
How to Use OLED SEEED 96×96 (SSD1327): Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
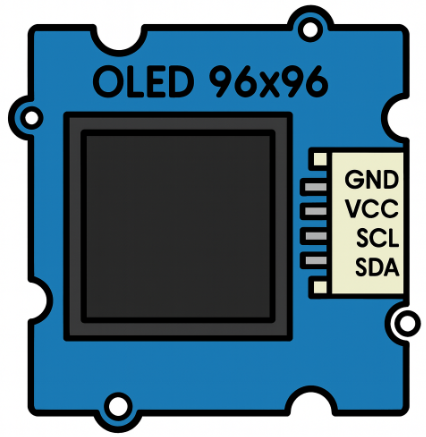
 Design with OLED SEEED 96×96 (SSD1327) in Cirkit Designer
Design with OLED SEEED 96×96 (SSD1327) in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The OLED SEEED 96×96 (SKU 104030011) is a compact, low-power OLED display module manufactured by SEEED. It features a resolution of 96x96 pixels and is driven by the SSD1327 controller. This display is ideal for applications requiring a small, high-contrast visual output, such as wearable devices, IoT projects, and embedded systems.
Explore Projects Built with OLED SEEED 96×96 (SSD1327)

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with OLED SEEED 96×96 (SSD1327)

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Wearable devices and smart gadgets
- IoT dashboards and status indicators
- Compact user interfaces for embedded systems
- Graphical data visualization in portable devices
- Educational and hobbyist electronics projects
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the OLED SEEED 96×96 display:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | SEEED |
| Manufacturer Part ID | SKU 104030011 |
| Display Type | OLED |
| Resolution | 96x96 pixels |
| Controller | SSD1327 |
| Interface | I2C |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V to 5V |
| Operating Current | ~10mA (typical) |
| Dimensions | 26.7mm x 26.7mm |
| Pixel Color Depth | 4-bit grayscale (16 levels) |
| Viewing Angle | >160° |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The OLED SEEED 96×96 module has a 4-pin interface for I2C communication. The pinout is as follows:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground connection |
| 2 | VCC | Power supply (3.3V to 5V) |
| 3 | SCL | I2C clock line |
| 4 | SDA | I2C data line |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the
VCCpin to a 3.3V or 5V power source and theGNDpin to ground. - I2C Communication: Connect the
SCLandSDApins to the corresponding I2C pins on your microcontroller. For an Arduino UNO:SCLconnects to A5.SDAconnects to A4.
- Pull-Up Resistors: Ensure that the I2C lines (SCL and SDA) have pull-up resistors (typically 4.7kΩ to 10kΩ) if not already present on the module.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Compatibility: Ensure the microcontroller's I2C pins are compatible with the display's voltage levels (3.3V or 5V).
- I2C Address: The default I2C address of the SSD1327 controller is
0x3D. Verify this in your code or datasheet. - Initialization: Properly initialize the SSD1327 controller in your code before sending data to the display.
- Grayscale Rendering: The display supports 4-bit grayscale, allowing for 16 levels of brightness per pixel.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the OLED SEEED 96×96 display with an Arduino UNO. This code uses the Adafruit SSD1327 library.
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_GFX.h>
#include <Adafruit_SSD1327.h>
// Define the I2C address for the SSD1327 display
#define SCREEN_ADDRESS 0x3D
// Create an instance of the SSD1327 display
Adafruit_SSD1327 display(96, 96, &Wire);
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Initializing OLED...");
// Initialize the display
if (!display.begin(SSD1327_I2C_ADDRESS, SCREEN_ADDRESS)) {
Serial.println("SSD1327 initialization failed!");
while (1); // Halt execution if initialization fails
}
// Clear the display buffer
display.clearDisplay();
// Display a welcome message
display.setTextSize(1); // Set text size to 1
display.setTextColor(SSD1327_WHITE); // Set text color to white
display.setCursor(0, 0); // Set cursor to top-left corner
display.println("SEEED OLED 96x96");
display.println("SSD1327 Example");
display.display(); // Update the display with the buffer content
delay(2000); // Wait for 2 seconds
}
void loop() {
// Clear the display buffer
display.clearDisplay();
// Draw a rectangle
display.drawRect(10, 10, 76, 76, SSD1327_WHITE);
// Draw a filled circle
display.fillCircle(48, 48, 20, SSD1327_WHITE);
// Update the display with the buffer content
display.display();
// Wait for 1 second before refreshing
delay(1000);
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Display Not Turning On:
- Verify the power supply connections (
VCCandGND). - Ensure the I2C address in the code matches the display's default address (
0x3D).
- Verify the power supply connections (
No Output on the Display:
- Check the I2C connections (
SCLandSDA) and ensure they are correctly wired. - Confirm that pull-up resistors are present on the I2C lines.
- Check the I2C connections (
Flickering or Unstable Display:
- Ensure a stable power supply with sufficient current capacity.
- Check for loose or poor-quality connections.
Grayscale Rendering Issues:
- Ensure the library and code properly support 4-bit grayscale rendering.
FAQs
Q: Can I use this display with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, the OLED SEEED 96×96 is compatible with both 3.3V and 5V systems.
Q: What is the maximum frame rate of the display?
A: The SSD1327 controller supports a frame rate of up to 100Hz, depending on the configuration.
Q: Does the display require an external backlight?
A: No, OLED displays are self-emissive and do not require a backlight.
Q: Can I use this display with platforms other than Arduino?
A: Yes, the display can be used with any platform that supports I2C communication, such as Raspberry Pi, ESP32, and STM32.
Q: How do I change the I2C address of the display?
A: The I2C address is fixed at 0x3D for this module and cannot be changed.