
How to Use DFRobot Stepdown : Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with DFRobot Stepdown in Cirkit Designer
Design with DFRobot Stepdown in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The DFRobot Stepdown (DFR1208) is a DC-DC step-down converter designed to efficiently reduce a higher input voltage to a stable, lower output voltage. This component is ideal for powering devices that require a specific voltage level, such as microcontrollers, sensors, and other electronic modules. Its compact design and high efficiency make it a versatile choice for a wide range of applications, including robotics, IoT devices, and portable electronics.
Explore Projects Built with DFRobot Stepdown
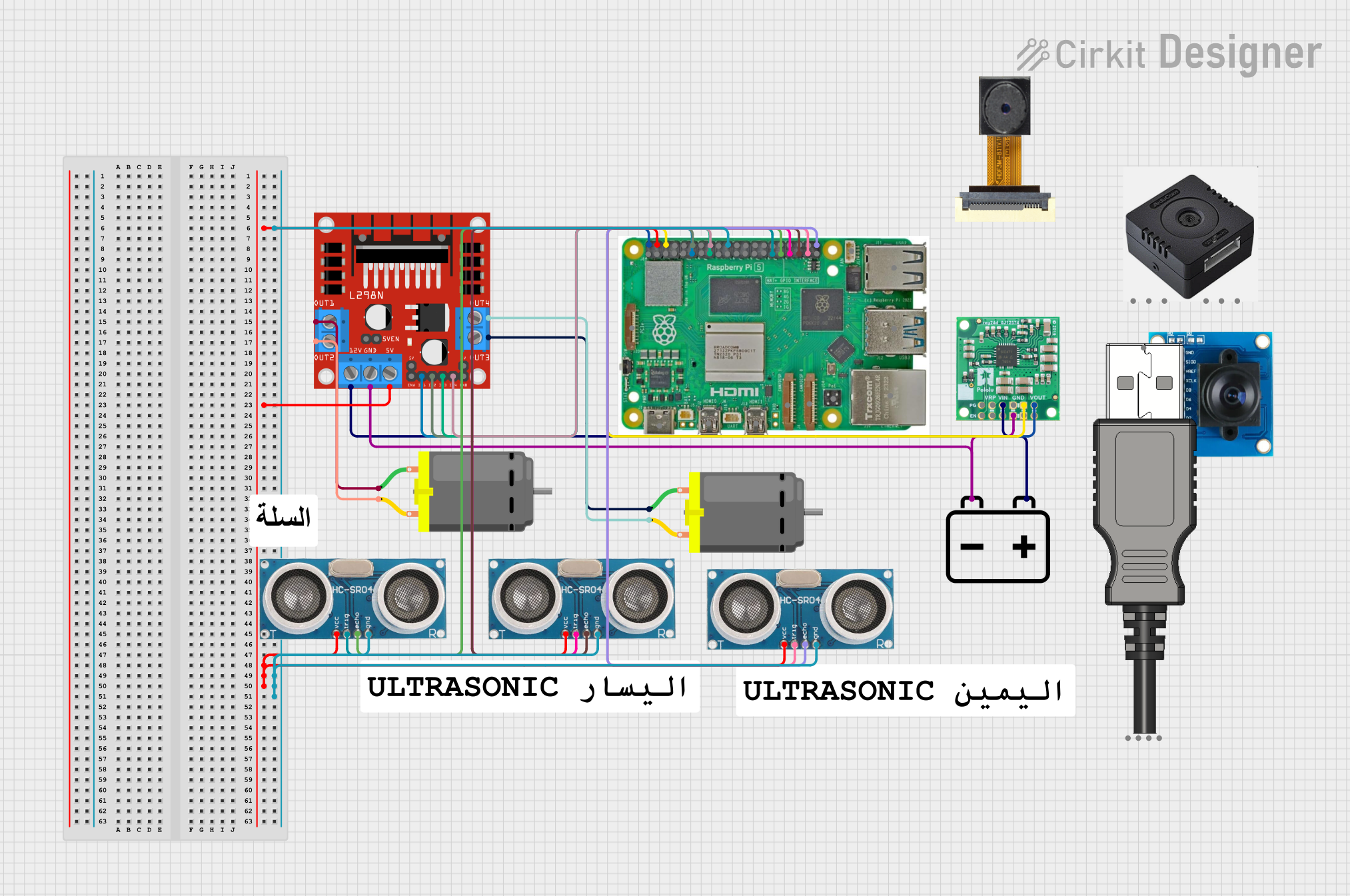
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer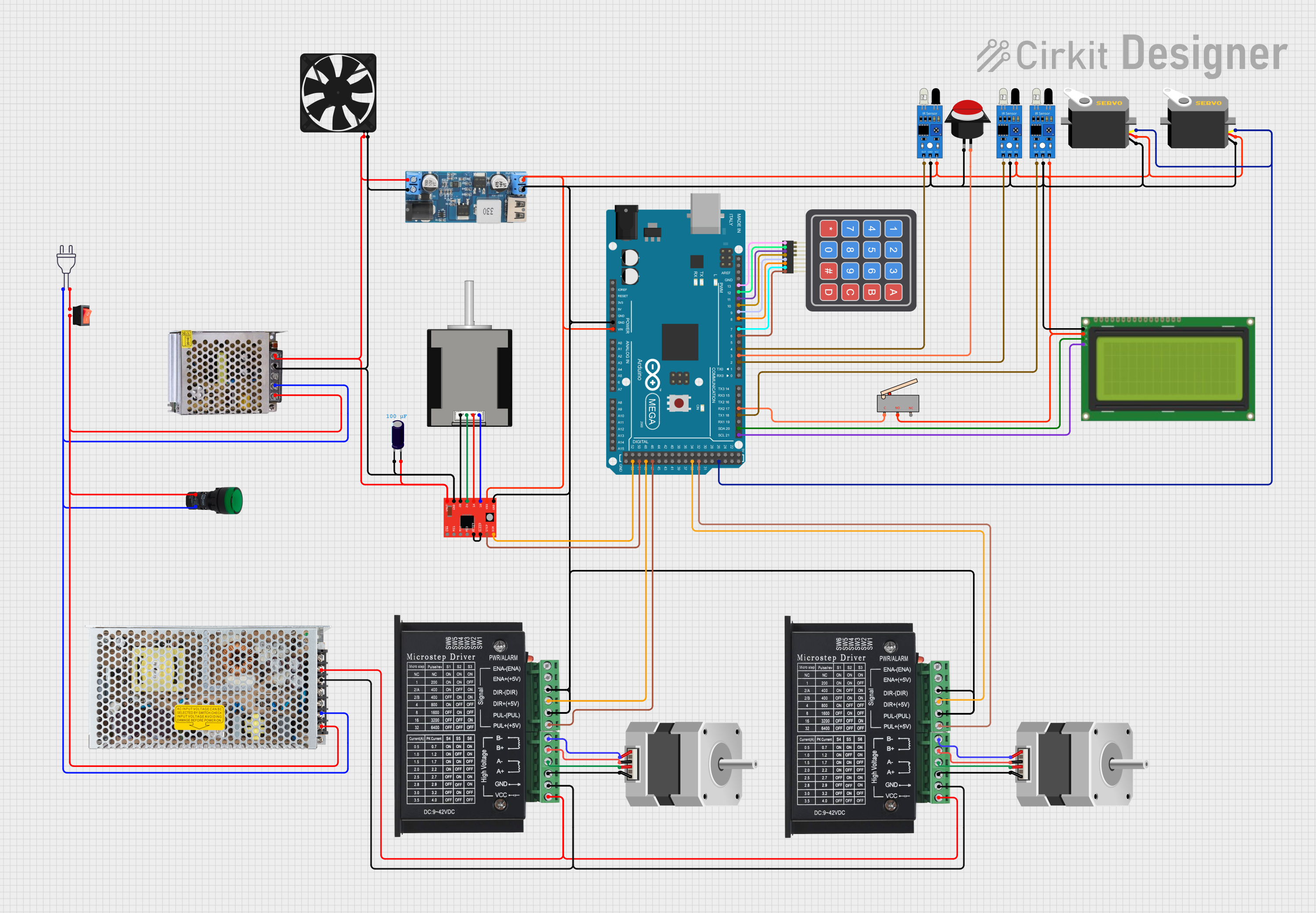
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer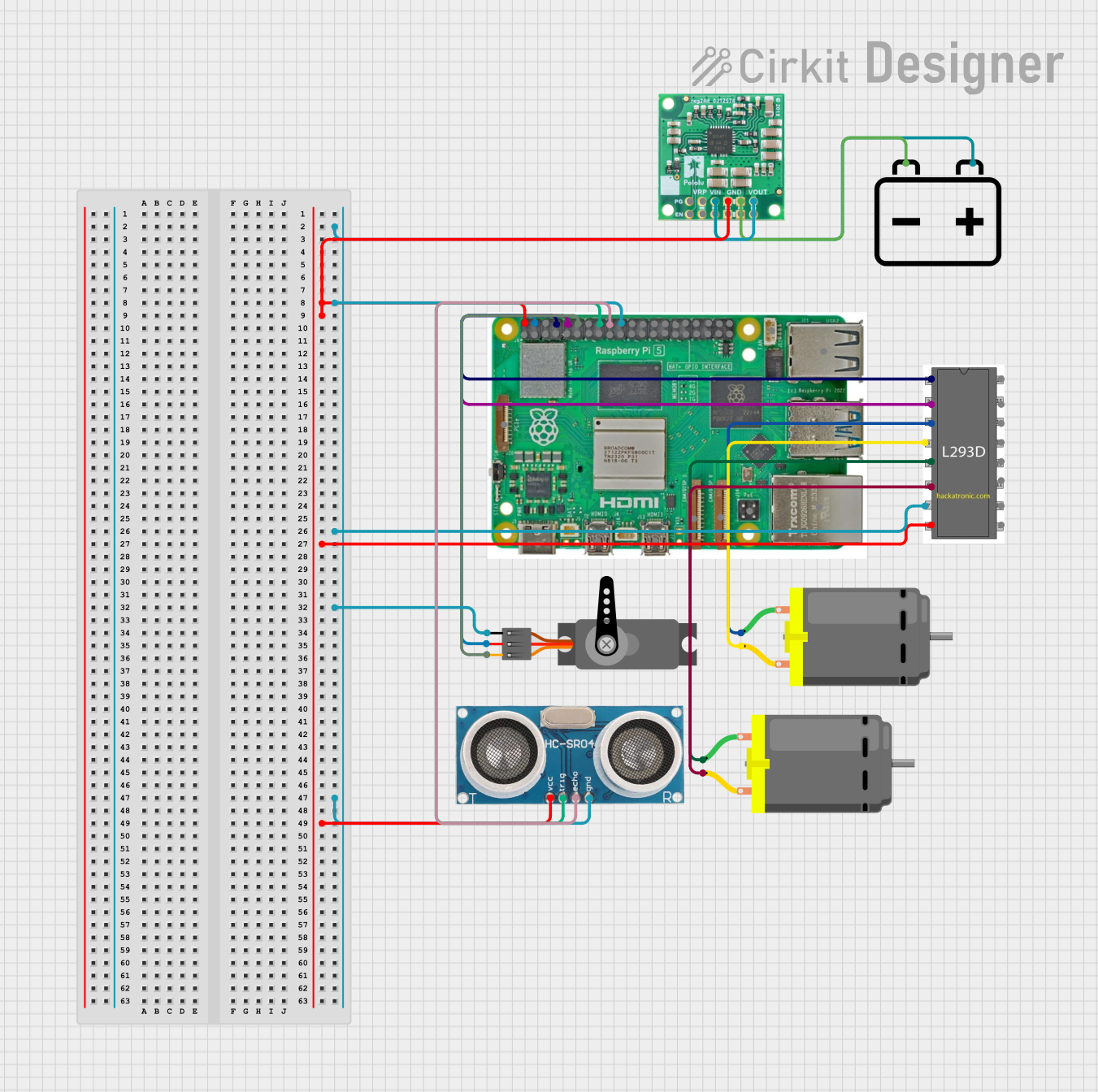
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with DFRobot Stepdown

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Powering microcontrollers (e.g., Arduino, Raspberry Pi) from higher voltage sources.
- Supplying stable voltage to sensors and modules in IoT projects.
- Voltage regulation in battery-powered systems.
- Robotics and automation systems requiring multiple voltage levels.
Technical Specifications
The DFRobot Stepdown (DFR1208) offers the following key technical specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 4.5V to 24V |
| Output Voltage Range | 0.8V to 15V (adjustable) |
| Output Current | Up to 3A |
| Efficiency | Up to 96% |
| Switching Frequency | 340 kHz |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Dimensions | 22mm x 17mm x 4mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The DFR1208 has the following pin layout:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN | Input voltage pin. Connect to the higher voltage source (4.5V to 24V). |
| GND | Ground pin. Connect to the ground of the power source and the load circuit. |
| VOUT | Output voltage pin. Provides the regulated voltage (0.8V to 15V). |
| EN | Enable pin. Pull high to enable the module; pull low to disable it. |
| ADJ | Voltage adjustment pin. Use a potentiometer or resistor to set the output voltage. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connect the Input Voltage:
- Connect the VIN pin to the positive terminal of your power source (e.g., a 12V battery or adapter).
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of your power source.
Set the Output Voltage:
- Use the ADJ pin to adjust the output voltage. This can be done by connecting a potentiometer or a fixed resistor to set the desired voltage level.
- Measure the output voltage at the VOUT pin using a multimeter to ensure it matches your requirements.
Connect the Load:
- Connect the VOUT pin to the positive terminal of your load (e.g., a microcontroller or sensor).
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of your load.
Enable the Module:
- Ensure the EN pin is pulled high (connected to VIN or a logic high signal) to enable the module. If the EN pin is left floating or pulled low, the module will be disabled.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Input Voltage Range: Ensure the input voltage is within the specified range (4.5V to 24V). Exceeding this range may damage the module.
- Output Current Limit: Do not exceed the maximum output current of 3A to prevent overheating or damage.
- Heat Dissipation: For high current loads, consider adding a heatsink or ensuring proper ventilation to maintain safe operating temperatures.
- Voltage Adjustment: When adjusting the output voltage, do so gradually and monitor the voltage with a multimeter to avoid overshooting the desired value.
- Polarity Protection: Double-check the polarity of your connections to avoid damaging the module.
Example: Using the DFR1208 with an Arduino UNO
The DFR1208 can be used to power an Arduino UNO from a 12V power source. Here's how to set it up:
- Connect the VIN pin of the DFR1208 to the positive terminal of the 12V power source.
- Connect the GND pin of the DFR1208 to the ground of the power source.
- Adjust the output voltage to 5V using the ADJ pin.
- Connect the VOUT pin of the DFR1208 to the 5V pin of the Arduino UNO.
- Connect the GND pin of the DFR1208 to the GND pin of the Arduino UNO.
Here is an example Arduino code to blink an LED, powered by the DFR1208:
// This code blinks an LED connected to pin 13 of the Arduino UNO.
// Ensure the Arduino is powered by the DFR1208 with a stable 5V output.
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output pin
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Voltage:
- Cause: The EN pin is not pulled high.
- Solution: Ensure the EN pin is connected to VIN or a logic high signal.
Output Voltage is Incorrect:
- Cause: The ADJ pin is not properly configured.
- Solution: Recheck the resistor or potentiometer connected to the ADJ pin and adjust as needed.
Module Overheating:
- Cause: Excessive current draw or poor ventilation.
- Solution: Ensure the load does not exceed 3A and improve airflow around the module.
No Power to the Load:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or polarity.
- Solution: Double-check all connections and ensure correct polarity.
FAQs
Q: Can the DFR1208 be used with a 24V input to power a 3.3V device?
A: Yes, the DFR1208 can step down a 24V input to 3.3V, provided the output current does not exceed 3A.
Q: Is the module protected against reverse polarity?
A: No, the DFR1208 does not have built-in reverse polarity protection. Always double-check your connections.
Q: Can I use the DFR1208 to charge a battery?
A: The DFR1208 is not specifically designed for battery charging. Use a dedicated battery charging module for this purpose.
Q: How do I know if the module is enabled?
A: Check the voltage at the VOUT pin. If the module is enabled, it will output the set voltage. If disabled, the output will be 0V.