
How to Use TFT Display 0.96": Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with TFT Display 0.96" in Cirkit Designer
Design with TFT Display 0.96" in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The TFT Display 0.96" is a compact, vibrant thin-film transistor (TFT) display module with a diagonal size of 0.96 inches. It is widely used in embedded systems and microcontroller-based projects for displaying colorful graphics, text, and images. This display is ideal for applications requiring a small form factor and high-quality visuals, such as wearable devices, IoT dashboards, and portable electronics.
Explore Projects Built with TFT Display 0.96"
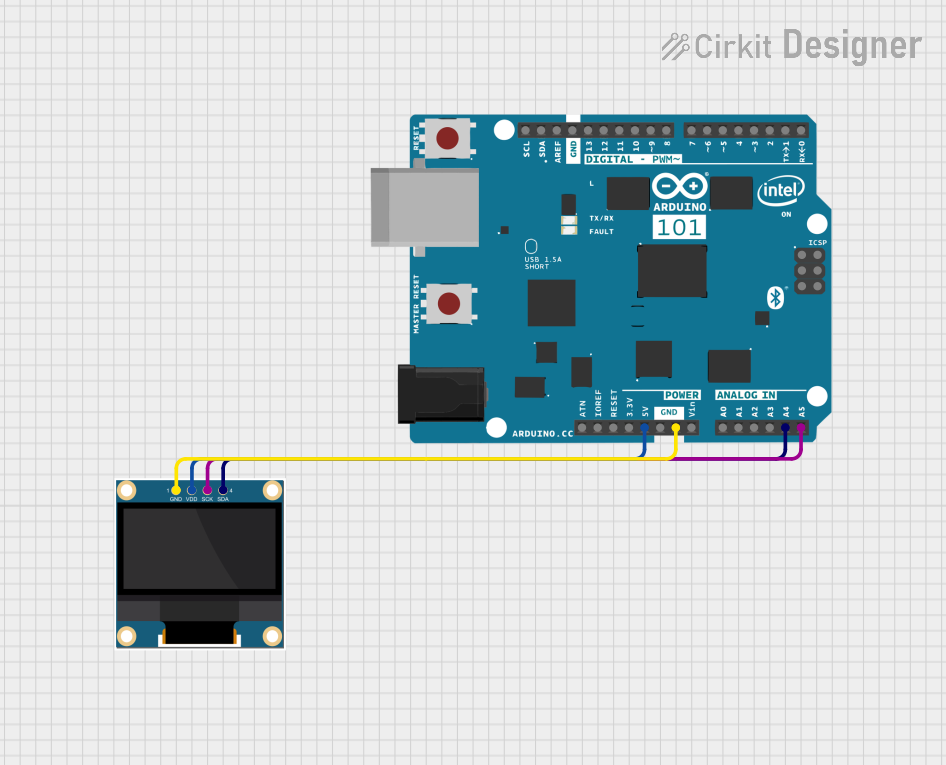
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer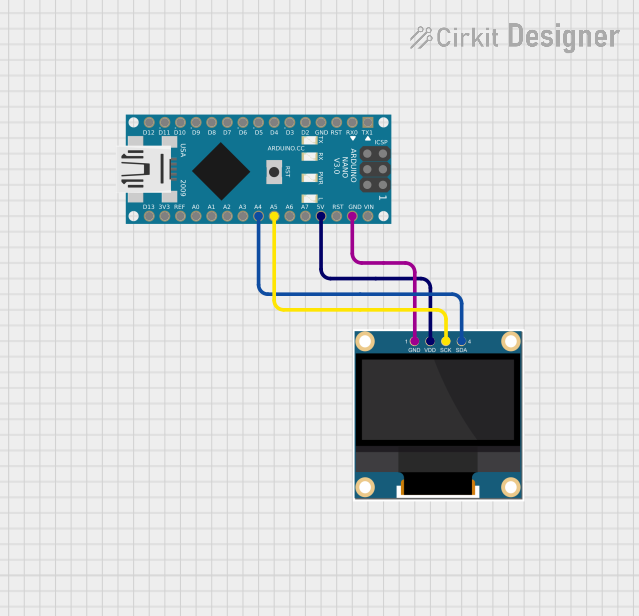
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer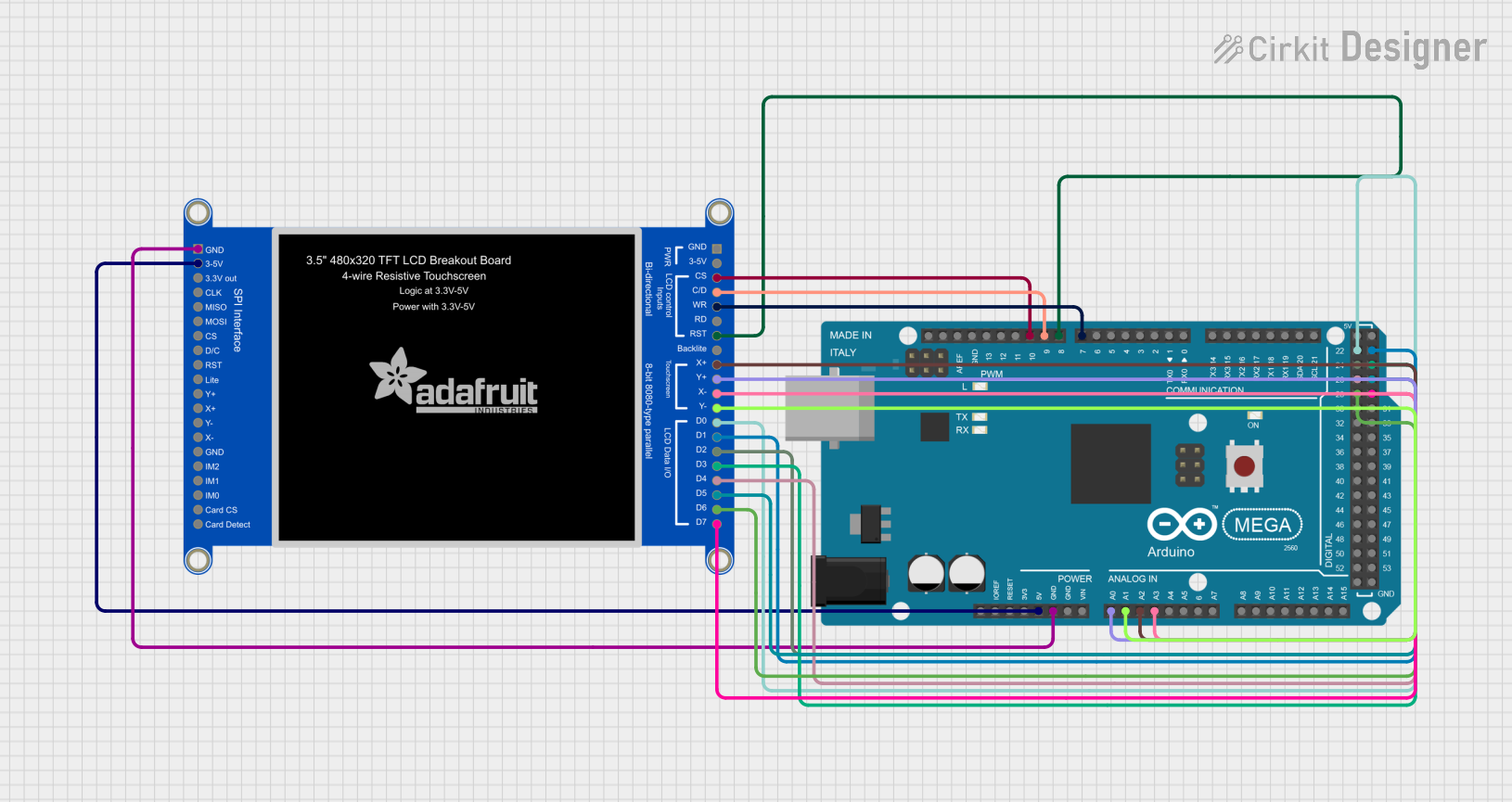
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TFT Display 0.96"

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Wearable devices (e.g., smartwatches, fitness trackers)
- IoT devices and dashboards
- Portable measurement tools
- Small-scale gaming consoles
- Embedded systems requiring graphical user interfaces
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the TFT Display 0.96":
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Display Type | TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) |
| Screen Size | 0.96 inches (diagonal) |
| Resolution | 160 x 80 pixels |
| Color Depth | 65K colors (16-bit RGB) |
| Interface | SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V (logic level) |
| Backlight Voltage | 3.3V |
| Current Consumption | ~20mA (typical) |
| Driver IC | ST7735 |
| Viewing Angle | ~160° |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to 70°C |
Pin Configuration
The TFT Display 0.96" typically has an 8-pin interface. Below is the pinout description:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground connection |
| 2 | VCC | Power supply (3.3V) |
| 3 | SCL | Serial Clock Line (SPI clock input) |
| 4 | SDA | Serial Data Line (SPI data input/output) |
| 5 | RES | Reset pin (active low, used to reset the display) |
| 6 | DC | Data/Command pin (high for data, low for command) |
| 7 | CS | Chip Select (active low, used to enable communication with the display module) |
| 8 | BLK | Backlight control (connect to 3.3V for constant backlight or PWM for dimming) |
Usage Instructions
Connecting the TFT Display 0.96" to an Arduino UNO
To use the TFT Display 0.96" with an Arduino UNO, follow these steps:
Wiring the Display: Connect the pins of the display to the Arduino as shown below:
- GND → GND
- VCC → 3.3V
- SCL → Pin 13 (SPI Clock)
- SDA → Pin 11 (SPI MOSI)
- RES → Pin 8
- DC → Pin 9
- CS → Pin 10
- BLK → 3.3V (or a PWM pin for brightness control)
Install Required Libraries: Install the
Adafruit_GFXandAdafruit_ST7735libraries in the Arduino IDE. These libraries provide functions for controlling the display.Upload Example Code: Use the following example code to display text and graphics on the screen:
#include <Adafruit_GFX.h> // Core graphics library
#include <Adafruit_ST7735.h> // Library for ST7735 driver
// Define pins for the TFT display
#define TFT_CS 10 // Chip Select pin
#define TFT_RST 8 // Reset pin
#define TFT_DC 9 // Data/Command pin
// Initialize the display object
Adafruit_ST7735 tft = Adafruit_ST7735(TFT_CS, TFT_DC, TFT_RST);
void setup() {
tft.initR(INITR_BLACKTAB); // Initialize the display with a specific tab color
tft.fillScreen(ST77XX_BLACK); // Clear the screen with black color
// Display some text
tft.setTextColor(ST77XX_WHITE); // Set text color to white
tft.setTextSize(1); // Set text size to 1 (smallest)
tft.setCursor(0, 0); // Set cursor to top-left corner
tft.println("Hello, TFT!"); // Print text to the display
// Draw a red rectangle
tft.fillRect(10, 20, 50, 30, ST77XX_RED); // x, y, width, height, color
}
void loop() {
// Nothing to do here
}
Important Considerations
- Voltage Levels: Ensure the display operates at 3.3V logic levels. If using a 5V microcontroller, use level shifters to avoid damaging the display.
- Backlight Control: For adjustable brightness, connect the BLK pin to a PWM-capable pin on the microcontroller.
- SPI Speed: Use an appropriate SPI clock speed (e.g., 4 MHz) to ensure stable communication.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Display Not Turning On:
- Check the power connections (VCC and GND).
- Ensure the backlight (BLK) pin is connected to 3.3V or a PWM pin.
No Output on the Screen:
- Verify the SPI connections (SCL, SDA, CS, DC).
- Ensure the
Adafruit_GFXandAdafruit_ST7735libraries are installed correctly. - Check the initialization code for the correct driver and tab color.
Flickering or Unstable Display:
- Reduce the SPI clock speed in the library settings.
- Ensure proper grounding between the display and the microcontroller.
Incorrect Colors or Artifacts:
- Verify the wiring of the DC and CS pins.
- Ensure the display is initialized with the correct tab color (e.g.,
INITR_BLACKTAB).
FAQs
Q: Can I use this display with a 5V microcontroller?
A: Yes, but you must use level shifters to convert the 5V logic signals to 3.3V to avoid damaging the display.
Q: How do I display images on the screen?
A: Use the Adafruit_GFX library's drawBitmap() function or convert images to a compatible format using tools like LCD Image Converter.
Q: Can I control the backlight brightness?
A: Yes, connect the BLK pin to a PWM-capable pin on your microcontroller and use PWM to adjust brightness.
Q: Is this display compatible with other microcontrollers?
A: Yes, it can be used with other microcontrollers like ESP32, STM32, or Raspberry Pi, provided they support SPI communication.