
How to Use AC MCB (Blue): Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with AC MCB (Blue) in Cirkit Designer
Design with AC MCB (Blue) in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
An AC Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) is a compact, electromechanical safety device designed to protect electrical circuits from damage caused by overloads or short circuits. It automatically disconnects the circuit when the current exceeds a predefined limit, ensuring the safety of wiring and connected devices. The blue color of the MCB often signifies a specific current rating or application, such as lighting circuits or specialized equipment.
Explore Projects Built with AC MCB (Blue)

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer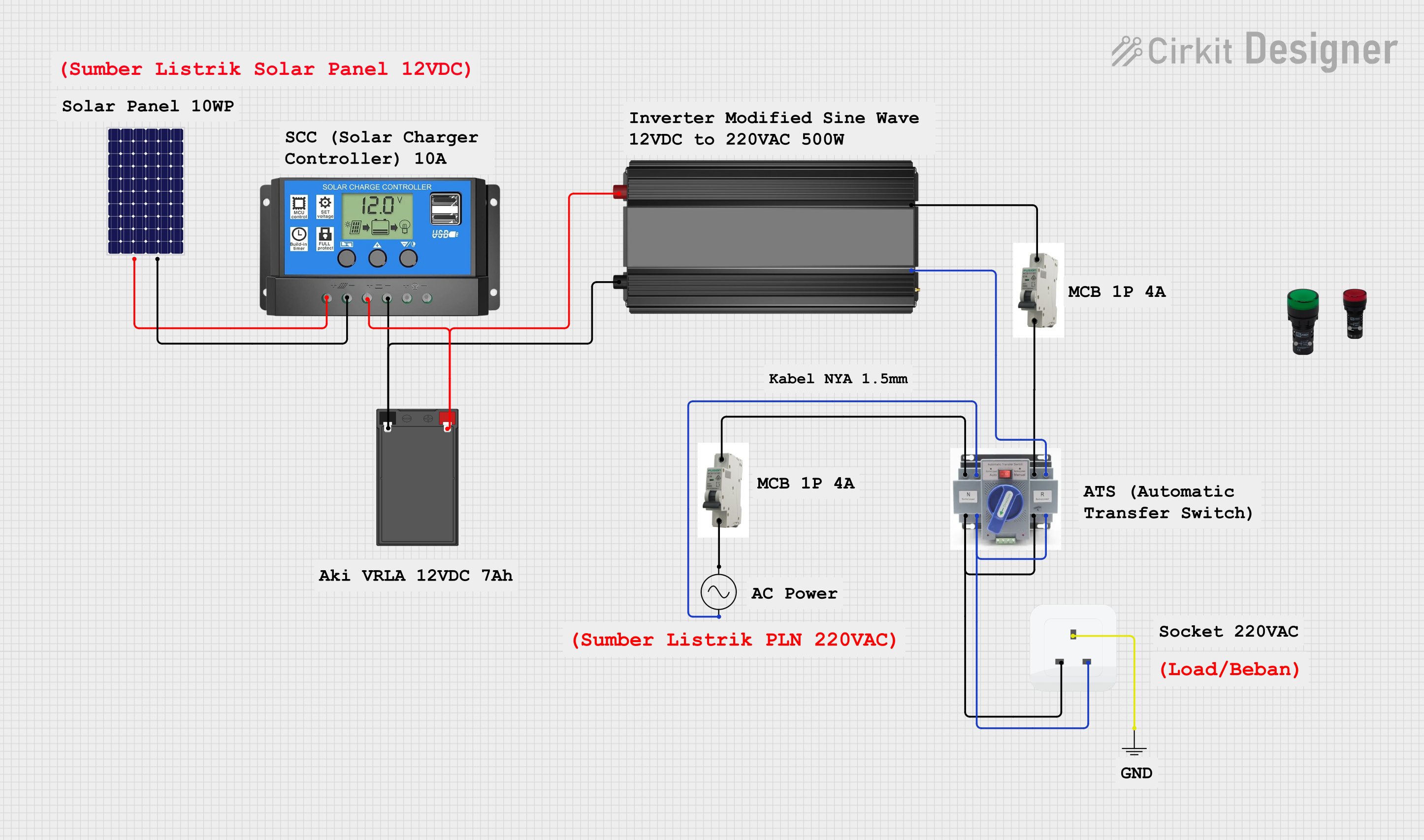
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer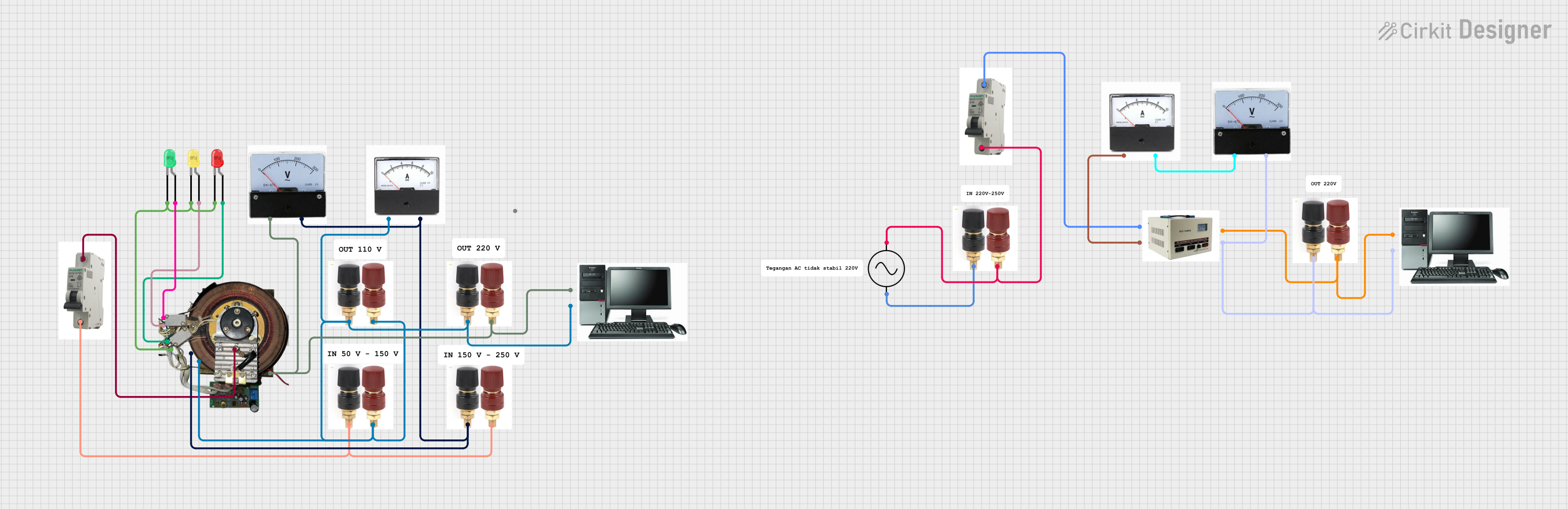
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with AC MCB (Blue)

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Residential and commercial electrical distribution systems
- Protection of lighting circuits and small appliances
- Industrial control panels and machinery
- Renewable energy systems (e.g., solar inverters)
- Motor protection in HVAC systems
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| Rated Voltage | 230V AC (Single-phase) or 400V AC (Three-phase) |
| Rated Current | Typically 6A, 10A, 16A, 20A, or 32A (varies by model) |
| Breaking Capacity | 6kA or 10kA (depending on the model) |
| Tripping Curve | Type B, C, or D (defines response to overload) |
| Frequency | 50/60 Hz |
| Operating Temperature | -5°C to +40°C |
| Mounting Type | DIN Rail (35mm standard) |
| Housing Material | Flame-retardant thermoplastic |
| Color Code (Blue) | Indicates specific current rating or application |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin/Terminal | Description |
|---|---|
| Line (L) | Input terminal for the live wire |
| Neutral (N) | Input terminal for the neutral wire |
| Load (L) | Output terminal for the live wire to the load |
| Load (N) | Output terminal for the neutral wire to the load |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Turn Off Power: Ensure the main power supply is turned off before installation.
- Mounting: Securely mount the MCB onto a standard 35mm DIN rail in the distribution box.
- Wiring:
- Connect the live wire from the power source to the
Line (L)terminal. - Connect the neutral wire from the power source to the
Neutral (N)terminal. - Connect the load wires to the corresponding
Load (L)andLoad (N)terminals.
- Connect the live wire from the power source to the
- Check Connections: Verify all connections are secure and properly tightened.
- Power On: Turn on the main power supply and switch the MCB to the "ON" position.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Current Rating: Always select an MCB with a current rating suitable for the connected load.
- Tripping Curve: Choose the appropriate tripping curve (B, C, or D) based on the application:
- Type B: For resistive loads (e.g., lighting).
- Type C: For inductive loads (e.g., motors).
- Type D: For high inrush current loads (e.g., transformers).
- Overload Protection: Ensure the MCB's breaking capacity matches or exceeds the maximum fault current of the circuit.
- Regular Maintenance: Periodically inspect the MCB for signs of wear, damage, or loose connections.
Arduino UNO Integration
While MCBs are not directly connected to microcontrollers like the Arduino UNO, they can be used in circuits that power Arduino-based systems. For example, an MCB can protect the power supply feeding an Arduino project.
Here is an example of Arduino code to monitor the status of an MCB using a current sensor:
/*
This code monitors the current in a circuit protected by an MCB.
If the current exceeds a threshold, it triggers an alert.
*/
const int currentSensorPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the current sensor
const float currentThreshold = 10.0; // Current threshold in amps
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
pinMode(currentSensorPin, INPUT); // Set the sensor pin as input
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(currentSensorPin); // Read sensor value
float current = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0); // Convert to current (example scaling)
Serial.print("Current: ");
Serial.print(current);
Serial.println(" A");
if (current > currentThreshold) {
Serial.println("Warning: Current exceeds threshold!");
// Add additional actions here, such as triggering a relay or alarm
}
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| MCB trips frequently | Overloaded circuit | Reduce the load or use a higher-rated MCB |
| MCB does not trip during a fault | Faulty MCB or incorrect wiring | Inspect wiring and replace the MCB if necessary |
| MCB does not turn on | Loose connections or damaged terminals | Check and tighten all connections |
| Burning smell or discoloration | Overheating due to loose connections | Turn off power and inspect connections |
FAQs
What does the blue color signify?
- The blue color typically indicates a specific current rating or application, such as lighting circuits.
Can I use an AC MCB for DC circuits?
- No, AC MCBs are designed for alternating current and may not function correctly in DC circuits. Use a DC-rated MCB for such applications.
How do I select the right MCB for my circuit?
- Consider the load's current rating, the type of load (resistive or inductive), and the maximum fault current of the circuit.
Can an MCB be reset after tripping?
- Yes, after addressing the cause of the trip, you can reset the MCB by switching it back to the "ON" position.
By following this documentation, users can safely and effectively integrate the AC MCB (Blue) into their electrical systems.