
How to Use USB 2.0 Female Module: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
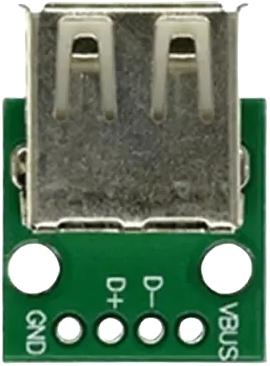
 Design with USB 2.0 Female Module in Cirkit Designer
Design with USB 2.0 Female Module in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The USB 2.0 Female Module is a connector designed to interface USB devices with electronic circuits. It facilitates both data transfer and power supply, making it an essential component in projects involving USB peripherals such as flash drives, keyboards, mice, and other USB-enabled devices. This module is widely used in prototyping, embedded systems, and DIY electronics projects.
Explore Projects Built with USB 2.0 Female Module
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with USB 2.0 Female Module

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Connecting USB devices to microcontrollers or development boards (e.g., Arduino, Raspberry Pi).
- Powering circuits via USB power (5V).
- Enabling data communication between USB devices and custom circuits.
- USB-based charging circuits for small devices.
Technical Specifications
The USB 2.0 Female Module adheres to the USB 2.0 standard, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of USB devices. Below are the key technical details:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Voltage Rating | 5V DC (standard USB power supply) |
| Current Rating | Up to 500mA (standard USB 2.0) |
| Data Transfer Rate | Up to 480 Mbps (USB 2.0 High Speed) |
| Connector Type | USB Type-A Female |
| Dimensions | Varies by module, typically compact |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to 70°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The USB 2.0 Female Module typically has four pins, as described in the table below:
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply pin (5V DC) |
| 2 | D- | Data line for differential signaling (negative) |
| 3 | D+ | Data line for differential signaling (positive) |
| 4 | GND | Ground connection |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the USB 2.0 Female Module in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a 5V power source and the GND pin to the circuit ground. This will provide power to the USB device connected to the module.
- Data Communication: Connect the D+ and D- pins to the corresponding data pins of your microcontroller or USB interface IC. Ensure proper impedance matching for reliable data transfer.
- Mounting: Secure the module to your PCB or breadboard using soldering or connectors, depending on the module design.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Regulation: Ensure that the connected circuit does not exceed the 5V and 500mA limits of the USB 2.0 standard.
- Data Line Protection: Use pull-up or pull-down resistors on the D+ and D- lines as required by your microcontroller or USB interface IC.
- ESD Protection: Consider adding ESD protection diodes to the data lines to safeguard against electrostatic discharge.
- Cable Length: Keep USB cable lengths within the USB 2.0 specification (maximum 5 meters) to maintain signal integrity.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
The USB 2.0 Female Module can be used to interface USB devices with an Arduino UNO. Below is an example of how to connect the module and read data from a USB device.
Circuit Connections
- Connect the module's VCC pin to the Arduino's 5V pin.
- Connect the module's GND pin to the Arduino's GND pin.
- Connect the D+ and D- pins to the appropriate data pins on a USB-to-serial converter IC (e.g., FT232) or a USB host shield.
Sample Code
If using a USB host shield with the Arduino UNO, you can use the USB_Host_Shield_Library to communicate with USB devices. Below is an example sketch:
#include <Usb.h>
#include <usbhub.h>
// Initialize USB host object
USB Usb;
USBHub Hub(&Usb);
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Start serial communication at 9600 baud
if (Usb.Init() == -1) {
Serial.println("USB initialization failed. Check connections.");
while (1); // Halt execution if initialization fails
}
Serial.println("USB initialized successfully.");
}
void loop() {
Usb.Task(); // Process USB tasks
// Add code here to interact with connected USB devices
}
Note: The above code requires the USB Host Shield and its associated library. Ensure the library is installed in your Arduino IDE.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
USB Device Not Recognized
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient power supply.
- Solution: Double-check the connections and ensure the power supply provides 5V and sufficient current.
Data Transfer Errors
- Cause: Poor signal integrity or incorrect pull-up/pull-down resistors.
- Solution: Verify the D+ and D- connections and add appropriate resistors as specified by your microcontroller or USB IC datasheet.
Overheating
- Cause: Excessive current draw from the USB device.
- Solution: Ensure the connected device does not exceed the 500mA current limit of USB 2.0.
FAQs
Q: Can this module be used with USB 3.0 devices?
A: Yes, USB 3.0 devices are backward compatible with USB 2.0, but the data transfer rate will be limited to USB 2.0 speeds (480 Mbps).Q: Can I use this module to charge devices?
A: Yes, the module can supply 5V power to charge devices, but ensure the current draw does not exceed 500mA.Q: Do I need additional components to use this module with an Arduino?
A: If you are only using the module for power, no additional components are needed. For data communication, you may need a USB host shield or USB-to-serial converter IC.