
How to Use INA260: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
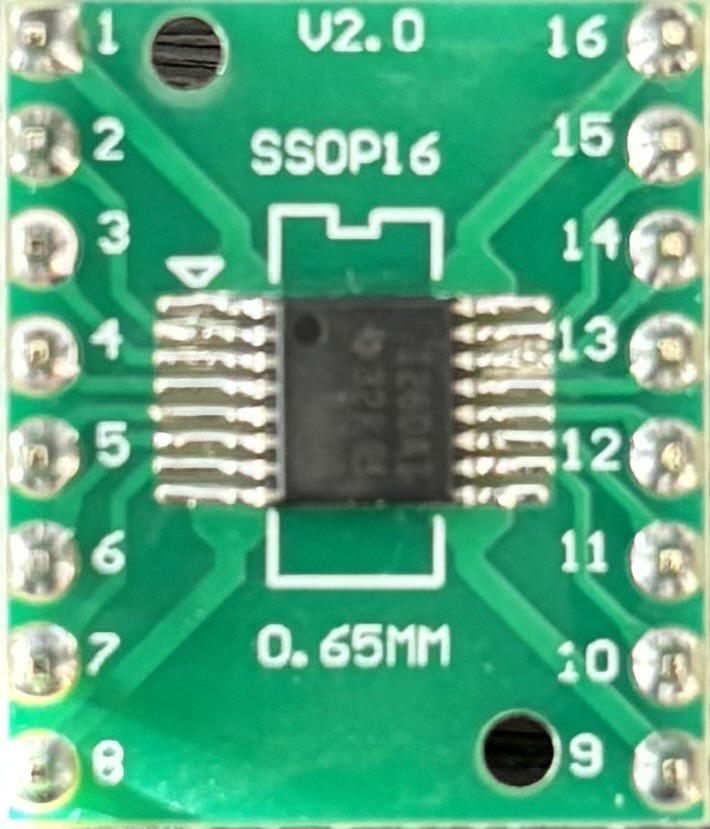
 Design with INA260 in Cirkit Designer
Design with INA260 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The INA260 is a high-side current shunt monitor with an integrated I2C interface, designed to measure voltage, current, and power in a single device. It features a built-in precision shunt resistor, eliminating the need for external components, and offers high accuracy and a wide input voltage range. These features make the INA260 ideal for power monitoring applications in industrial, automotive, and consumer electronics systems.
Explore Projects Built with INA260
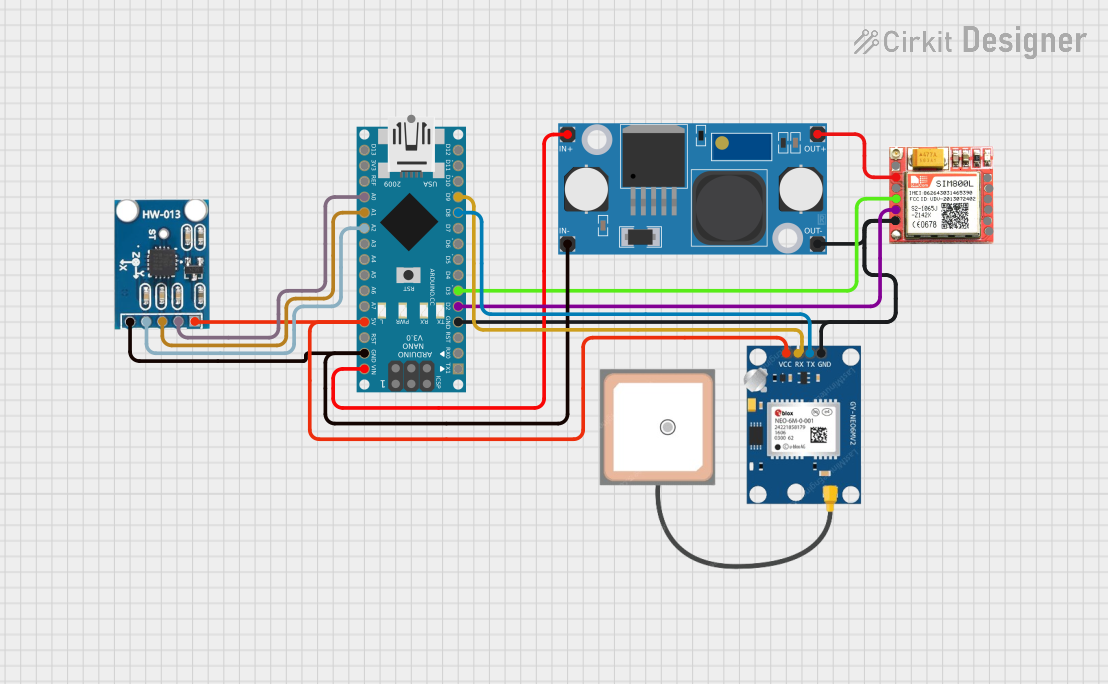
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer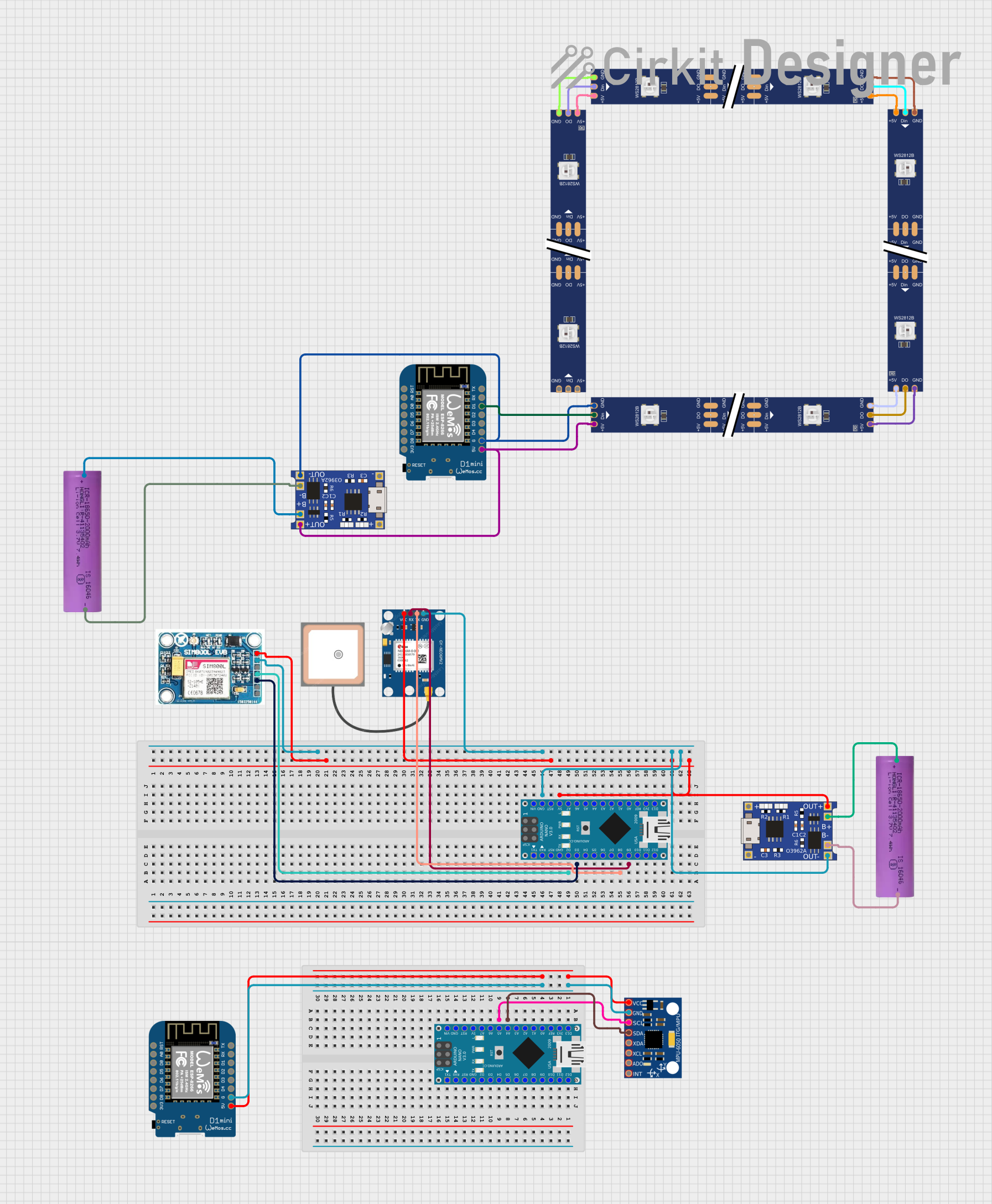
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer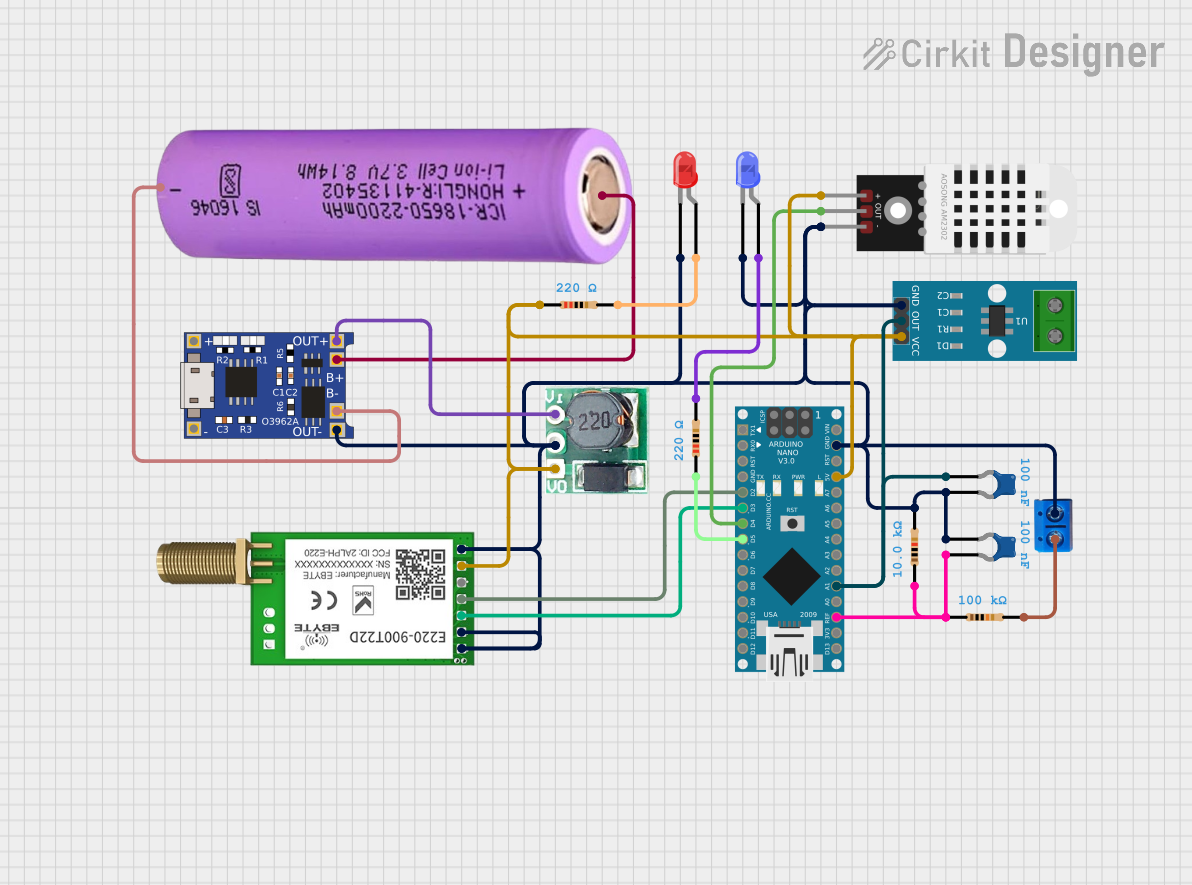
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with INA260

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Power monitoring in battery-operated devices
- Energy metering in industrial systems
- Current and voltage measurement in power supplies
- Monitoring power consumption in IoT devices
Technical Specifications
The INA260 is a versatile and precise device with the following key specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Supply Voltage (VCC) | 2.7V to 5.5V |
| Input Voltage Range | 0V to 36V |
| Current Measurement Range | ±15A |
| Power Measurement Range | 0W to 558W (at 36V, 15A) |
| Shunt Resistor Value | 2 mΩ (integrated) |
| Communication Interface | I2C (up to 1 MHz) |
| Accuracy | ±0.1% (typical) |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +125°C |
Pin Configuration
The INA260 is available in a 10-pin VSSOP package. The pinout and descriptions are as follows:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VIN+ | Positive input for differential voltage measurement. Connect to the load side. |
| 2 | VIN- | Negative input for differential voltage measurement. Connect to the supply side. |
| 3 | GND | Ground reference for the device. |
| 4 | SCL | I2C clock line. |
| 5 | SDA | I2C data line. |
| 6 | ALERT | Alert output pin for programmable threshold monitoring. |
| 7 | ADDR0 | I2C address selection pin 0. |
| 8 | ADDR1 | I2C address selection pin 1. |
| 9 | VCC | Power supply input (2.7V to 5.5V). |
| 10 | NC | No connection. Leave unconnected or grounded. |
Usage Instructions
Connecting the INA260
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a 3.3V or 5V power source, and the GND pin to the ground.
- Voltage and Current Measurement: Connect VIN+ to the load side and VIN- to the supply side of the circuit.
- I2C Communication: Connect the SCL and SDA pins to the corresponding I2C lines of your microcontroller. Use pull-up resistors (typically 4.7 kΩ) on these lines if not already present.
- Address Configuration: Use ADDR0 and ADDR1 pins to set the I2C address. These pins can be connected to GND, VCC, or left floating to select one of 16 possible addresses.
- Alert Pin: Optionally, connect the ALERT pin to a microcontroller GPIO for threshold-based alerts.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
The following example demonstrates how to use the INA260 with an Arduino UNO to measure voltage, current, and power:
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_INA260.h>
// Create an INA260 object
Adafruit_INA260 ina260;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial) {
delay(10); // Wait for Serial Monitor to open
}
// Initialize I2C communication and INA260
if (!ina260.begin()) {
Serial.println("Failed to find INA260 chip");
while (1) {
delay(10); // Halt if initialization fails
}
}
Serial.println("INA260 initialized successfully!");
}
void loop() {
// Read and print voltage, current, and power
float voltage = ina260.readBusVoltage(); // Voltage in volts
float current = ina260.readCurrent(); // Current in amps
float power = ina260.readPower(); // Power in watts
Serial.print("Voltage: ");
Serial.print(voltage);
Serial.println(" V");
Serial.print("Current: ");
Serial.print(current);
Serial.println(" A");
Serial.print("Power: ");
Serial.print(power);
Serial.println(" W");
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before the next reading
}
Best Practices
- Ensure proper decoupling by placing a 0.1 µF capacitor close to the VCC pin.
- Avoid exceeding the maximum input voltage (36V) or current (15A) to prevent damage.
- Use appropriate pull-up resistors on the I2C lines if not already present in your circuit.
- Configure the ALERT pin for overcurrent or undervoltage protection if needed.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
No Communication with the INA260
- Ensure the I2C address is correctly configured using ADDR0 and ADDR1 pins.
- Verify that pull-up resistors are present on the SDA and SCL lines.
- Check the wiring for loose or incorrect connections.
Incorrect Voltage or Current Readings
- Confirm that the input voltage does not exceed the specified range (0V to 36V).
- Ensure the load current is within the ±15A range.
- Verify that the VIN+ and VIN- pins are connected correctly.
Alert Pin Not Functioning
- Check the alert configuration in the INA260 registers.
- Ensure the microcontroller GPIO pin connected to ALERT is properly configured.
FAQs
Q: Can the INA260 measure negative currents?
A: Yes, the INA260 can measure bidirectional currents within the ±15A range.
Q: What is the resolution of the INA260?
A: The INA260 provides a resolution of 1.25 mA for current, 1.25 mV for voltage, and 31.25 mW for power.
Q: Can I use the INA260 with a 1.8V microcontroller?
A: The INA260 requires a supply voltage of 2.7V to 5.5V, but its I2C lines are 1.8V logic-compatible if proper pull-up resistors are used.
Q: How do I set the I2C address?
A: Use the ADDR0 and ADDR1 pins to select one of 16 possible I2C addresses. Refer to the datasheet for the address mapping.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the INA260 into your projects for accurate power monitoring and measurement.