
How to Use MAX1704X: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with MAX1704X in Cirkit Designer
Design with MAX1704X in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The MAX1704X voltage regulator is a compact, adjustable output voltage regulator designed for a wide range of electronic applications. Its ability to provide a stable output voltage makes it ideal for use in power supply circuits, battery-operated devices, and any application where a regulated voltage is required to ensure the proper operation of electronic components.
Explore Projects Built with MAX1704X

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer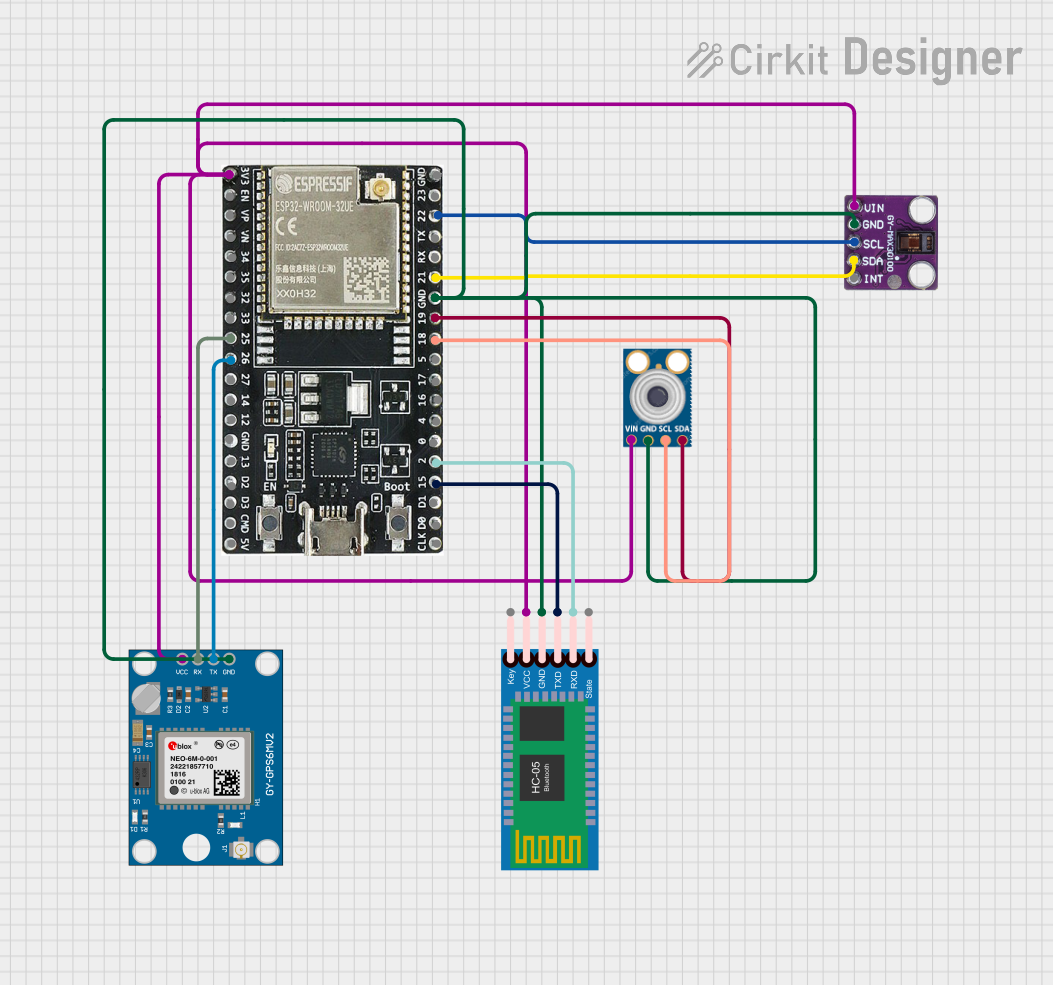
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer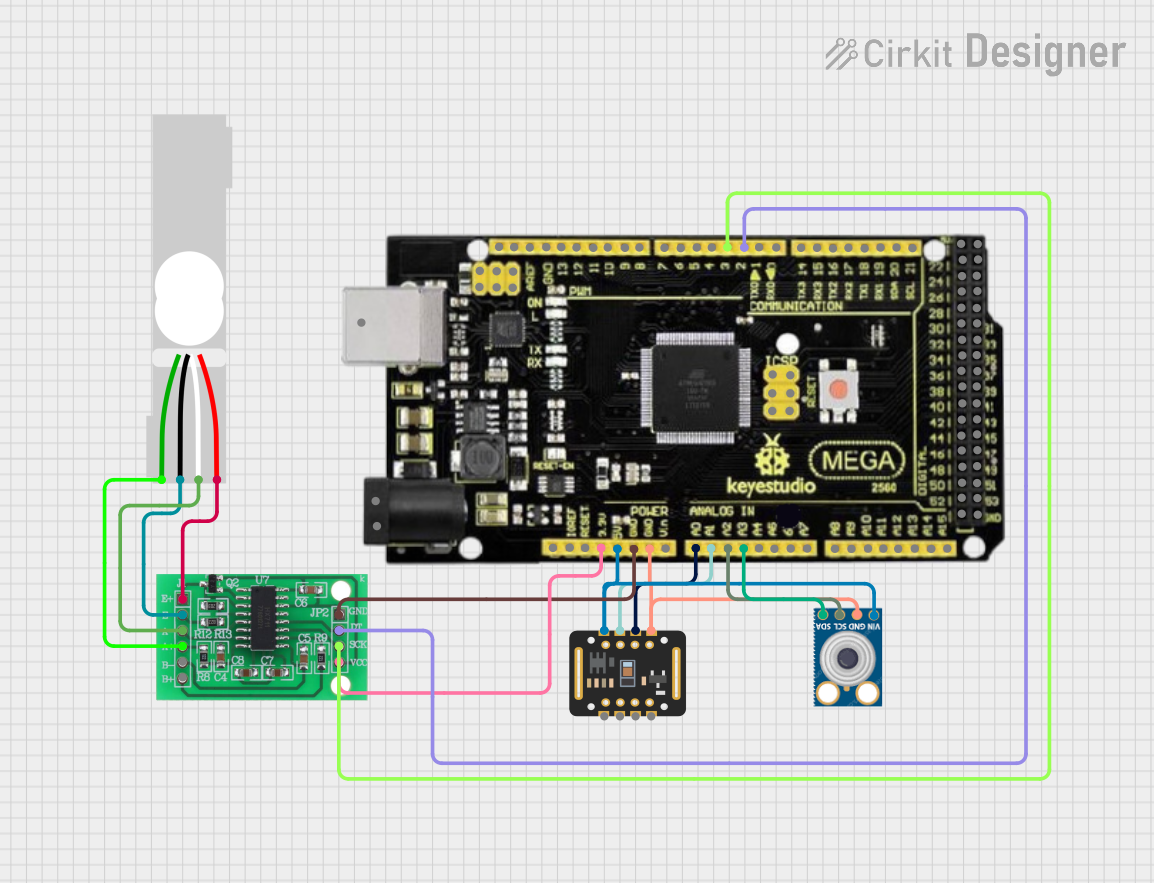
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer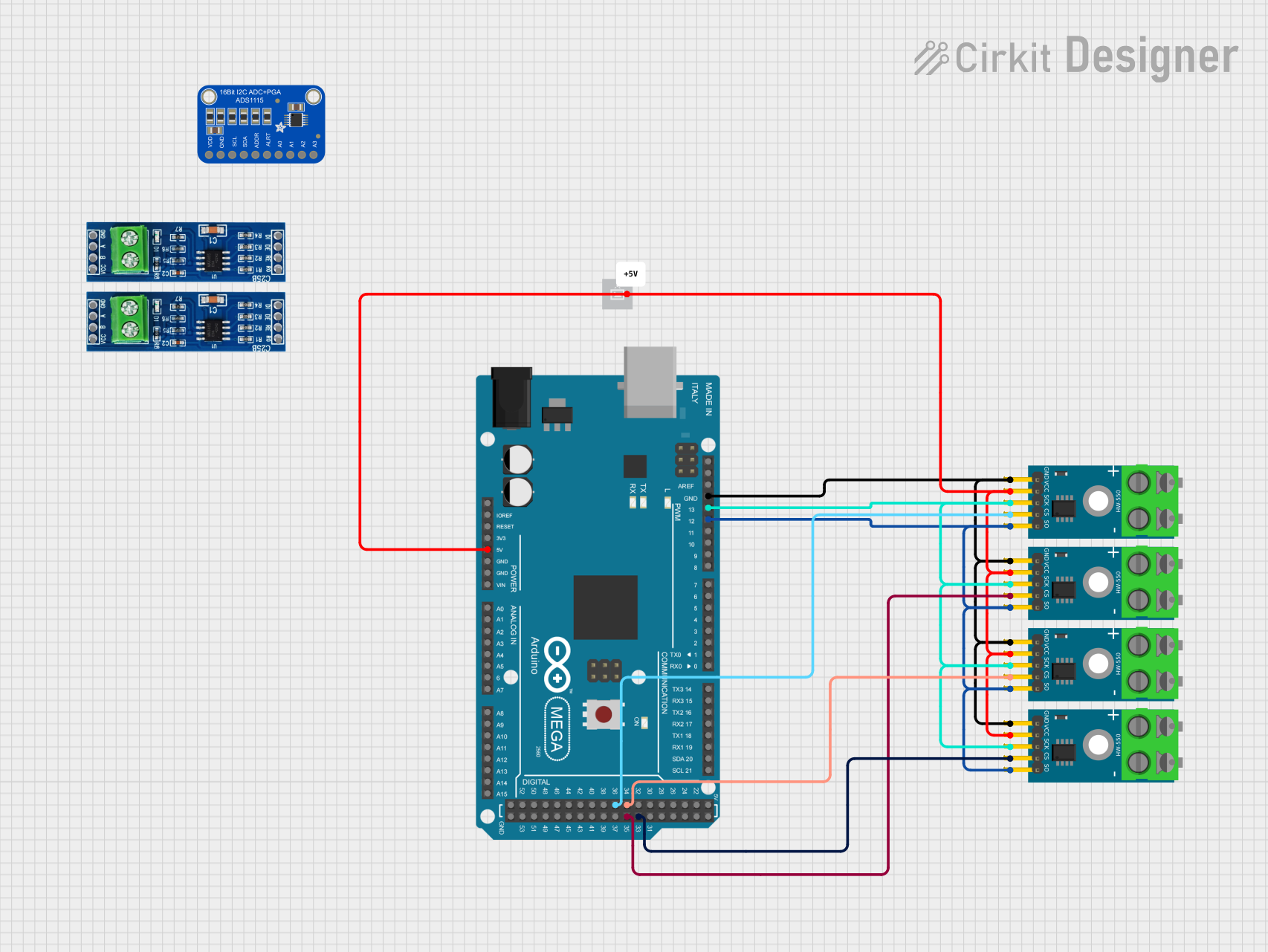
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with MAX1704X

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Power supplies for electronic devices
- Battery chargers and management systems
- Voltage regulation for microcontrollers and digital circuits
- Portable electronics requiring stable power supply
- Automotive electronics for regulating sensor and accessory voltages
Technical Specifications
The MAX1704X voltage regulator's technical specifications are crucial for ensuring compatibility and optimal performance in electronic circuits.
Key Technical Details
- Input Voltage Range: 4.5V to 28V
- Output Voltage Range: Adjustable from 1.25V to 27V
- Output Current: Up to 1.5A (with proper heat sinking)
- Quiescent Current: Typically 5mA
- Temperature Range: -40°C to +125°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | IN | Input voltage supply. Connect to the source voltage. |
| 2 | OUT | Regulated output voltage. Connect to the load. |
| 3 | ADJ | Adjustable pin to set the output voltage. Connect to a resistor divider network. |
| 4 | GND | Ground reference for the regulator. Connect to the system ground. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the MAX1704X in a Circuit
- Connect the Input Voltage: Apply the source voltage to the IN pin, ensuring it is within the specified input voltage range.
- Set the Output Voltage: Connect a resistor divider network between the OUT, ADJ, and GND pins to set the desired output voltage.
- Connect the Load: Attach the load to the OUT pin.
- Capacitors for Stability: Place a capacitor between the IN and GND pins and another between the OUT and GND pins to ensure stability and reduce noise.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Always verify that the input voltage does not exceed the maximum rating.
- Use capacitors with low equivalent series resistance (ESR) for better performance.
- Ensure that the output current does not exceed the maximum rating, considering thermal limitations.
- Provide adequate heat sinking if the regulator is expected to dissipate significant power.
- Avoid long wire runs between the regulator and the load to minimize voltage drops and noise.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Output Voltage Fluctuation: Ensure capacitors are correctly placed and are of the recommended value.
- Overheating: Check if the current draw is within the limit and improve heat sinking if necessary.
- No Output Voltage: Verify connections, input voltage, and the resistor divider network.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Double-check the wiring and solder joints for any shorts or opens.
- Measure the input voltage to ensure it is within the specified range.
- Use a multimeter to verify the resistor values in the divider network.
- If the regulator overheats, reduce the load current or improve heat dissipation.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the MAX1704X without an adjustable resistor network? A: Yes, but the output voltage will be fixed based on the internal reference voltage.
Q: What is the maximum power dissipation of the MAX1704X? A: The maximum power dissipation depends on the input voltage, output voltage, load current, and thermal resistance of the heat sink.
Q: How do I calculate the resistor values for a specific output voltage? A: Use the formula provided in the datasheet, typically involving the reference voltage and desired output voltage.
Example Connection with Arduino UNO
// No direct code is required for the MAX1704X as it is a hardware component.
// However, you can monitor the output voltage using an Arduino UNO by reading the voltage through an analog pin.
const int analogPin = A0; // Connect the OUT pin of MAX1704X to A0 on Arduino
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(analogPin); // Read the voltage
float voltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0); // Convert to voltage
Serial.println(voltage); // Print the voltage to the Serial Monitor
delay(1000); // Wait for a second
}
Note: The code above assumes that the output voltage of the MAX1704X is within the 0-5V range that the Arduino can measure. If the voltage is higher, a voltage divider network is required to bring the voltage within the Arduino's measurement range.