
How to Use MOSFET Drivkort 2-kan 50V 10A: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
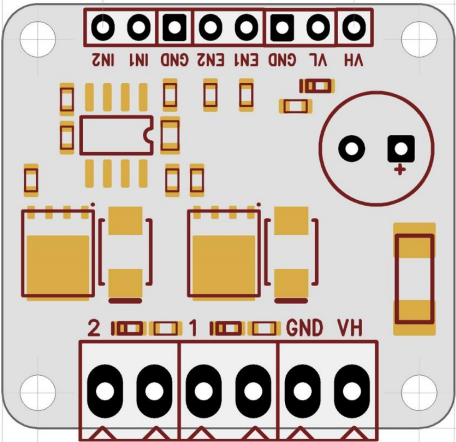
 Design with MOSFET Drivkort 2-kan 50V 10A in Cirkit Designer
Design with MOSFET Drivkort 2-kan 50V 10A in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The MOSFET Drivkort 2-kan 50V 10A (Manufacturer Part ID: EKM013 - UCC27524) is a dual-channel MOSFET driver circuit designed by Texas Instruments. It is capable of driving MOSFETs with a maximum voltage of 50V and a current rating of 10A. This component is optimized for high-speed switching applications, making it ideal for use in motor control, power supplies, and other high-efficiency systems.
Explore Projects Built with MOSFET Drivkort 2-kan 50V 10A
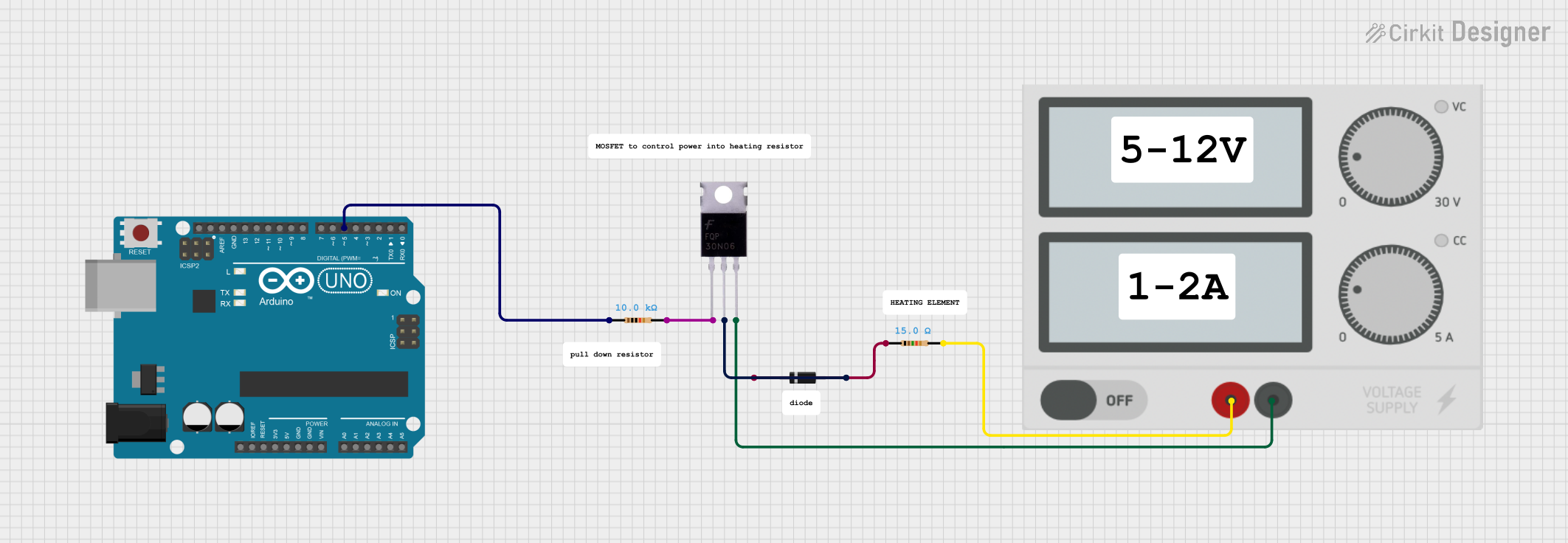
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer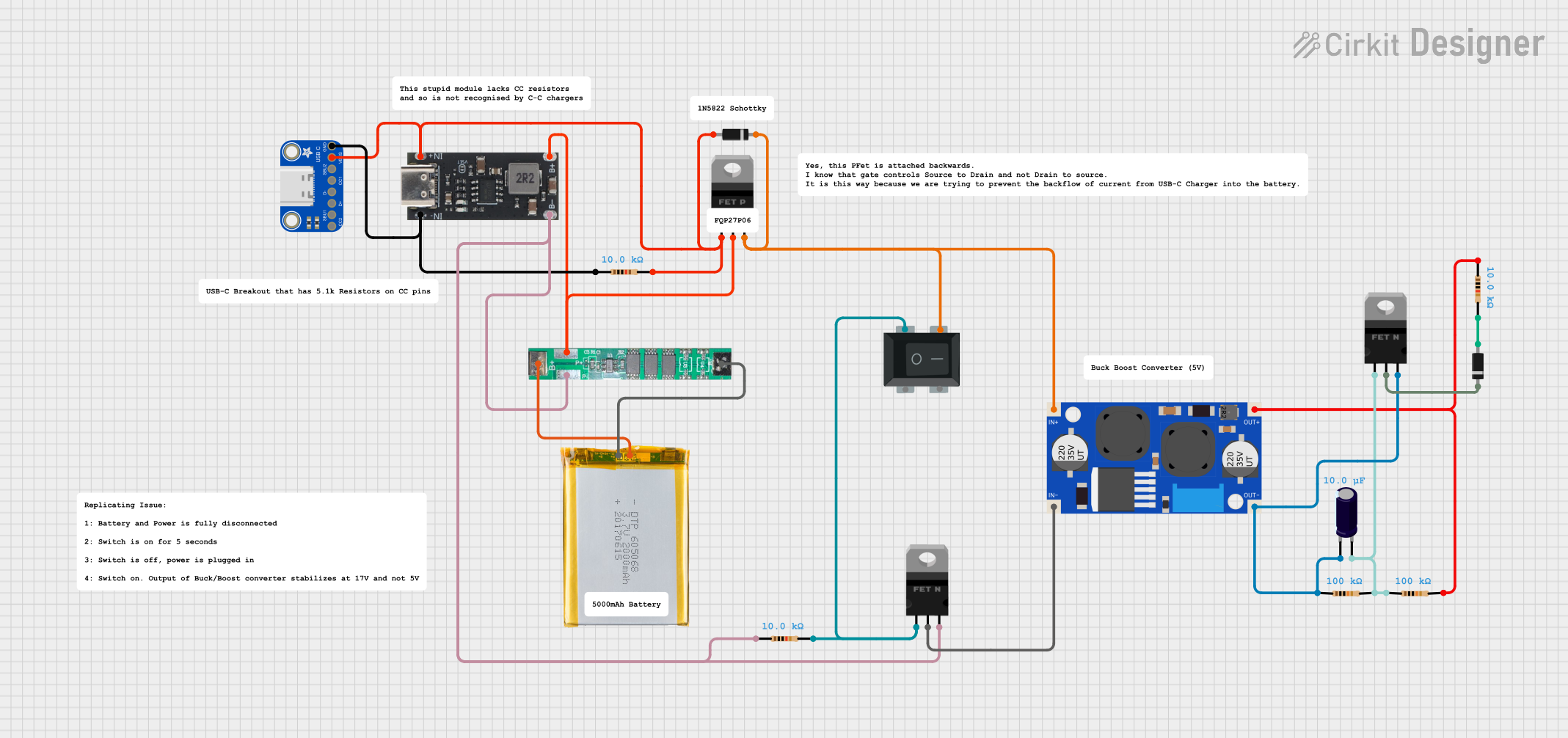
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer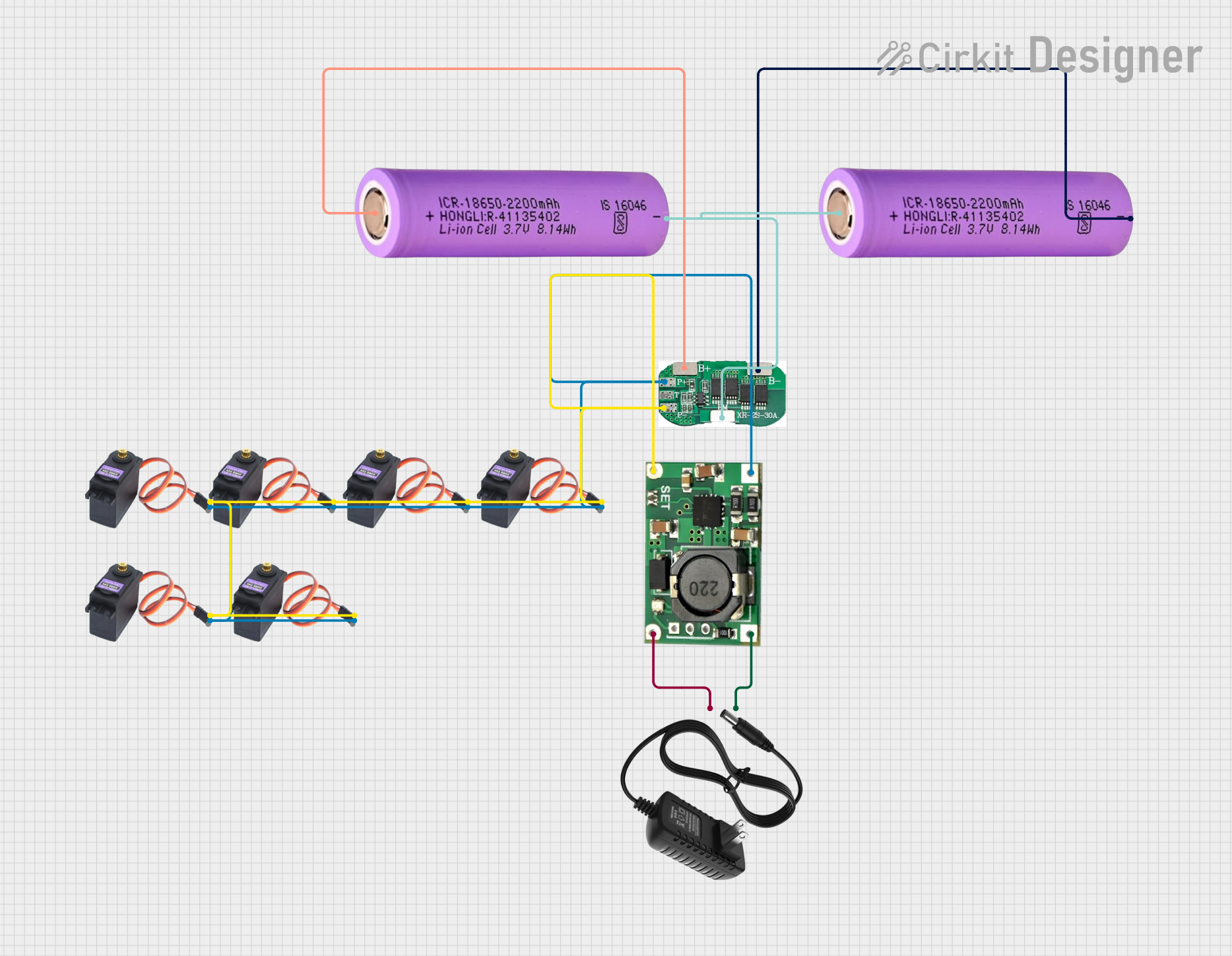
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer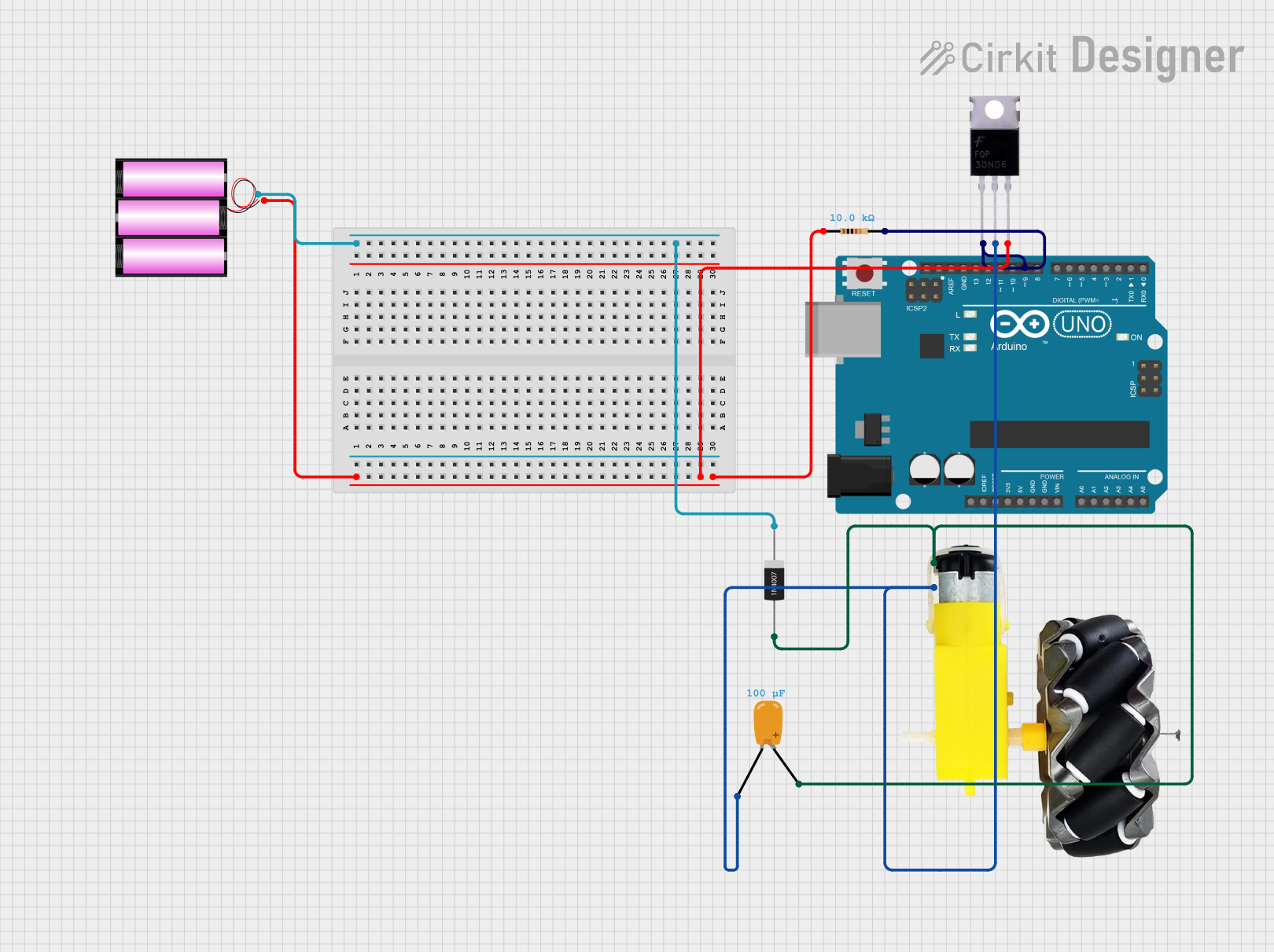
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with MOSFET Drivkort 2-kan 50V 10A

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Motor control systems
- DC-DC converters
- High-speed switching circuits
- Synchronous rectification
- Power inverters
- LED drivers
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical specifications of the MOSFET Drivkort 2-kan 50V 10A:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Supply Voltage (VDD) | 4.5V to 18V |
| Maximum Output Voltage | 50V |
| Maximum Output Current | 10A |
| Propagation Delay | 13 ns (typical) |
| Input Threshold Voltage | TTL/CMOS compatible |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +140°C |
| Channels | 2 |
| Package Type | SOIC-8 or VSON-8 |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The MOSFET Drivkort 2-kan 50V 10A has an 8-pin configuration. The table below describes each pin:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | IN1 | Input signal for Channel 1 (TTL/CMOS compatible) |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | IN2 | Input signal for Channel 2 (TTL/CMOS compatible) |
| 4 | VDD | Supply voltage (4.5V to 18V) |
| 5 | OUT2 | Output signal for Channel 2 (drives the MOSFET gate) |
| 6 | GND | Ground connection (shared with Pin 2) |
| 7 | OUT1 | Output signal for Channel 1 (drives the MOSFET gate) |
| 8 | NC | No connection (leave unconnected or use as a mechanical support point) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VDD pin to a stable power supply within the range of 4.5V to 18V. Ensure the ground (GND) is properly connected to the circuit's ground.
- Input Signals: Provide TTL/CMOS-compatible input signals to the IN1 and IN2 pins to control the two channels independently.
- Output Connections: Connect the OUT1 and OUT2 pins to the gates of the MOSFETs you wish to drive. Ensure the MOSFETs are rated for the desired voltage and current.
- Bypass Capacitor: Place a decoupling capacitor (e.g., 0.1 µF ceramic) close to the VDD pin to stabilize the power supply and reduce noise.
- Load Considerations: Ensure the load connected to the MOSFETs does not exceed the maximum current and voltage ratings of the driver.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Thermal Management: Ensure adequate cooling or heat dissipation for the MOSFETs and driver circuit, especially in high-power applications.
- Signal Integrity: Use short and low-inductance traces for the input and output connections to minimize noise and signal degradation.
- Dead Time: If used in a half-bridge or full-bridge configuration, ensure proper dead time between switching to prevent shoot-through currents.
- Protection: Add appropriate protection components (e.g., diodes, resistors) to safeguard the circuit from voltage spikes or transients.
Example: Using with Arduino UNO
The following example demonstrates how to control the MOSFET Drivkort 2-kan 50V 10A using an Arduino UNO to drive two MOSFETs.
// Define the input pins for the MOSFET driver
const int channel1 = 9; // PWM pin for Channel 1
const int channel2 = 10; // PWM pin for Channel 2
void setup() {
// Set the pins as outputs
pinMode(channel1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(channel2, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Example: Generate a PWM signal on Channel 1
analogWrite(channel1, 128); // 50% duty cycle (value range: 0-255)
// Example: Generate a PWM signal on Channel 2
analogWrite(channel2, 192); // 75% duty cycle (value range: 0-255)
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
// Turn off both channels
analogWrite(channel1, 0);
analogWrite(channel2, 0);
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Signal:
- Cause: Incorrect power supply or loose connections.
- Solution: Verify the VDD and GND connections. Ensure the supply voltage is within the specified range (4.5V to 18V).
MOSFET Overheating:
- Cause: Insufficient dead time or excessive load current.
- Solution: Add dead time in the control signals and ensure the load does not exceed the MOSFET's ratings.
High Noise or Instability:
- Cause: Poor PCB layout or lack of decoupling capacitors.
- Solution: Use short traces for high-speed signals and place a 0.1 µF capacitor close to the VDD pin.
Driver Not Responding to Input:
- Cause: Input signal not TTL/CMOS compatible.
- Solution: Verify the input signal levels and ensure they meet the driver's requirements.
FAQs
Q1: Can this driver be used for IGBTs instead of MOSFETs?
A1: Yes, the driver can be used for IGBTs as long as the voltage and current requirements are within the specified limits.
Q2: What is the maximum switching frequency supported?
A2: The driver supports high-speed switching with a typical propagation delay of 13 ns, making it suitable for frequencies up to several MHz.
Q3: Can I use this driver with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A3: Yes, the input pins are TTL/CMOS compatible and can accept signals as low as 3.3V.
Q4: Is it necessary to use both channels?
A4: No, you can use a single channel if your application only requires one MOSFET to be driven. Leave the unused channel's input unconnected or tied to GND.