
How to Use Servo Motor (SG90): Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Servo Motor (SG90) in Cirkit Designer
Design with Servo Motor (SG90) in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The SG90 Servo Motor is a small, lightweight, and inexpensive servo motor commonly used in hobbyist projects for precise control of angular position. It is widely popular in robotics, RC (Radio Control) vehicles, and various DIY electronics projects due to its ease of use and affordability.
Explore Projects Built with Servo Motor (SG90)
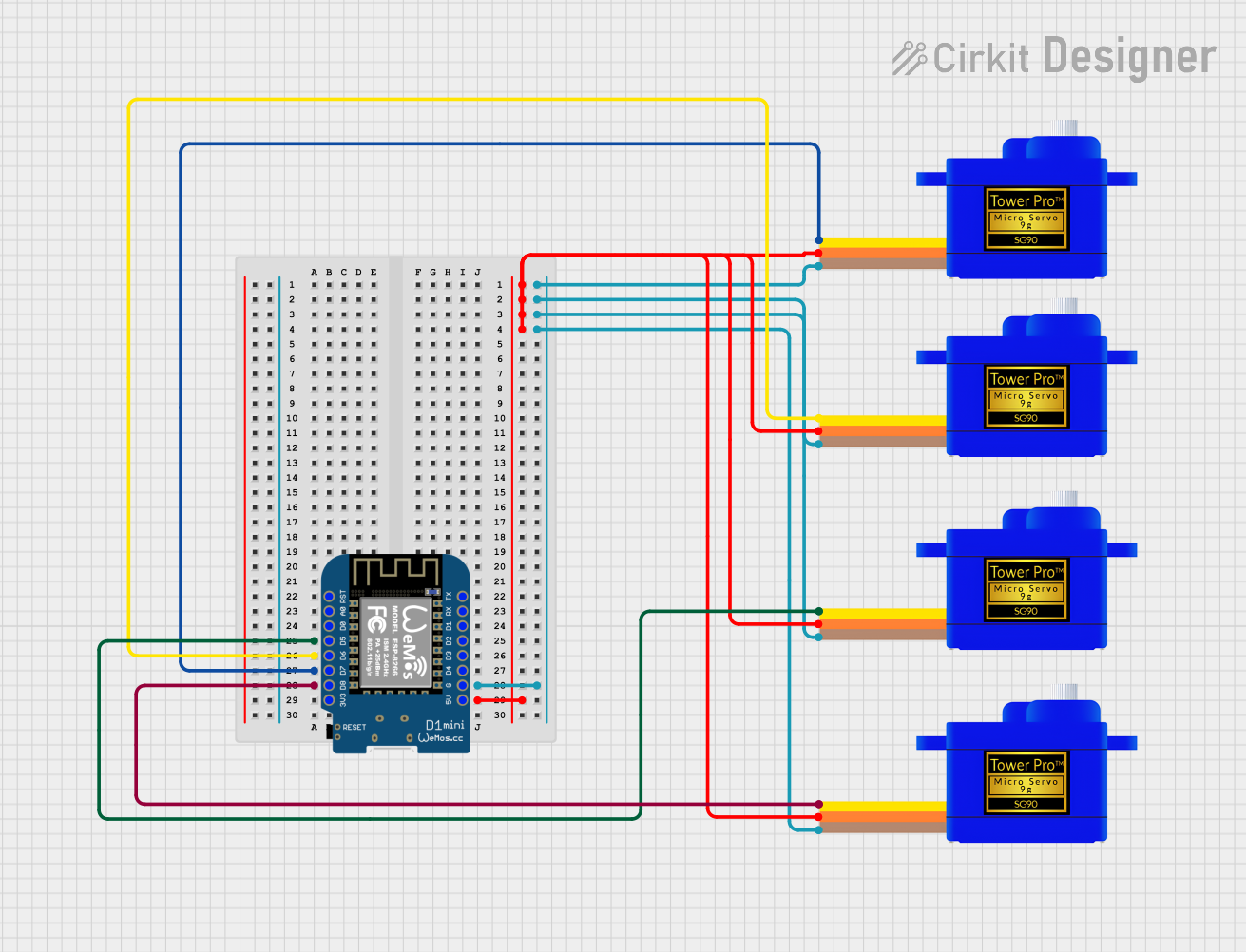
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer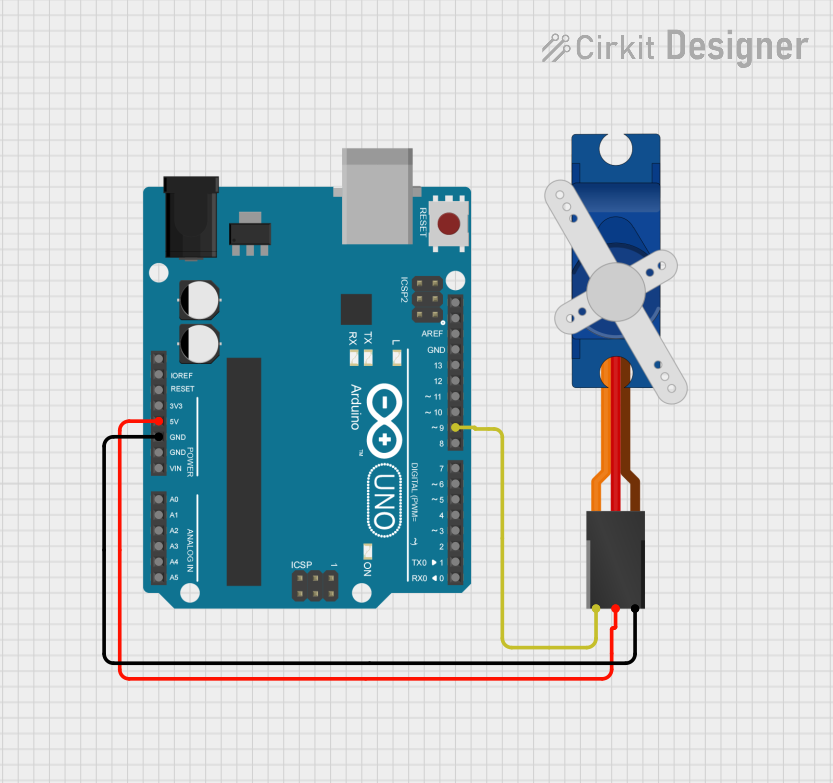
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer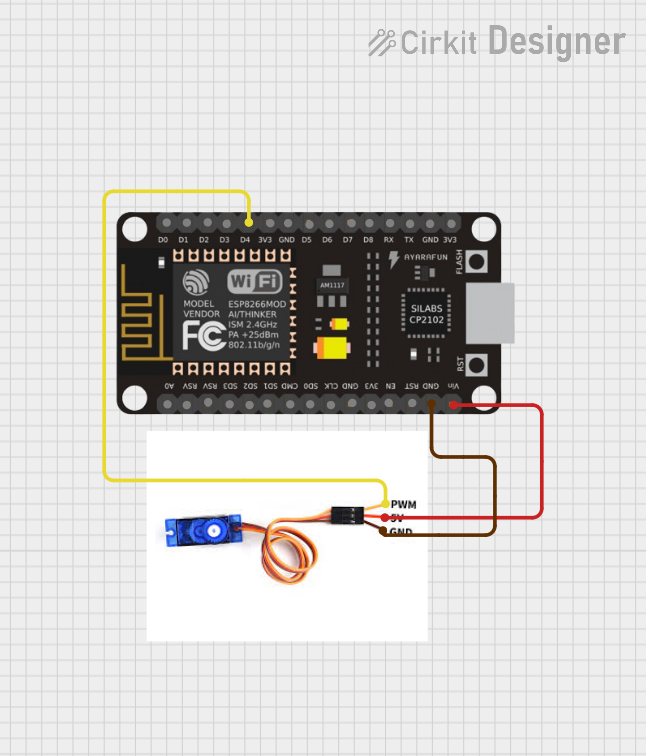
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer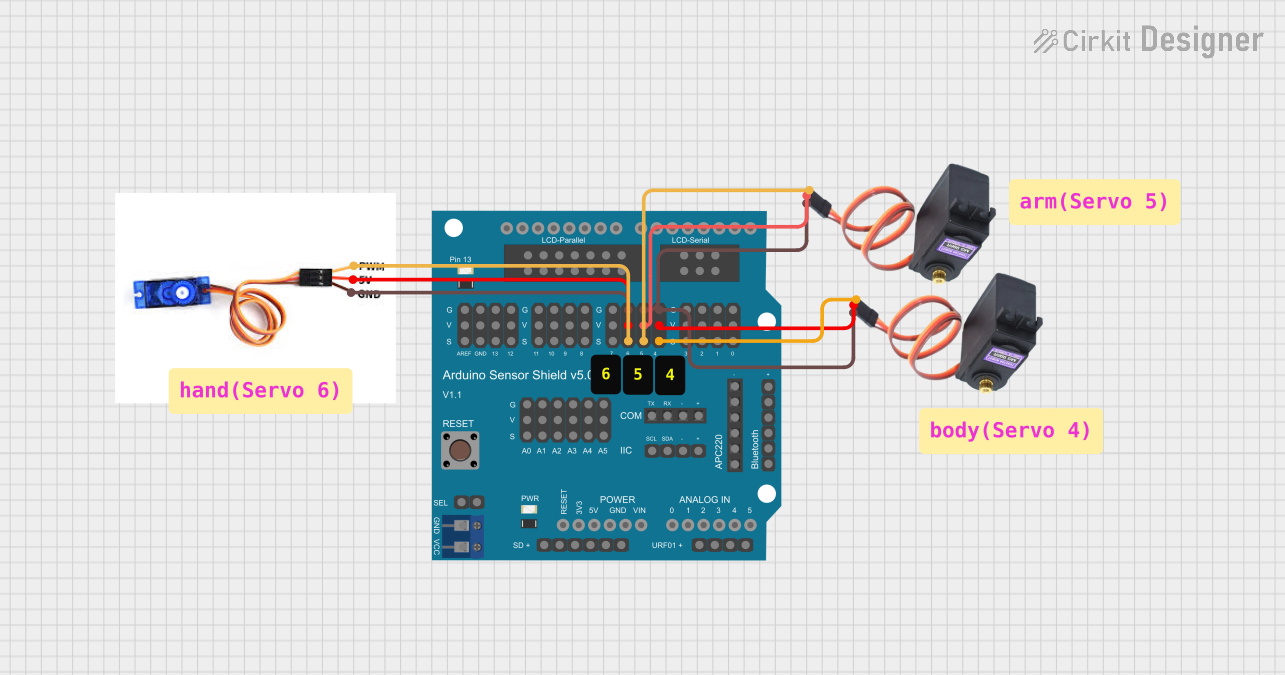
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Servo Motor (SG90)

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Robotics: Used for controlling the movement of robot arms, legs, and other parts.
- RC Vehicles: Employed in steering mechanisms and throttle control.
- DIY Projects: Ideal for creating automated systems, such as opening/closing doors, rotating cameras, and more.
- Educational Purposes: Great for teaching the basics of servo motors and control systems.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Specification | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 4.8V - 6.0V |
| Stall Torque | 1.8 kgf·cm (4.8V), 2.2 kgf·cm (6.0V) |
| Operating Speed | 0.1 s/60° (4.8V), 0.08 s/60° (6.0V) |
| Control Signal | PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) |
| Angle Range | 0° to 180° |
| Weight | 9g |
| Dimensions | 22.2mm x 11.8mm x 31mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground |
| 2 | VCC | Power Supply (4.8V - 6.0V) |
| 3 | Signal | PWM Signal Input for Position Control |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Power Connection:
- Connect the VCC pin of the SG90 to a 5V power supply.
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of the power supply.
Signal Connection:
- Connect the Signal pin to a PWM-capable output pin of a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino).
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Ensure that the power supply can provide sufficient current. The SG90 can draw significant current, especially under load.
- PWM Signal: Use a PWM signal with a frequency of 50Hz. The pulse width determines the angle of the servo.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not force the servo beyond its mechanical limits (0° to 180°) to prevent damage.
- Heat Management: Prolonged use under heavy load may cause the servo to heat up. Allow it to cool down periodically.
Example: Connecting SG90 to Arduino UNO
Circuit Diagram
Arduino UNO SG90 Servo Motor
----------------- -----------------
5V ----------------> VCC
GND ----------------> GND
Pin 9 --------------> Signal
Arduino Code Example
#include <Servo.h> // Include the Servo library
Servo myServo; // Create a Servo object
void setup() {
myServo.attach(9); // Attach the servo to pin 9
}
void loop() {
myServo.write(0); // Move to 0 degrees
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
myServo.write(90); // Move to 90 degrees
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
myServo.write(180); // Move to 180 degrees
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
Servo Not Moving:
- Solution: Check the power connections and ensure the PWM signal is correctly connected. Verify that the power supply provides sufficient current.
Servo Jittering:
- Solution: Ensure a stable power supply. Noise in the power line can cause jittering. Adding a capacitor across the power supply can help stabilize it.
Limited Range of Motion:
- Solution: Verify that the PWM signal is within the correct range (1ms to 2ms pulse width). Adjust the code to ensure the servo receives the correct pulse width.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the SG90 with a 3.3V microcontroller?
- A: The SG90 is designed for 4.8V to 6.0V operation. Using it with a 3.3V microcontroller may not provide reliable performance. Use a level shifter or a separate 5V power supply.
Q: How do I increase the torque of the SG90?
- A: The torque is determined by the design of the servo. To increase torque, consider using a servo with a higher torque rating.
Q: Can I control multiple SG90 servos with one Arduino?
- A: Yes, you can control multiple servos using different PWM-capable pins on the Arduino. Ensure the power supply can handle the combined current draw of all servos.
This documentation provides a comprehensive guide to understanding, using, and troubleshooting the SG90 Servo Motor. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced user, this guide aims to help you make the most of this versatile component.