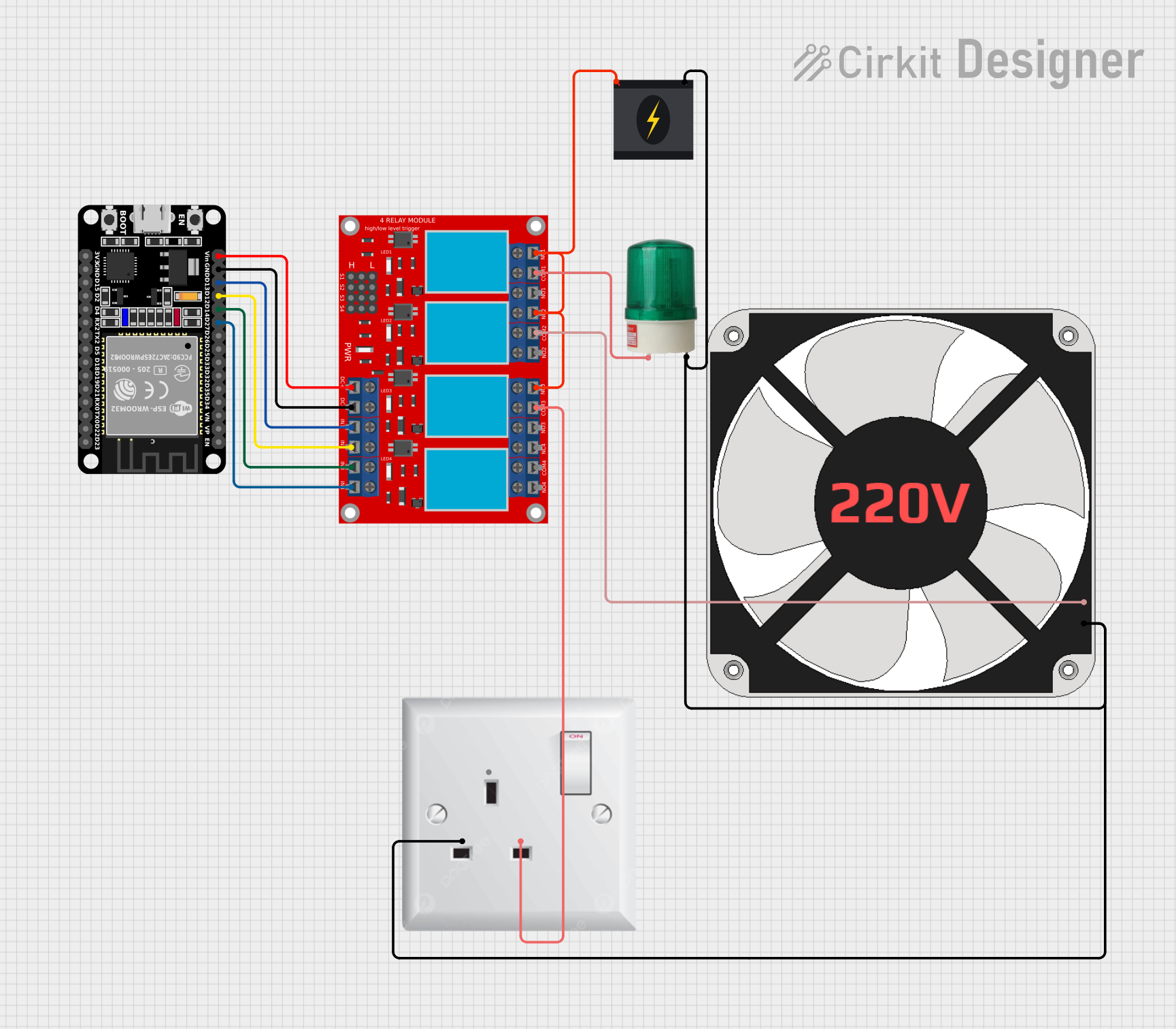
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer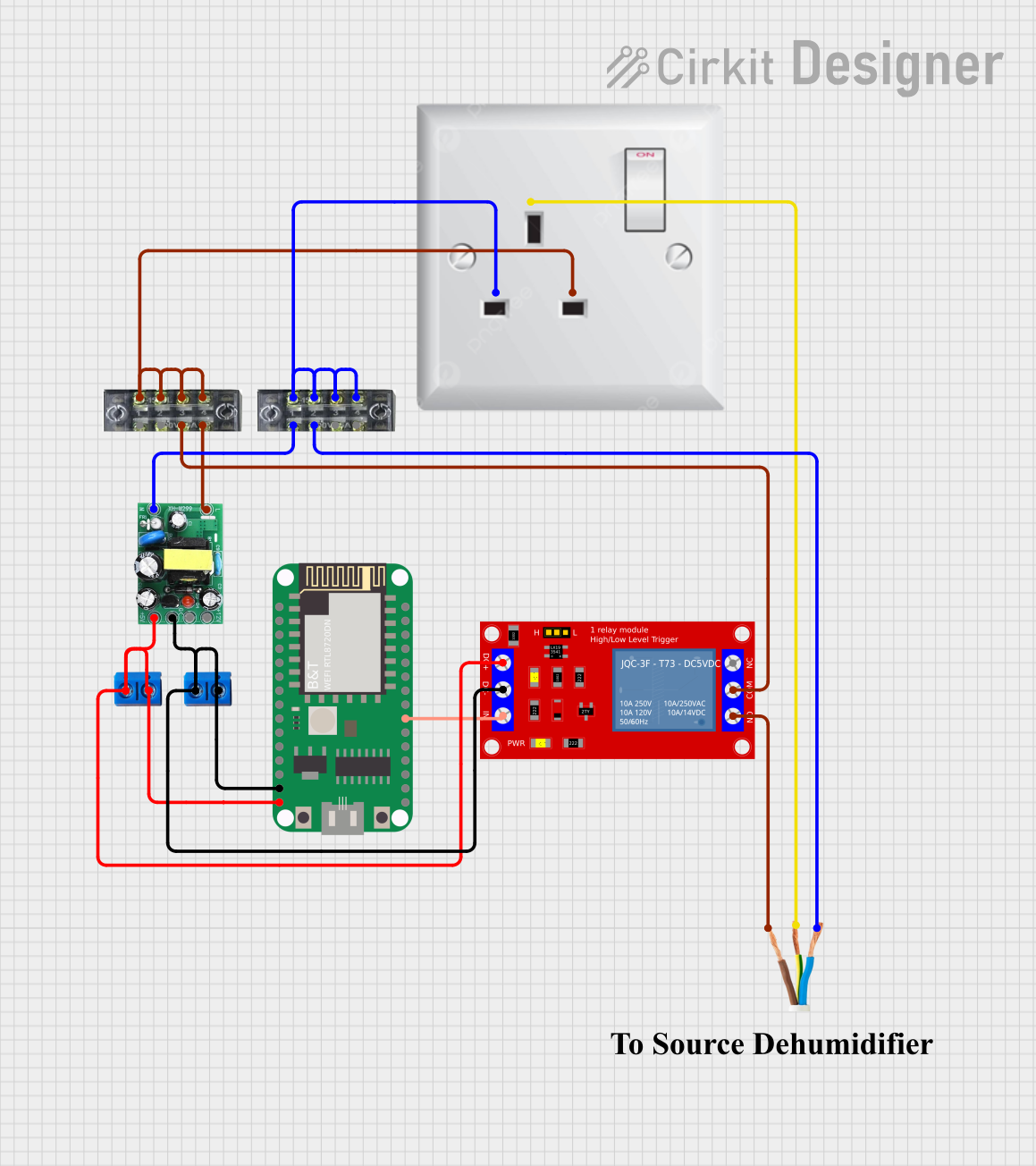
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer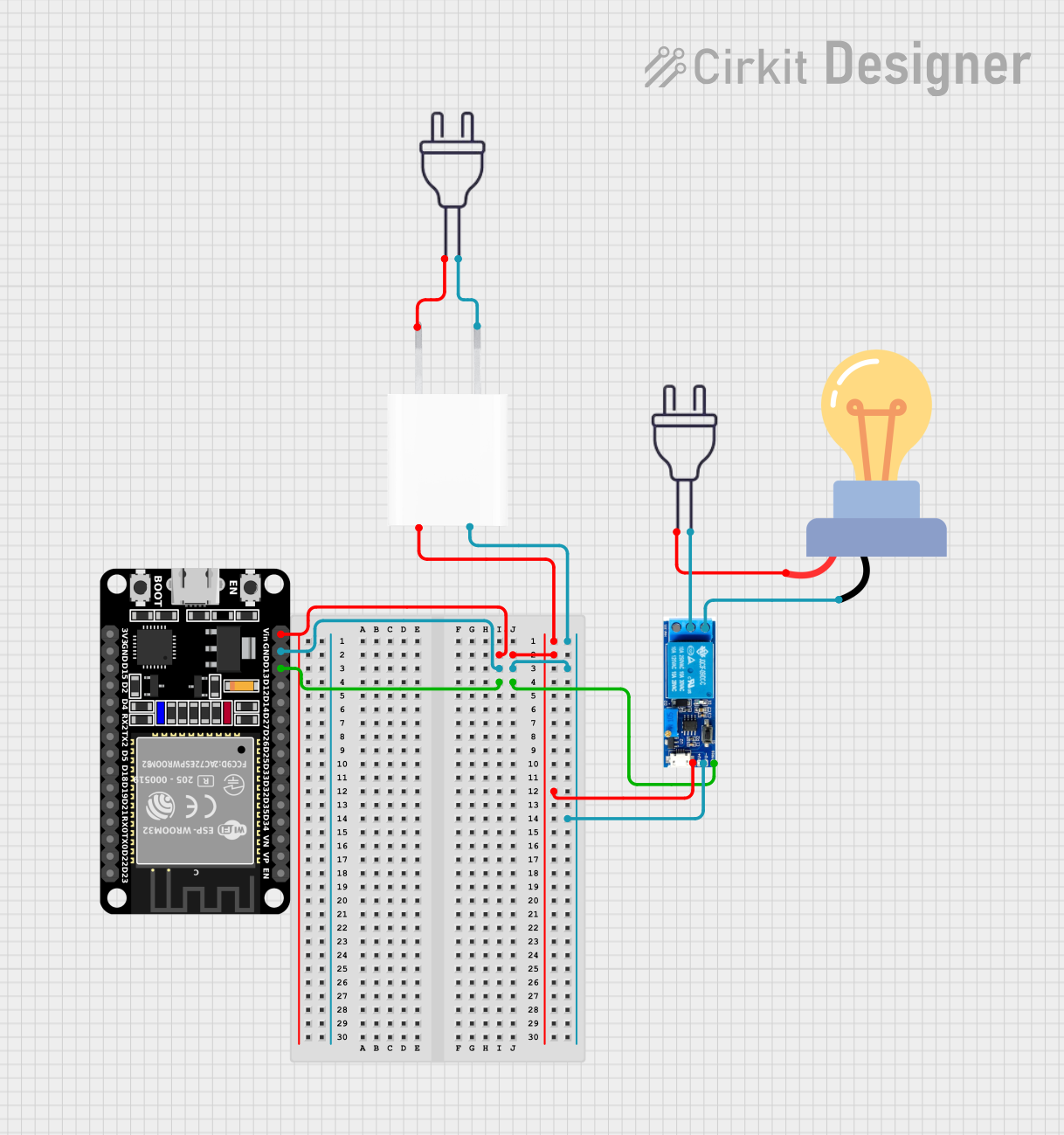
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Relay Module 30 A / 250 VAC

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Home automation systems (e.g., controlling appliances or lighting)
- Industrial equipment control
- Motor and pump control
- HVAC systems
- Smart energy management systems
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Operating Voltage (Control Side): 5V DC (typical)
- Trigger Current: 15-20 mA
- Relay Contact Ratings:
- Maximum Voltage: 250 VAC / 30 A
- Maximum Current: 30 A
- Relay Type: SPDT (Single Pole Double Throw)
- Electrical Isolation: Optocoupler-based
- Indicator LED: Onboard LED to indicate relay activation
- Dimensions: Varies by manufacturer, typically compact for easy integration
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The relay module typically has the following pins:
Control Side (Low Voltage)
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Connect to the 5V DC power supply. |
| GND | Connect to the ground of the power supply or microcontroller. |
| IN | Control signal input. A HIGH signal activates the relay, and a LOW signal deactivates it. |
Load Side (High Voltage)
| Terminal Name | Description |
|---|---|
| COM | Common terminal for the relay. Connect to the power source or load. |
| NO | Normally Open terminal. The circuit is open when the relay is inactive. |
| NC | Normally Closed terminal. The circuit is closed when the relay is inactive. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power the Module:
- Connect the VCC pin to a 5V DC power supply and the GND pin to the ground.
- Control Signal:
- Connect the IN pin to a digital output pin of a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO).
- When the microcontroller outputs a HIGH signal, the relay will activate, closing the NO terminal and opening the NC terminal.
- Load Connection:
- Connect the high-power load to the COM and NO terminals if you want the load to turn on when the relay is activated.
- Alternatively, connect the load to the COM and NC terminals if you want the load to turn off when the relay is activated.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Electrical Isolation: Ensure proper isolation between the control and load sides to prevent damage to the microcontroller.
- Flyback Diode: If controlling an inductive load (e.g., motor), use a flyback diode across the load to suppress voltage spikes.
- Heat Dissipation: Ensure adequate ventilation or heat dissipation for high-current loads to prevent overheating.
- Safety Precautions: Always handle high-voltage connections with care. Disconnect power before wiring the load side.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control the relay module using an Arduino UNO:
// Define the pin connected to the relay module's IN pin
const int relayPin = 7;
void setup() {
// Set the relay pin as an output
pinMode(relayPin, OUTPUT);
// Ensure the relay is off at startup
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW);
}
void loop() {
// Turn the relay on (activate the connected load)
digitalWrite(relayPin, HIGH);
delay(5000); // Keep the relay on for 5 seconds
// Turn the relay off (deactivate the connected load)
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW);
delay(5000); // Keep the relay off for 5 seconds
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Relay Not Activating:
- Cause: Insufficient control voltage or current.
- Solution: Ensure the control signal is 5V and the source can supply at least 15-20 mA.
Load Not Switching:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring on the load side.
- Solution: Verify the connections to the COM, NO, and NC terminals.
Microcontroller Resetting:
- Cause: Voltage spikes from the relay coil or load.
- Solution: Use a flyback diode across the relay coil and/or load.
Relay Stuck in One State:
- Cause: Relay contacts may be damaged due to overcurrent.
- Solution: Ensure the load does not exceed the relay's 30 A / 250 VAC rating.
FAQs
Q: Can I use this relay module with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Most relay modules require a 5V control signal. If using a 3.3V microcontroller, you may need a level shifter or a transistor to boost the control signal to 5V.
Q: Is it safe to use this relay module for DC loads?
A: Yes, but ensure the DC load does not exceed the relay's current and voltage ratings. Note that DC loads may cause faster wear on the relay contacts.
Q: Can I control multiple relays with one microcontroller?
A: Yes, as long as the microcontroller has enough GPIO pins and can supply the required current for each relay's control circuit.