
How to Use 8-channel-mux: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with 8-channel-mux in Cirkit Designer
Design with 8-channel-mux in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
An 8-channel multiplexer (mux) is a digital switching device that enables the selection of one input signal from up to eight available inputs and routes it to a single output line. The selection is controlled by a set of binary control signals. This component is widely used in applications such as data routing, signal processing, communication systems, and microcontroller-based projects.
Explore Projects Built with 8-channel-mux
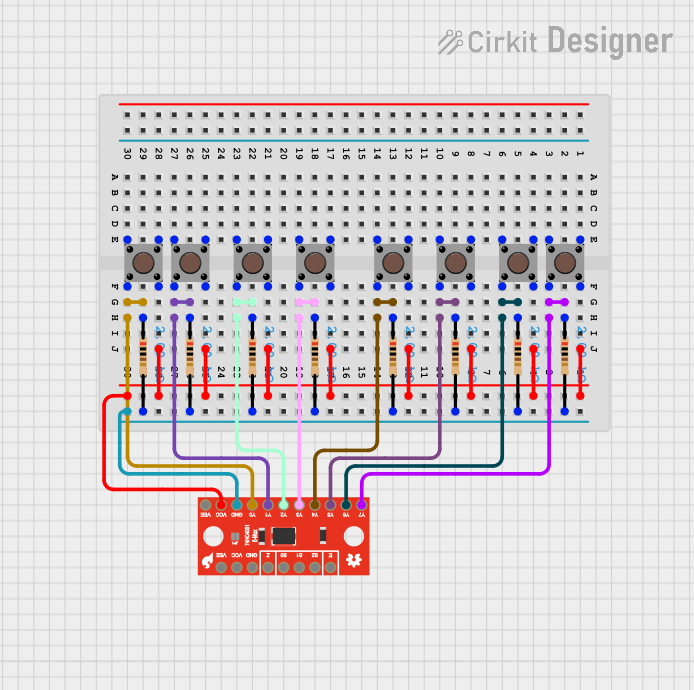
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer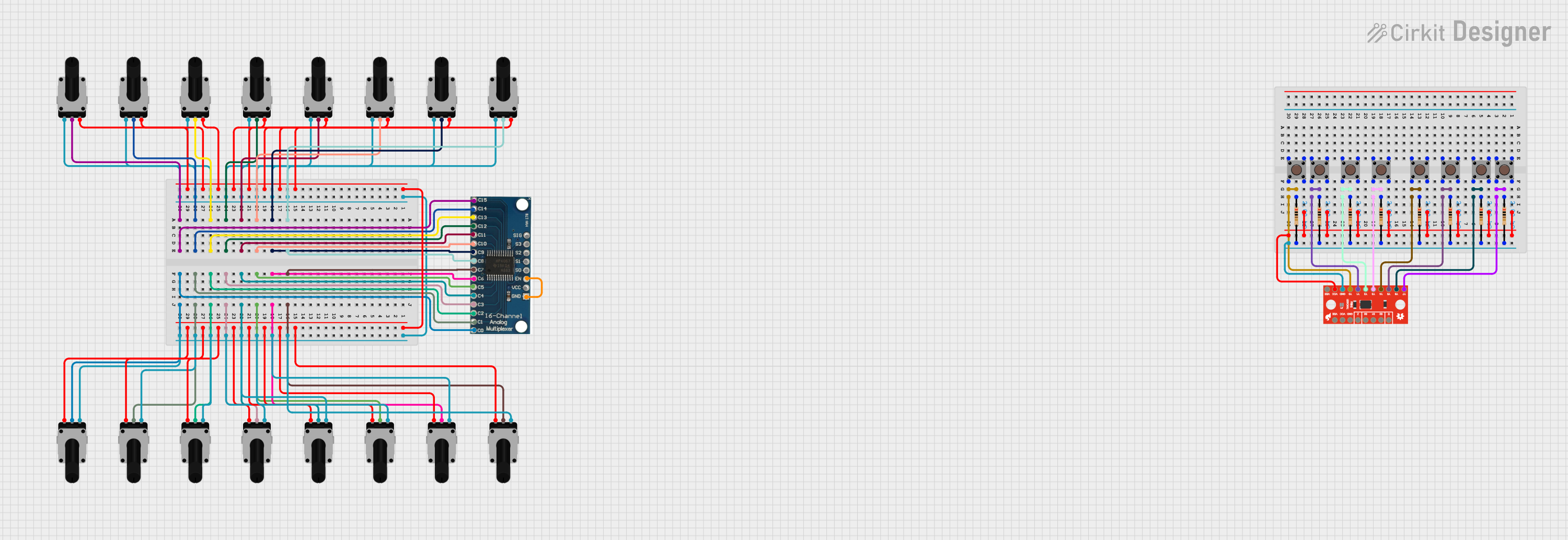
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer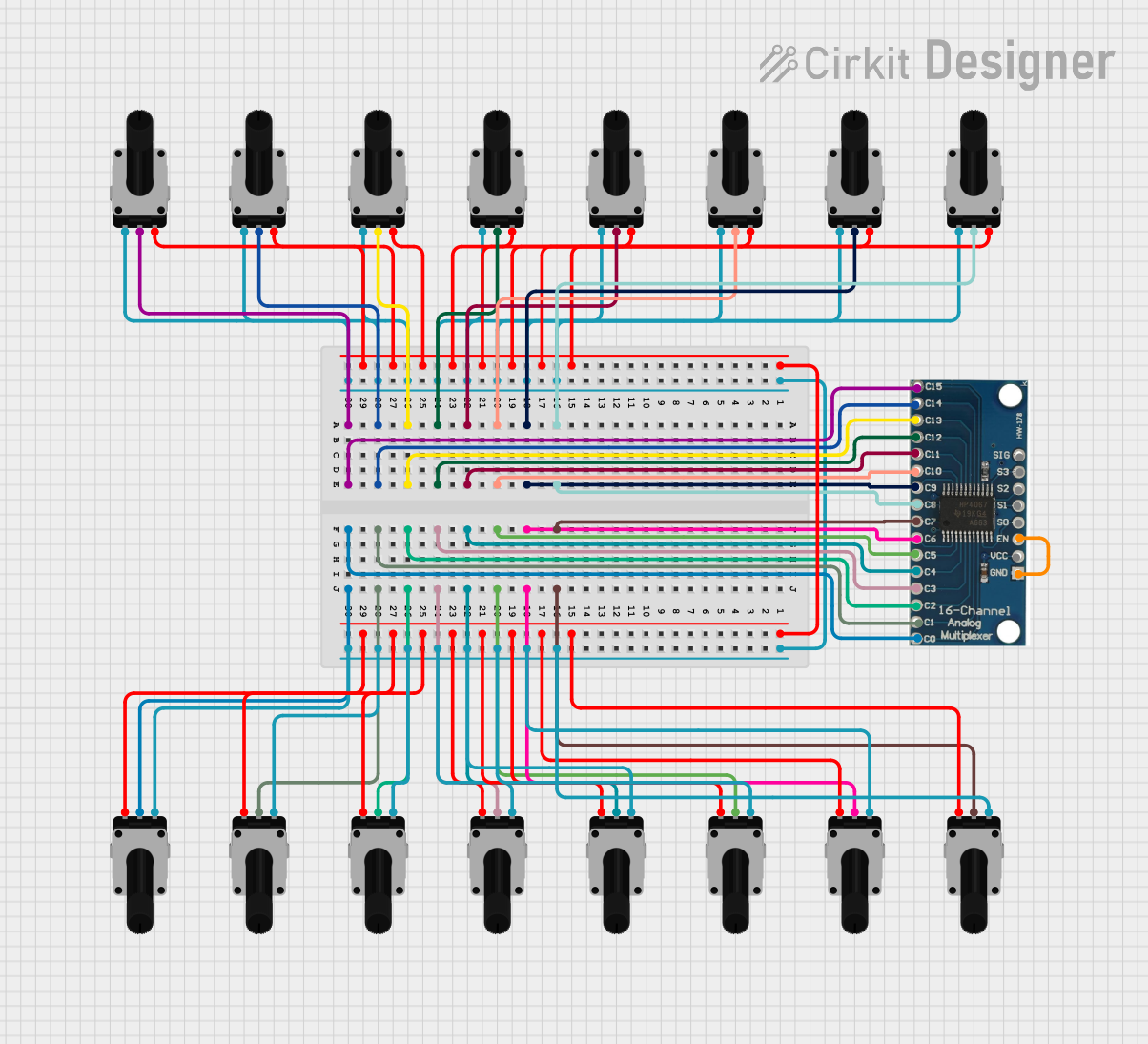
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer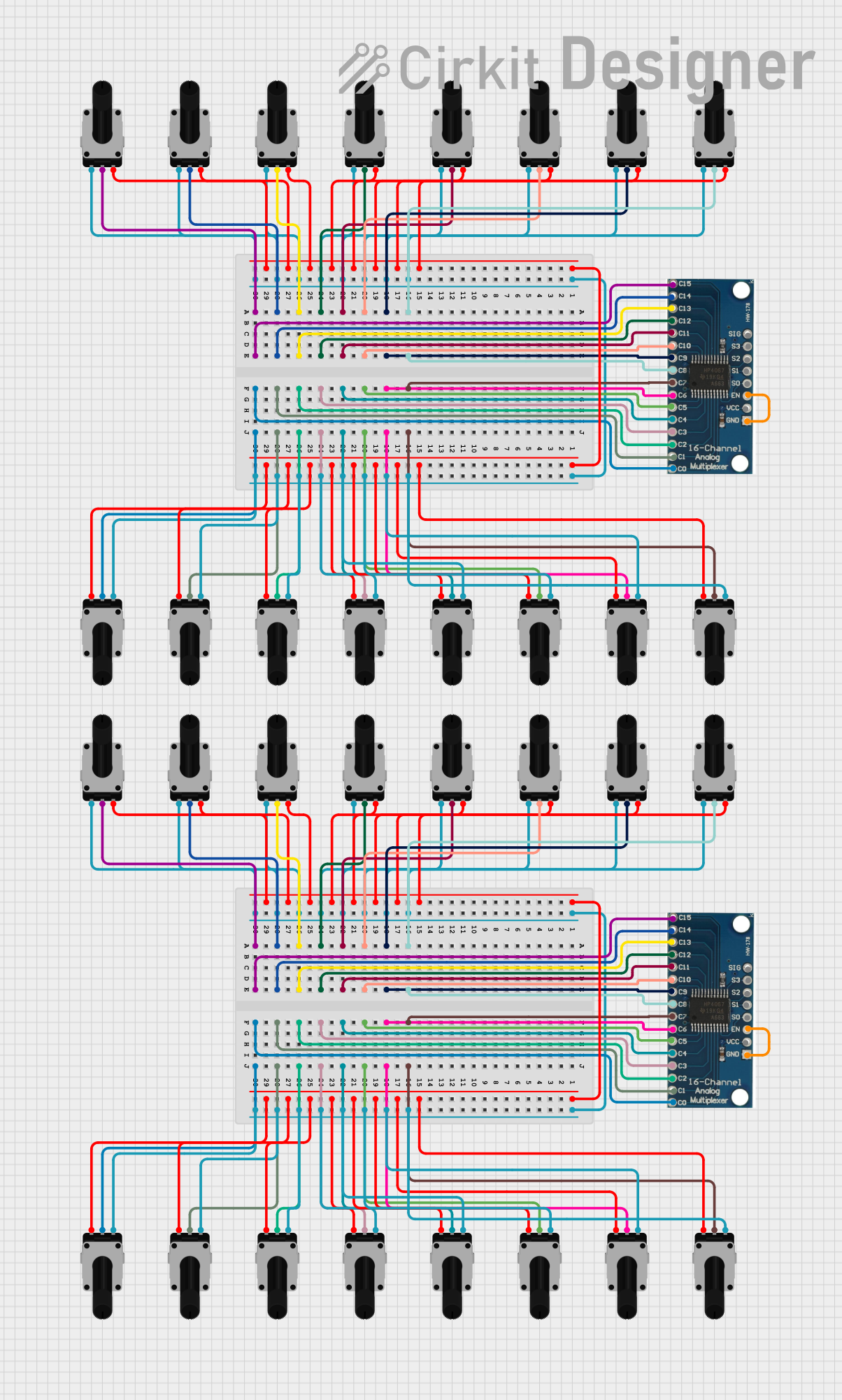
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 8-channel-mux

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Signal selection in microcontroller projects
- Data acquisition systems
- Communication systems for channel selection
- Expanding the number of input/output pins in microcontrollers
- Audio and video signal routing
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the 8-channel multiplexer:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | ARDUINO |
| Part ID | UNO |
| Number of Channels | 8 |
| Supply Voltage (Vcc) | 2V to 6V |
| Input Voltage Range | 0V to Vcc |
| Control Signal Levels | TTL/CMOS compatible |
| Propagation Delay | ~10ns to 50ns (varies by model) |
| Power Consumption | Low power (varies by usage) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The 8-channel mux typically has the following pin configuration:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | S0 | Control signal 0 (Least Significant Bit of the selection input) |
| 2 | S1 | Control signal 1 |
| 3 | S2 | Control signal 2 (Most Significant Bit of the selection input) |
| 4 | IN0 | Input channel 0 |
| 5 | IN1 | Input channel 1 |
| 6 | IN2 | Input channel 2 |
| 7 | IN3 | Input channel 3 |
| 8 | IN4 | Input channel 4 |
| 9 | IN5 | Input channel 5 |
| 10 | IN6 | Input channel 6 |
| 11 | IN7 | Input channel 7 |
| 12 | OUT | Output signal (selected input is routed here) |
| 13 | GND | Ground |
| 14 | Vcc | Supply voltage |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the 8-Channel Mux in a Circuit
- Power the Mux: Connect the
Vccpin to a suitable power supply (e.g., 5V for Arduino UNO) and theGNDpin to ground. - Connect Input Signals: Attach up to eight input signals to the
IN0toIN7pins. - Control Signal Setup: Use three control pins (
S0,S1,S2) to select the desired input channel. The binary combination of these pins determines which input is routed to the output. - Output Connection: Connect the
OUTpin to the desired destination (e.g., an ADC pin on a microcontroller). - Control Logic: Use a microcontroller or external logic to set the control signals (
S0,S1,S2) based on the desired input channel.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure the input voltage levels are within the specified range (0V to Vcc).
- Use pull-down resistors on control pins if they are left floating to avoid unpredictable behavior.
- Minimize noise by keeping signal lines short and using decoupling capacitors near the power supply pins.
- Verify the propagation delay of the mux to ensure it meets the timing requirements of your application.
Example: Connecting the 8-Channel Mux to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect and control the 8-channel mux using an Arduino UNO:
Circuit Connections
- Connect
Vccto the 5V pin on the Arduino UNO. - Connect
GNDto the GND pin on the Arduino UNO. - Connect
S0,S1, andS2to digital pins 2, 3, and 4 on the Arduino UNO, respectively. - Connect
OUTto the A0 (analog input) pin on the Arduino UNO. - Connect input signals to
IN0throughIN7.
Arduino Code Example
// Define control pins for the 8-channel mux
const int S0 = 2; // Control signal 0
const int S1 = 3; // Control signal 1
const int S2 = 4; // Control signal 2
// Define the output pin of the mux
const int MUX_OUT = A0; // Analog input pin on Arduino
void setup() {
// Set control pins as outputs
pinMode(S0, OUTPUT);
pinMode(S1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(S2, OUTPUT);
// Initialize serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
for (int channel = 0; channel < 8; channel++) {
// Set the control pins to select the desired channel
digitalWrite(S0, channel & 0x01); // Least significant bit
digitalWrite(S1, (channel >> 1) & 0x01); // Second bit
digitalWrite(S2, (channel >> 2) & 0x01); // Most significant bit
// Read the selected input signal
int signalValue = analogRead(MUX_OUT);
// Print the channel number and signal value to the serial monitor
Serial.print("Channel ");
Serial.print(channel);
Serial.print(": ");
Serial.println(signalValue);
// Wait for a short period before switching to the next channel
delay(500);
}
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Signal:
- Verify that the
VccandGNDpins are properly connected. - Check the control signal connections and ensure they are set correctly.
- Ensure the input signal is within the specified voltage range.
- Verify that the
Unstable or Noisy Output:
- Use decoupling capacitors near the power supply pins to reduce noise.
- Keep signal lines as short as possible to minimize interference.
Incorrect Channel Selection:
- Double-check the binary values sent to the control pins (
S0,S1,S2). - Ensure the control pins are not left floating; use pull-down resistors if necessary.
- Double-check the binary values sent to the control pins (
FAQs
Q: Can I use the 8-channel mux with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, the mux supports a supply voltage range of 2V to 6V. Ensure the input signals and control signals are within the 3.3V logic level.
Q: What happens if multiple input channels are active simultaneously?
A: The mux will only route the input corresponding to the binary value of the control signals. Other inputs will be ignored.
Q: Can the mux handle analog signals?
A: Yes, the mux can route analog signals as long as they are within the specified voltage range (0V to Vcc).