
How to Use RGB: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
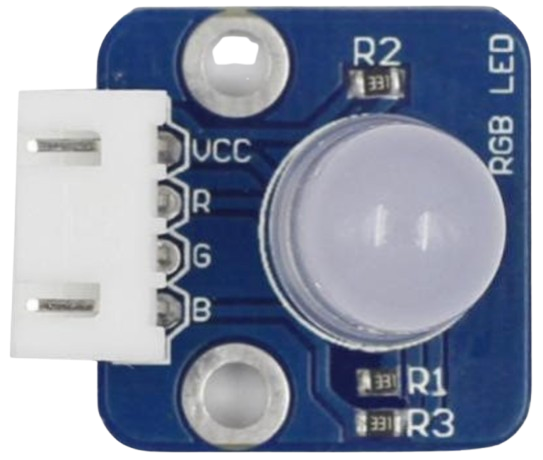
 Design with RGB in Cirkit Designer
Design with RGB in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
- An RGB LED is a light-emitting diode capable of producing a wide range of colors by combining the primary colors of light: Red, Green, and Blue. Each color is controlled by an individual LED within the component, and the intensity of each LED can be adjusted to create different colors.
- Common applications include decorative lighting, status indicators, display systems, and DIY electronics projects. RGB LEDs are widely used in Arduino and microcontroller-based projects for creating dynamic lighting effects.
Explore Projects Built with RGB
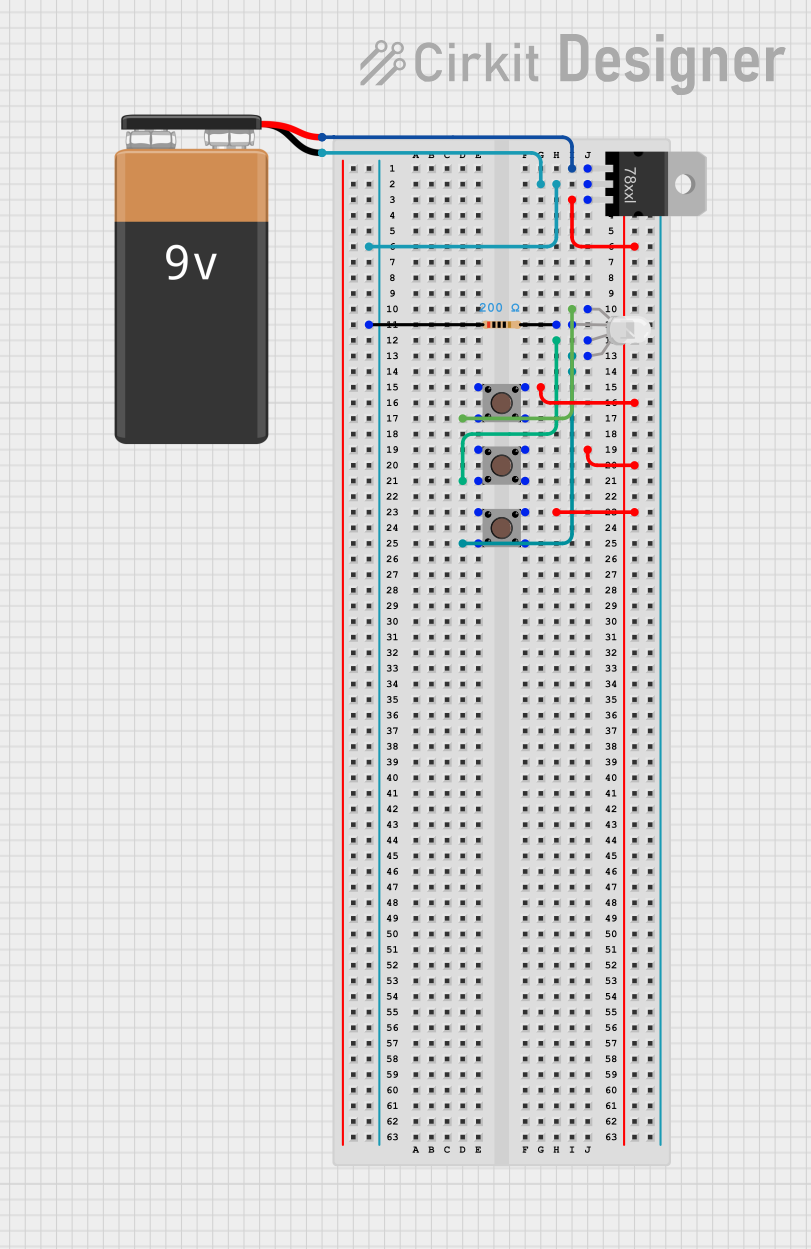
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer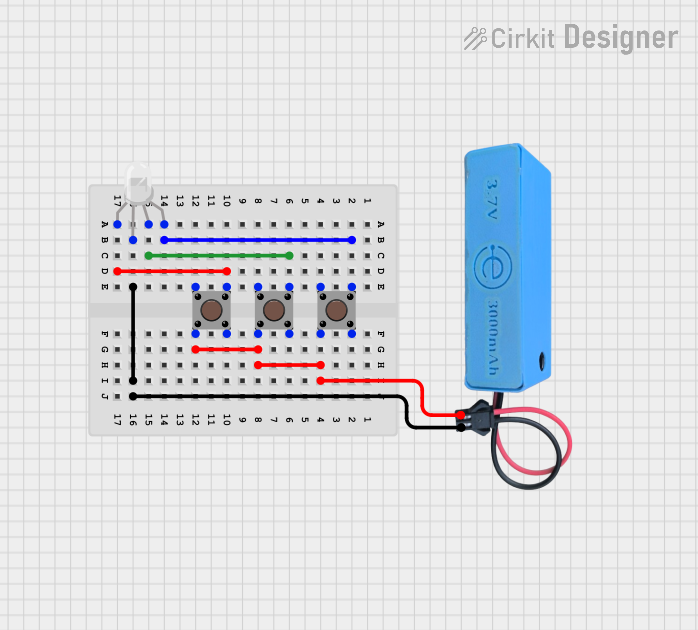
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer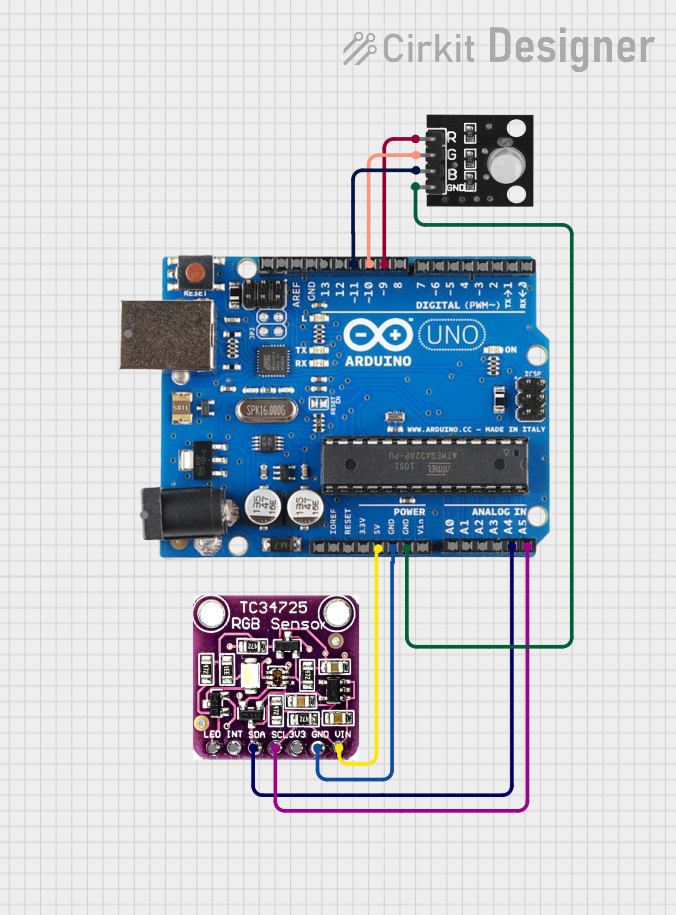
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer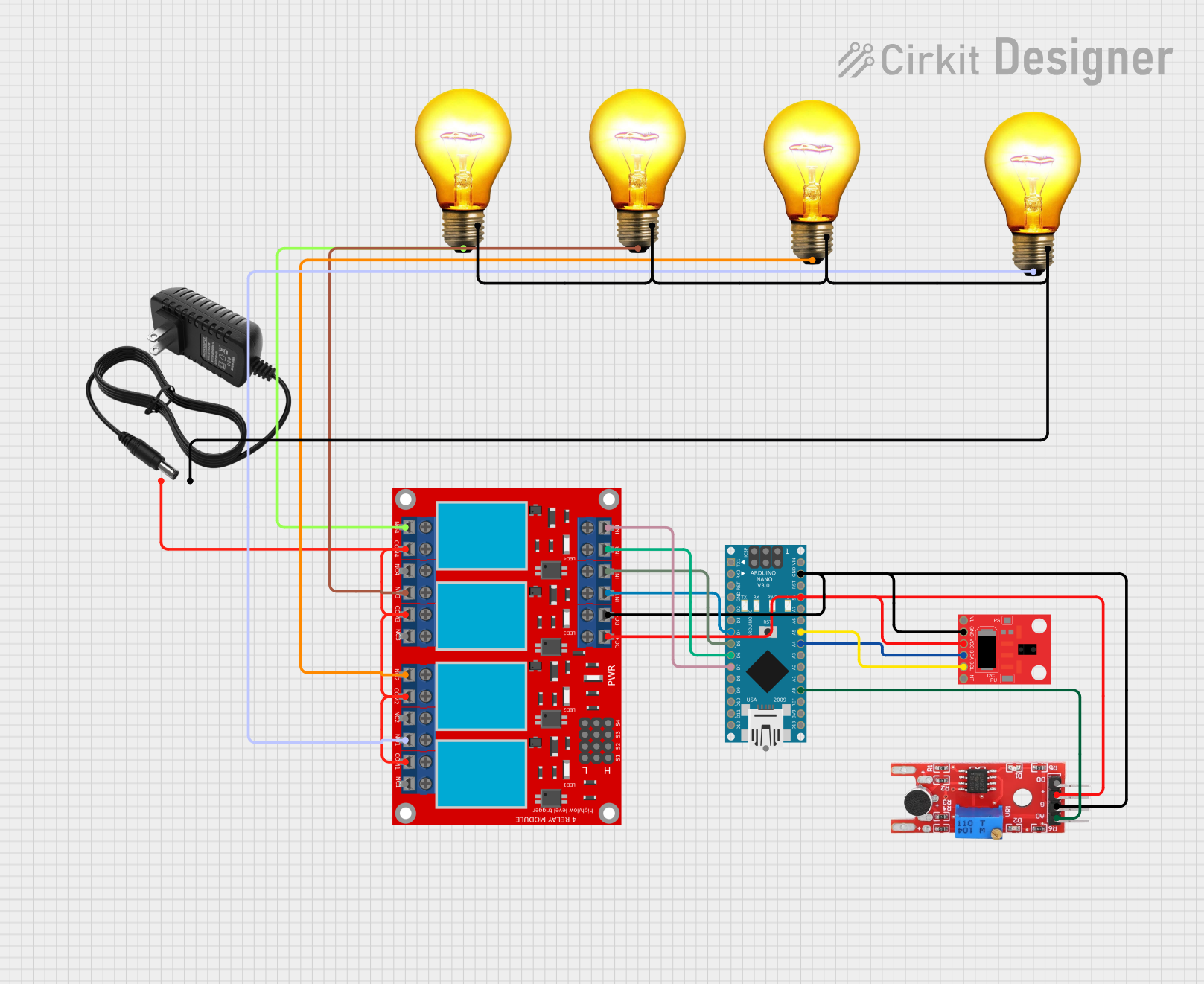
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with RGB

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
- Type: Common Cathode or Common Anode RGB LED
- Forward Voltage:
- Red: 1.8V - 2.2V
- Green: 3.0V - 3.2V
- Blue: 3.0V - 3.2V
- Forward Current: 20mA (per color channel)
- Power Dissipation: 60mW (maximum)
- Viewing Angle: Typically 120°
- Package: 4-pin through-hole or surface-mount
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The RGB LED typically has four pins. The configuration depends on whether it is a Common Cathode or Common Anode type.
| Pin Number | Common Cathode Description | Common Anode Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Red LED Cathode (-) | Red LED Anode (+) |
| 2 | Common Cathode (-) | Common Anode (+) |
| 3 | Green LED Cathode (-) | Green LED Anode (+) |
| 4 | Blue LED Cathode (-) | Blue LED Anode (+) |
Note: Always check the datasheet of your specific RGB LED to confirm the pinout.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the RGB LED in a Circuit
- Determine the Type: Identify whether your RGB LED is Common Cathode or Common Anode.
- For Common Cathode: Connect the common pin to ground (GND).
- For Common Anode: Connect the common pin to the positive voltage (VCC).
- Use Current-Limiting Resistors: To prevent damage, connect a resistor (typically 220Ω to 330Ω) in series with each color pin.
- Control the Colors: Use a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino) or a simple circuit with switches or potentiometers to adjust the intensity of each color.
Example Circuit with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect and control an RGB LED using an Arduino UNO.
Circuit Connections
- Connect the common pin of the RGB LED to GND (Common Cathode) or VCC (Common Anode).
- Connect the Red, Green, and Blue pins to Arduino digital PWM pins (e.g., D9, D10, D11) through 220Ω resistors.
Arduino Code Example
// Define the RGB LED pins
const int redPin = 9; // Red LED connected to pin 9
const int greenPin = 10; // Green LED connected to pin 10
const int bluePin = 11; // Blue LED connected to pin 11
void setup() {
// Set the RGB pins as output
pinMode(redPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(greenPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(bluePin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Example: Cycle through Red, Green, and Blue colors
setColor(255, 0, 0); // Red
delay(1000);
setColor(0, 255, 0); // Green
delay(1000);
setColor(0, 0, 255); // Blue
delay(1000);
setColor(255, 255, 0); // Yellow
delay(1000);
setColor(0, 255, 255); // Cyan
delay(1000);
setColor(255, 0, 255); // Magenta
delay(1000);
setColor(255, 255, 255); // White
delay(1000);
}
// Function to set the RGB LED color
void setColor(int redValue, int greenValue, int blueValue) {
analogWrite(redPin, redValue); // Set Red intensity
analogWrite(greenPin, greenValue); // Set Green intensity
analogWrite(bluePin, blueValue); // Set Blue intensity
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Resistor Selection: Always use appropriate resistors to limit current and prevent damage to the LEDs.
- Power Supply: Ensure the power supply voltage matches the requirements of the RGB LED.
- PWM Control: Use PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) to control the brightness of each color channel for smooth color transitions.
- Heat Management: Avoid exceeding the maximum current rating to prevent overheating.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
One or More Colors Not Lighting Up:
- Check the connections and ensure the pins are correctly wired.
- Verify that the resistors are not open or damaged.
- Confirm the RGB LED type (Common Cathode or Common Anode) and adjust the circuit accordingly.
Colors Are Dim or Incorrect:
- Ensure the resistors are of the correct value (220Ω to 330Ω is typical).
- Check the power supply voltage and ensure it meets the LED's requirements.
Flickering or Unstable Colors:
- Verify that the PWM signals are stable and not interrupted.
- Check for loose connections or poor soldering.
LED Not Working at All:
- Confirm the polarity of the connections (especially for Common Anode/Cathode types).
- Test the RGB LED with a multimeter or a simple circuit to ensure it is functional.
FAQs
Q: Can I use an RGB LED without a microcontroller?
A: Yes, you can use switches, potentiometers, or a simple circuit with resistors to control the colors manually.
Q: How do I create custom colors?
A: By adjusting the intensity of the Red, Green, and Blue channels using PWM, you can mix colors to create custom shades.
Q: What is the difference between Common Cathode and Common Anode RGB LEDs?
A: In a Common Cathode RGB LED, all cathodes are connected to GND, while in a Common Anode RGB LED, all anodes are connected to VCC.
Q: Can I connect an RGB LED directly to a power source?
A: No, you must use current-limiting resistors to prevent excessive current from damaging the LEDs.