
How to Use Pimoroni PGA2350: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Pimoroni PGA2350 in Cirkit Designer
Design with Pimoroni PGA2350 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Pimoroni PGA2350 is a high-performance programmable gain amplifier (PGA) designed for precise control of signal amplification. It features a digital interface, enabling seamless integration with microcontrollers and other digital systems. The PGA2350 is particularly well-suited for audio applications, sensor signal conditioning, and other scenarios requiring fine-tuned signal amplification.
Explore Projects Built with Pimoroni PGA2350
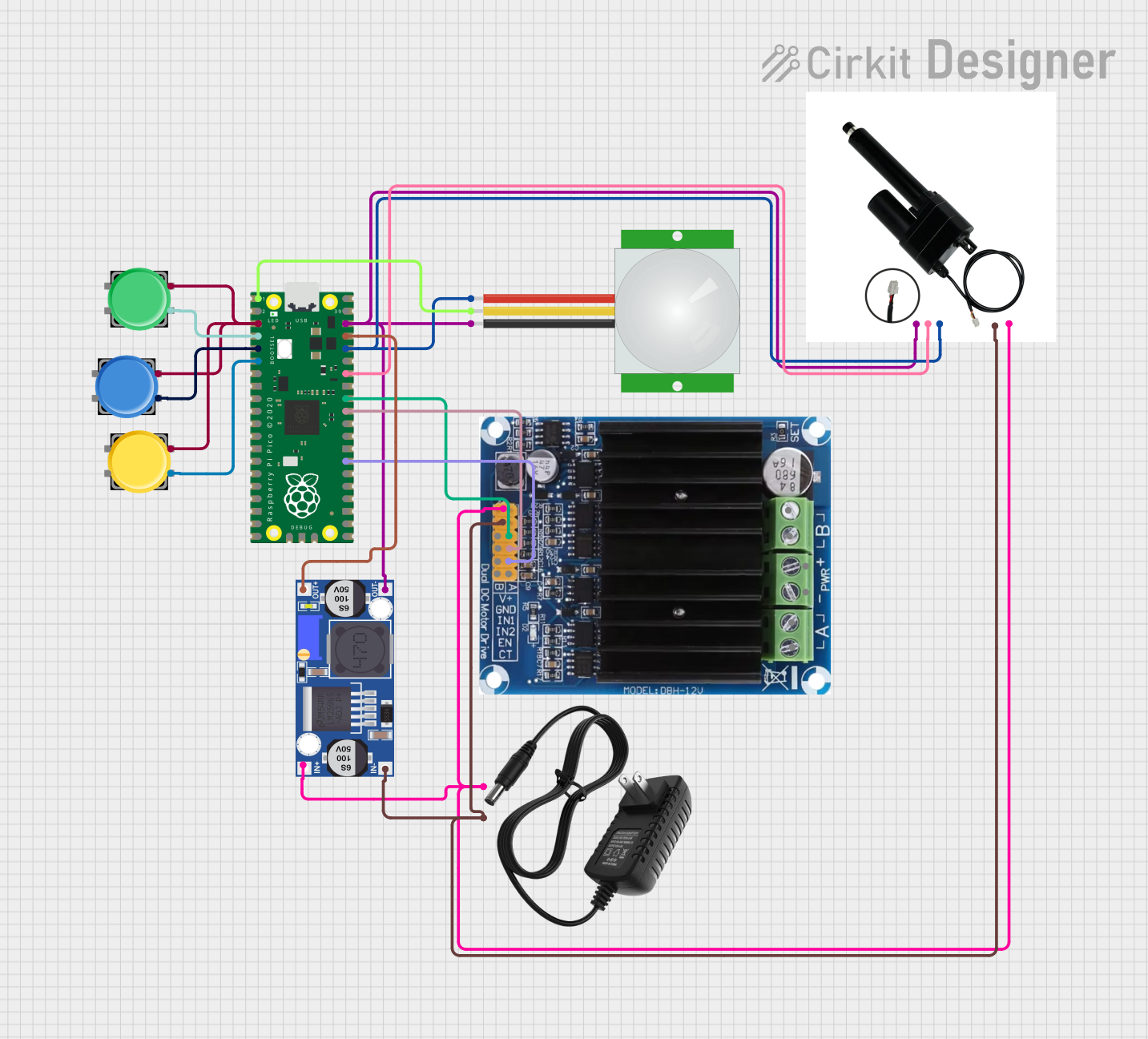
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer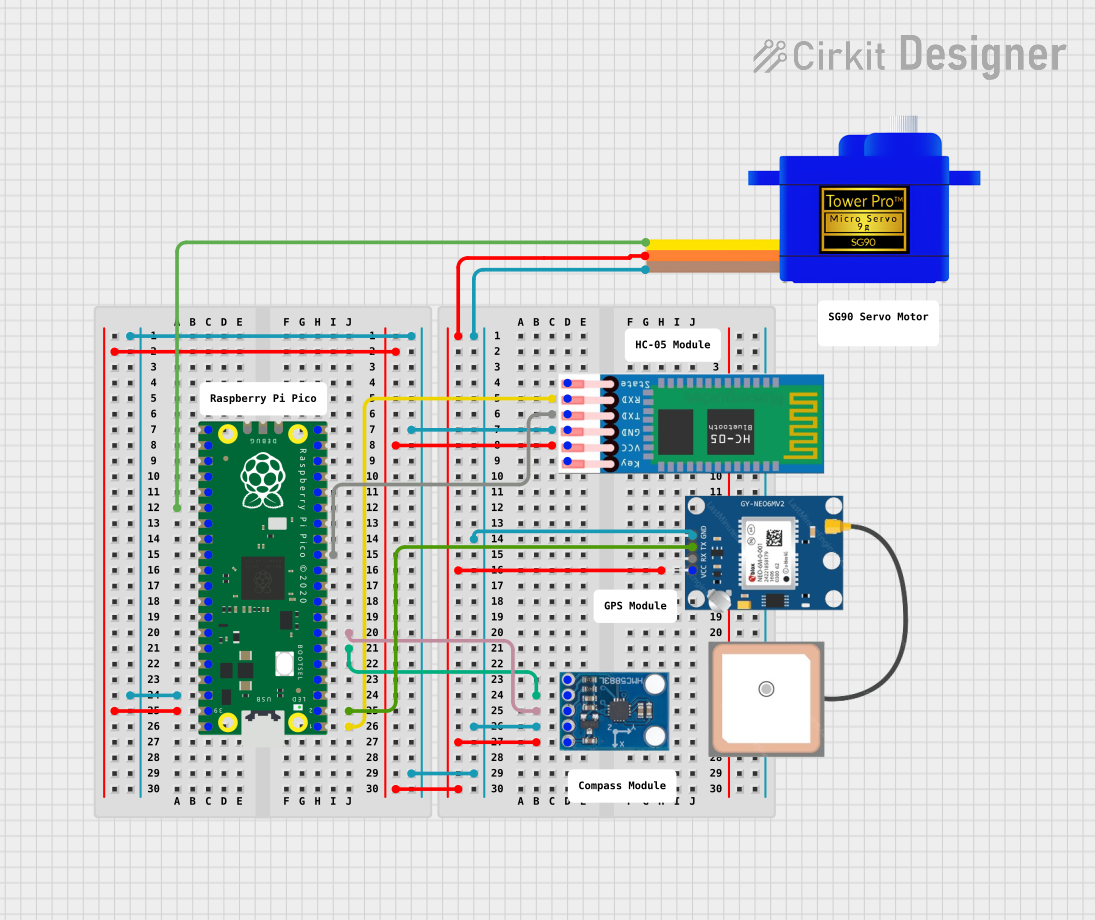
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer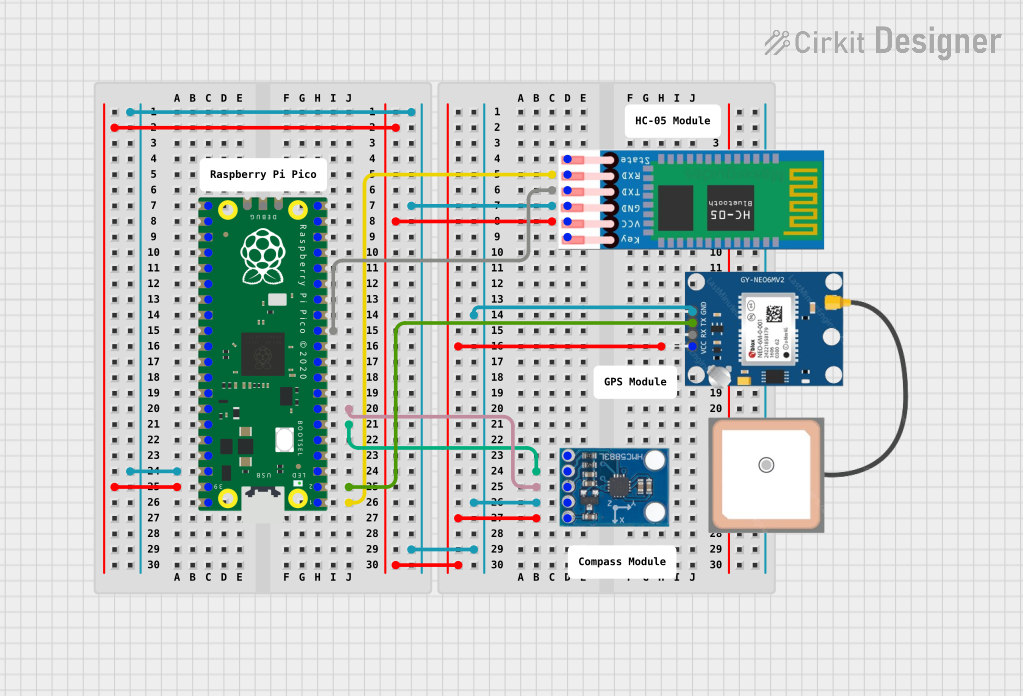
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer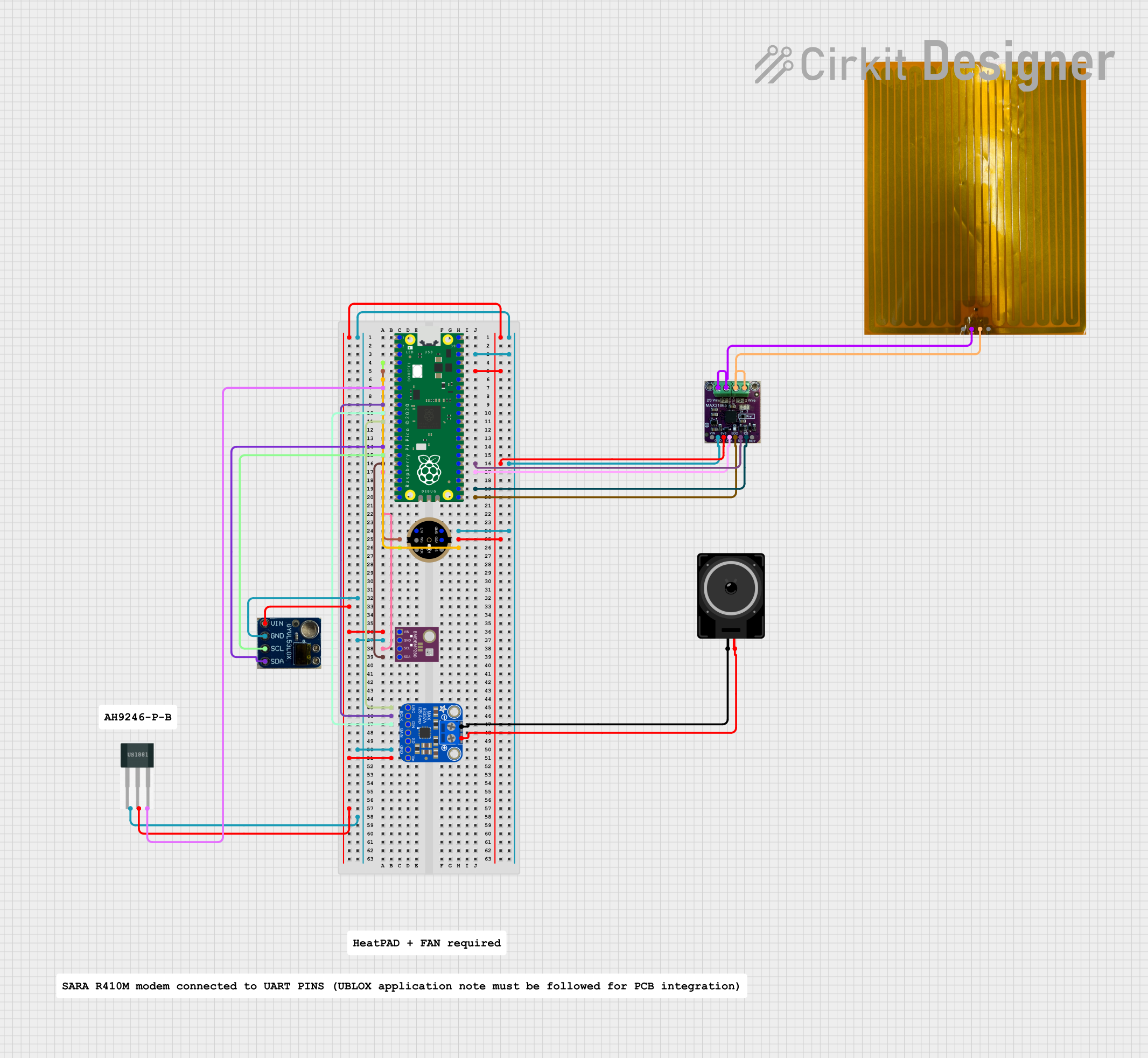
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Pimoroni PGA2350

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Audio signal processing and volume control
- Sensor signal conditioning for precise measurements
- Laboratory instrumentation and test equipment
- High-fidelity audio systems
- Industrial automation and control systems
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical specifications of the Pimoroni PGA2350:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Supply Voltage (VDD) | 4.5V to 5.5V |
| Gain Range | -95.5 dB to +31.5 dB (0.5 dB steps) |
| Control Interface | SPI |
| Input Impedance | 10 kΩ |
| Output Impedance | 100 Ω |
| Maximum Output Voltage | ±4.5V (at VDD = 5V) |
| Power Consumption | Low power operation |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Package Type | 16-pin SSOP |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Pimoroni PGA2350 is housed in a 16-pin SSOP package. The pinout and descriptions are as follows:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VDD | Positive power supply (4.5V to 5.5V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground |
| 3 | IN1 | Input signal channel 1 |
| 4 | IN2 | Input signal channel 2 |
| 5 | OUT1 | Output signal channel 1 |
| 6 | OUT2 | Output signal channel 2 |
| 7 | SCLK | SPI clock input |
| 8 | SDI | SPI data input |
| 9 | CS | Chip select (active low) |
| 10 | MUTE | Mute control (active high) |
| 11 | NC | No connection |
| 12 | NC | No connection |
| 13 | NC | No connection |
| 14 | NC | No connection |
| 15 | NC | No connection |
| 16 | NC | No connection |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the PGA2350 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VDD pin to a stable 5V power supply and the GND pin to ground.
- Input and Output: Connect the input signal to the IN1 and/or IN2 pins. The amplified output signal will be available at the OUT1 and/or OUT2 pins.
- SPI Communication: Use the SCLK, SDI, and CS pins to interface with a microcontroller via SPI. Ensure the SPI clock frequency is within the supported range.
- Gain Control: Configure the gain settings by sending appropriate commands over the SPI interface. The gain can be adjusted in 0.5 dB steps from -95.5 dB to +31.5 dB.
- Mute Function: Use the MUTE pin to mute the output signal when necessary. Drive the pin high to activate mute.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Decoupling Capacitors: Place decoupling capacitors (e.g., 0.1 µF and 10 µF) close to the VDD pin to ensure stable operation.
- Signal Integrity: Use short and shielded cables for input and output signals to minimize noise and interference.
- SPI Configuration: Ensure the microcontroller's SPI settings (clock polarity, phase, and speed) match the PGA2350's requirements.
- Thermal Management: Operate the device within the specified temperature range to avoid performance degradation.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control the PGA2350 using an Arduino UNO via SPI:
#include <SPI.h>
// Define SPI pins for the PGA2350
const int CS_PIN = 10; // Chip select pin
void setup() {
// Initialize SPI communication
SPI.begin();
pinMode(CS_PIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(CS_PIN, HIGH); // Set CS pin high (inactive)
// Configure SPI settings
SPI.beginTransaction(SPISettings(1000000, MSBFIRST, SPI_MODE0));
}
void setGain(float gain) {
// Convert gain to a 16-bit command
// Gain range: -95.5 dB to +31.5 dB in 0.5 dB steps
int gainSteps = (int)((gain + 95.5) * 2); // Convert gain to step value
byte highByte = (gainSteps >> 8) & 0xFF; // Extract high byte
byte lowByte = gainSteps & 0xFF; // Extract low byte
// Send the command to the PGA2350
digitalWrite(CS_PIN, LOW); // Activate chip select
SPI.transfer(highByte); // Send high byte
SPI.transfer(lowByte); // Send low byte
digitalWrite(CS_PIN, HIGH); // Deactivate chip select
}
void loop() {
// Example: Set gain to 0 dB
setGain(0.0);
delay(1000);
// Example: Set gain to -10 dB
setGain(-10.0);
delay(1000);
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Signal:
- Ensure the input signal is properly connected to the IN1/IN2 pins.
- Verify that the gain is set to an appropriate value via SPI.
- Check if the MUTE pin is accidentally activated (high).
Distorted Output:
- Ensure the input signal amplitude is within the acceptable range.
- Verify that the power supply voltage is stable and within the specified range.
SPI Communication Failure:
- Double-check the SPI wiring (SCLK, SDI, CS).
- Ensure the SPI clock frequency and settings match the PGA2350's requirements.
Excessive Noise:
- Use proper grounding and shielding techniques.
- Add decoupling capacitors near the power supply pins.
FAQs
Q: Can the PGA2350 be used with 3.3V microcontrollers?
A: Yes, but you will need level shifters for the SPI signals, as the PGA2350 operates at 5V logic levels.
Q: What is the maximum gain of the PGA2350?
A: The maximum gain is +31.5 dB, adjustable in 0.5 dB steps.
Q: How do I mute the output?
A: Drive the MUTE pin high to mute the output signal.