
Cirkit Designer
Your all-in-one circuit design IDE
Home /
Component Documentation
How to Use 4 Digit Seven Segment Display: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 4 Digit Seven Segment Display in Cirkit Designer
Design with 4 Digit Seven Segment Display in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 4 Digit Seven Segment Display is a versatile and widely used electronic component for displaying numerical information. It consists of four individual seven-segment displays, each capable of showing digits from 0 to 9. This component is commonly used in digital clocks, counters, and other devices that require numerical output.
Explore Projects Built with 4 Digit Seven Segment Display
Arduino UNO 4-Digit 7-Segment Display Counter
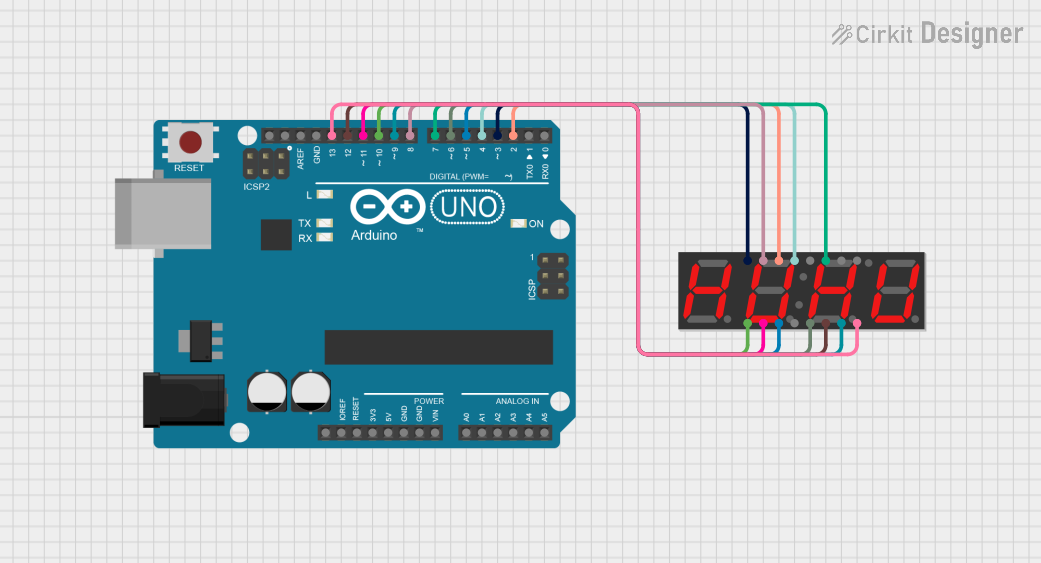
This circuit uses an Arduino UNO to control a 4-digit 7-segment display. The Arduino is programmed to sequentially display the numbers 1, 2, 3, and 4 on the display by driving the appropriate segments and digits.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerArduino UNO 4-Digit Seven Segment Display Counter
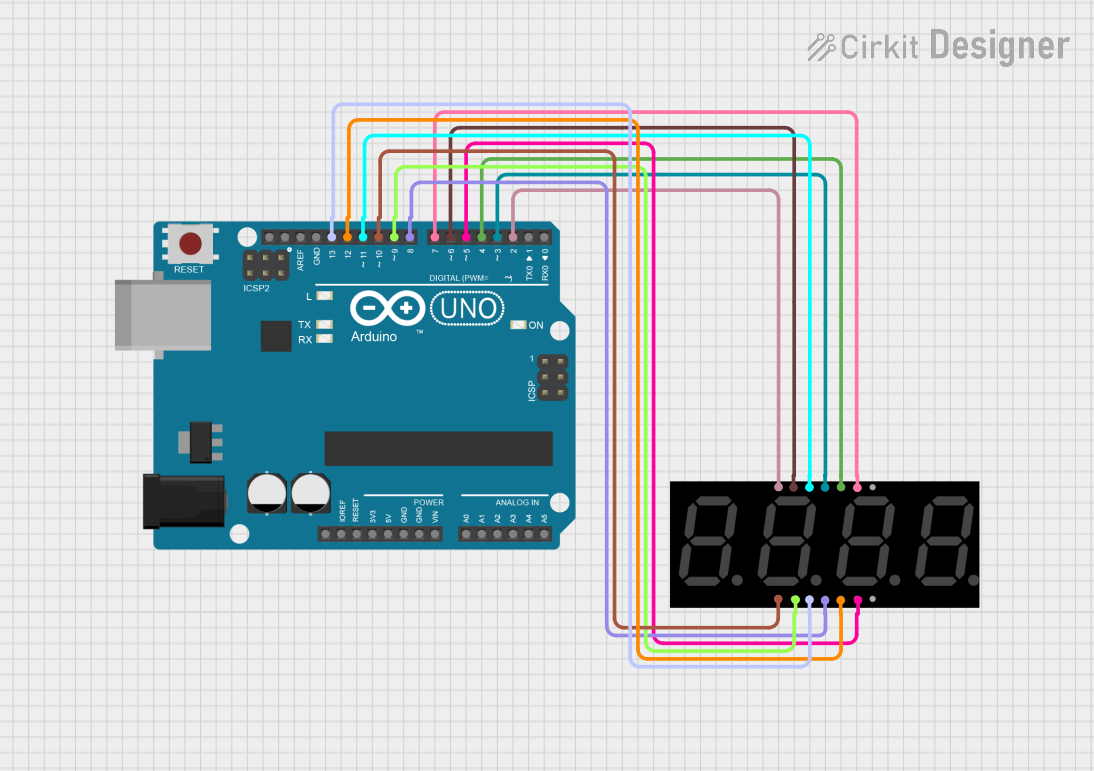
This circuit uses an Arduino UNO to control a 4-digit seven-segment display. The Arduino runs a program that counts up in deci-seconds and displays the count on the seven-segment display using the SevSeg library.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerArduino UNO Controlled Seven Segment Display
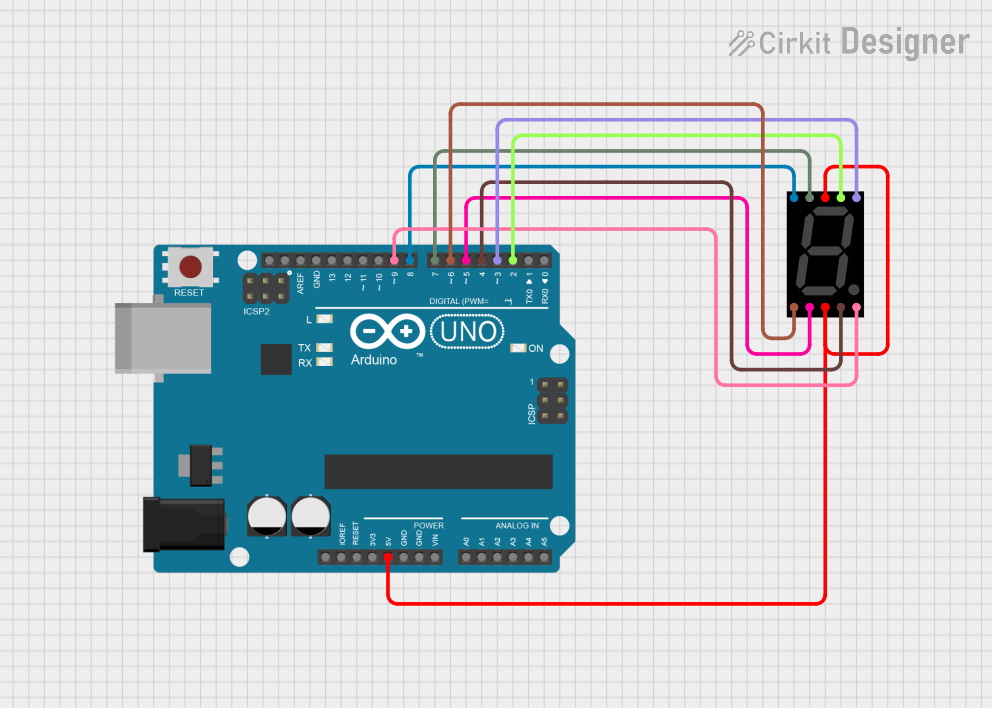
This circuit utilizes an Arduino UNO to control a seven-segment display, allowing it to display digits from 0 to 9 in a sequential manner. The Arduino is programmed to set the appropriate pins high or low to illuminate the segments of the display, creating the desired digit patterns. The display updates every second, providing a simple visual output for numerical representation.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerArduino UNO Controlled LED and 7-Segment Display Circuit
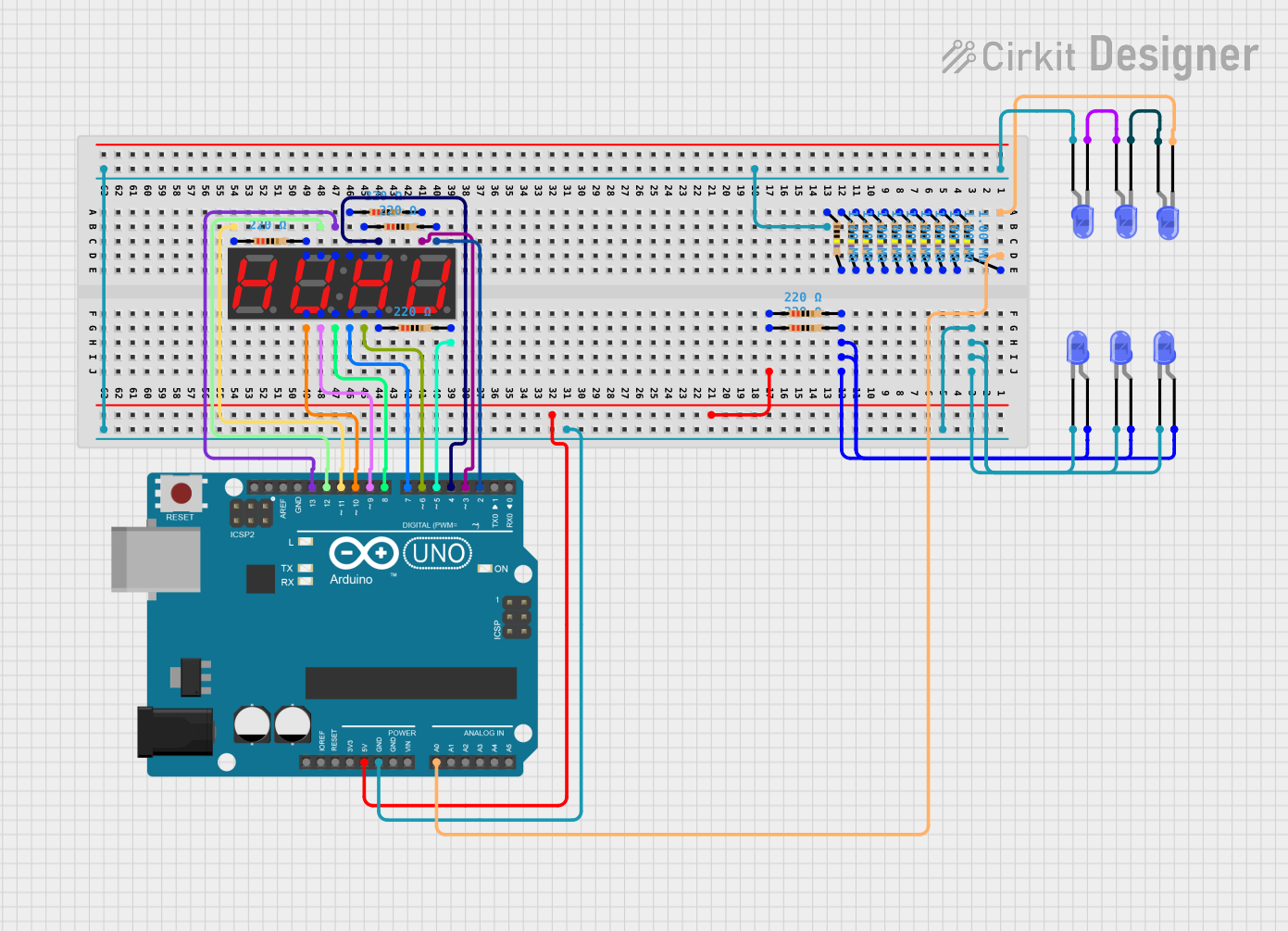
This circuit features an Arduino UNO controlling multiple blue LEDs and a 4-digit 7-segment display. The LEDs are configured with current-limiting resistors, and the display is interfaced with the Arduino for potential numeric or character output. The provided code for the Arduino is a template without specific functionality.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 4 Digit Seven Segment Display

Arduino UNO 4-Digit 7-Segment Display Counter
This circuit uses an Arduino UNO to control a 4-digit 7-segment display. The Arduino is programmed to sequentially display the numbers 1, 2, 3, and 4 on the display by driving the appropriate segments and digits.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Arduino UNO 4-Digit Seven Segment Display Counter
This circuit uses an Arduino UNO to control a 4-digit seven-segment display. The Arduino runs a program that counts up in deci-seconds and displays the count on the seven-segment display using the SevSeg library.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Arduino UNO Controlled Seven Segment Display
This circuit utilizes an Arduino UNO to control a seven-segment display, allowing it to display digits from 0 to 9 in a sequential manner. The Arduino is programmed to set the appropriate pins high or low to illuminate the segments of the display, creating the desired digit patterns. The display updates every second, providing a simple visual output for numerical representation.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Arduino UNO Controlled LED and 7-Segment Display Circuit
This circuit features an Arduino UNO controlling multiple blue LEDs and a 4-digit 7-segment display. The LEDs are configured with current-limiting resistors, and the display is interfaced with the Arduino for potential numeric or character output. The provided code for the Arduino is a template without specific functionality.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Digital clocks and timers
- Electronic meters and counters
- Scoreboards
- Temperature and humidity displays
- Simple user interfaces for embedded systems
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V to 5V |
| Current per Segment | 10mA to 20mA |
| Power Consumption | Varies with usage |
| Display Type | Common Anode or Common Cathode |
| Number of Digits | 4 |
| Segment Configuration | 7 segments + decimal point |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Common Anode Configuration
| Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Digit 1 Common Anode |
| 2 | Segment B |
| 3 | Segment A |
| 4 | Digit 2 Common Anode |
| 5 | Segment F |
| 6 | Segment G |
| 7 | Segment E |
| 8 | Segment D |
| 9 | Digit 3 Common Anode |
| 10 | Segment C |
| 11 | Decimal Point |
| 12 | Digit 4 Common Anode |
Common Cathode Configuration
| Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Digit 1 Common Cathode |
| 2 | Segment B |
| 3 | Segment A |
| 4 | Digit 2 Common Cathode |
| 5 | Segment F |
| 6 | Segment G |
| 7 | Segment E |
| 8 | Segment D |
| 9 | Digit 3 Common Cathode |
| 10 | Segment C |
| 11 | Decimal Point |
| 12 | Digit 4 Common Cathode |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Identify the Configuration: Determine whether your display is common anode or common cathode.
- Connect Power: Connect the common anode or cathode pins to the appropriate power supply (Vcc for common anode, GND for common cathode).
- Connect Segments: Connect the segment pins (A-G and DP) to the corresponding output pins of your microcontroller or driver IC.
- Control Digits: Use transistors or multiplexing techniques to control which digit is active at any given time.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Current Limiting Resistors: Always use current limiting resistors for each segment to prevent damage.
- Multiplexing: To reduce the number of required I/O pins, use multiplexing to control each digit sequentially.
- Brightness Control: Adjust the current through the segments to control the brightness of the display.
- Heat Dissipation: Ensure adequate heat dissipation if the display is used continuously at high brightness.
Example Circuit with Arduino UNO
// Example code to display numbers on a 4 Digit Seven Segment Display
// connected to an Arduino UNO. This example assumes a common cathode
// display and uses multiplexing to control the digits.
const int segmentPins[] = {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}; // Pins connected to segments A-G
const int digitPins[] = {9, 10, 11, 12}; // Pins connected to digit common cathodes
const byte digitPatterns[10] = {
0b00111111, // 0
0b00000110, // 1
0b01011011, // 2
0b01001111, // 3
0b01100110, // 4
0b01101101, // 5
0b01111101, // 6
0b00000111, // 7
0b01111111, // 8
0b01101111 // 9
};
void setup() {
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
pinMode(segmentPins[i], OUTPUT);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
pinMode(digitPins[i], OUTPUT);
}
}
void loop() {
displayNumber(1234); // Display the number 1234
}
void displayNumber(int number) {
for (int digit = 0; digit < 4; digit++) {
int digitValue = number % 10;
number /= 10;
displayDigit(digit, digitValue);
delay(5); // Small delay for multiplexing
}
}
void displayDigit(int digit, int value) {
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite(segmentPins[i], bitRead(digitPatterns[value], i));
}
digitalWrite(digitPins[digit], LOW); // Activate the digit
delay(1); // Short delay to allow the digit to be visible
digitalWrite(digitPins[digit], HIGH); // Deactivate the digit
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- Display Not Lighting Up: Check power connections and ensure the common anode/cathode is correctly connected.
- Incorrect Digits Displayed: Verify the segment connections and ensure the correct digit patterns are used.
- Dim Display: Check current limiting resistors and ensure adequate current is supplied to the segments.
- Flickering Display: Ensure proper multiplexing timing and reduce delays if necessary.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Double-Check Connections: Ensure all connections are secure and correctly mapped.
- Use a Multimeter: Check voltages and currents to ensure they are within the specified range.
- Test Individual Segments: Manually test each segment to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Review Code: Ensure the code logic for controlling the display is correct and matches the hardware configuration.
By following this documentation, users should be able to effectively utilize the 4 Digit Seven Segment Display in their projects, whether they are beginners or experienced electronics enthusiasts.