
How to Use Sound Sensor: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
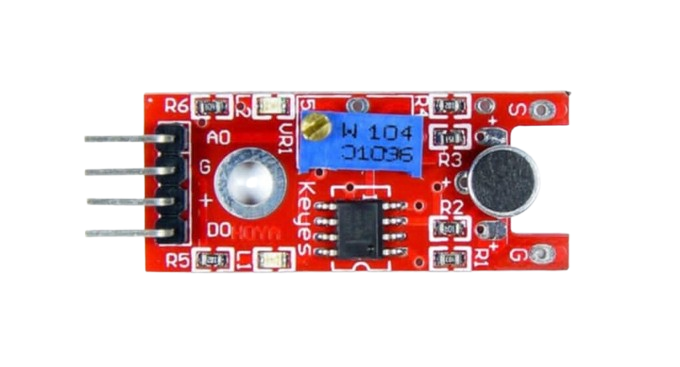
 Design with Sound Sensor in Cirkit Designer
Design with Sound Sensor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Sound Sensor is a device designed to detect sound levels and convert them into electrical signals. It typically consists of a microphone, an amplifier, and a signal processing circuit. This component is widely used in applications such as voice recognition systems, noise monitoring, and interactive projects like sound-activated lighting or robotics.
Common use cases include:
- Detecting claps or voice commands in smart home systems.
- Monitoring environmental noise levels.
- Enabling sound-based interaction in Arduino or Raspberry Pi projects.
Explore Projects Built with Sound Sensor
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer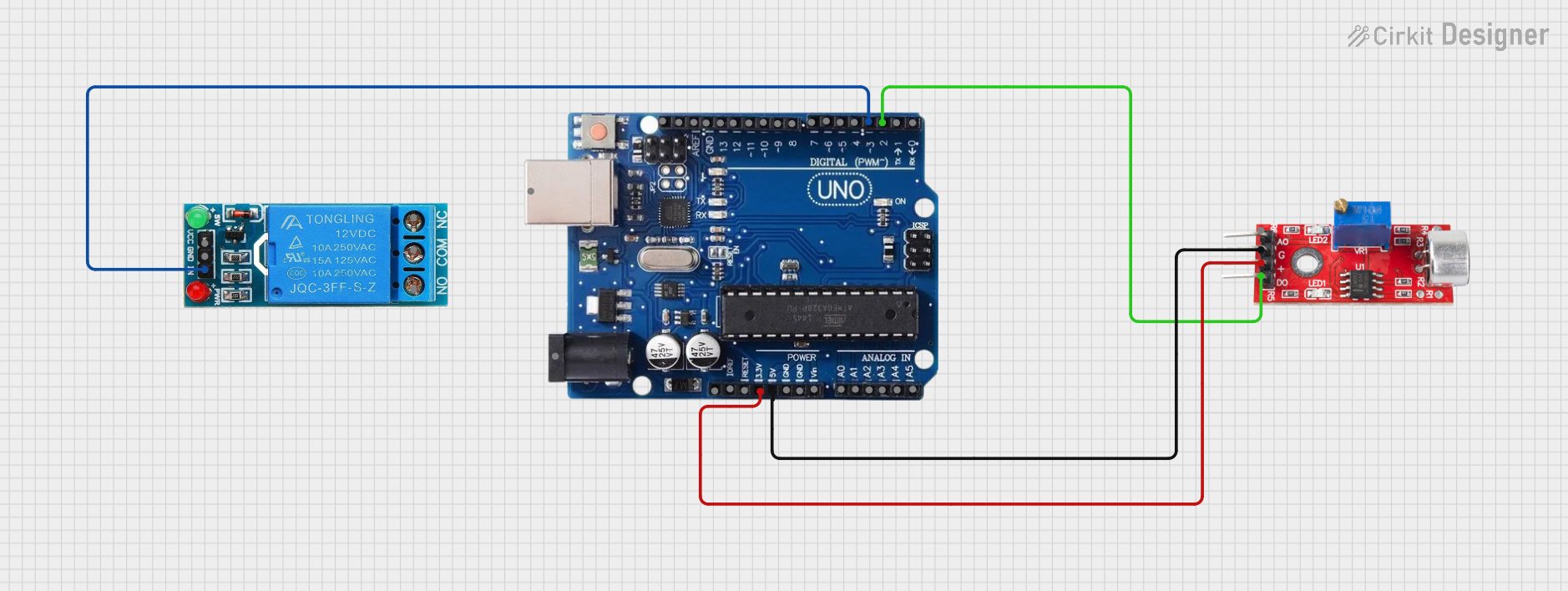
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Sound Sensor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of a typical sound sensor module:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V to 5V |
| Output Type | Analog and Digital |
| Sensitivity Adjustment | Potentiometer (onboard) |
| Microphone Type | Electret Condenser Microphone |
| Dimensions | ~32mm x 15mm x 8mm |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power supply pin (3.3V to 5V). Connect to the positive terminal of the power source. |
| GND | Ground pin. Connect to the ground of the circuit. |
| A0 | Analog output pin. Outputs a voltage proportional to the detected sound level. |
| D0 | Digital output pin. Outputs HIGH or LOW based on the sound threshold set via the potentiometer. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Sound Sensor in a Circuit
- Power the Sensor: Connect the
VCCpin to a 3.3V or 5V power source and theGNDpin to the ground. - Choose Output Type:
- Use the
A0pin for analog output to measure varying sound levels. - Use the
D0pin for digital output to detect sound above a set threshold.
- Use the
- Adjust Sensitivity: Use the onboard potentiometer to set the sensitivity for the digital output. Turning the potentiometer clockwise increases sensitivity.
- Connect to a Microcontroller: For example, connect the
A0orD0pin to an analog or digital input pin on an Arduino UNO.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the sound sensor with an Arduino UNO to read both analog and digital outputs.
Circuit Connections
VCC→ 5V on ArduinoGND→ GND on ArduinoA0→ A0 on Arduino (for analog output)D0→ D2 on Arduino (for digital output)
Arduino Code
// Sound Sensor Example Code
// Reads analog and digital outputs from the sound sensor and prints the values.
const int analogPin = A0; // Pin connected to the analog output (A0)
const int digitalPin = 2; // Pin connected to the digital output (D0)
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
pinMode(digitalPin, INPUT); // Set digital pin as input
}
void loop() {
int analogValue = analogRead(analogPin); // Read analog value from A0
int digitalValue = digitalRead(digitalPin); // Read digital value from D0
// Print the values to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Analog Value: ");
Serial.print(analogValue);
Serial.print(" | Digital Value: ");
Serial.println(digitalValue);
delay(500); // Wait for 500ms before the next reading
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Ensure the sensor is powered within its operating voltage range (3.3V to 5V).
- Noise Interference: Avoid placing the sensor near high-frequency noise sources, as this may affect its accuracy.
- Sensitivity Adjustment: Fine-tune the potentiometer to achieve the desired sensitivity for your application.
- Signal Stability: Use capacitors or filters if the analog output signal is too noisy for your application.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output from the Sensor:
- Check the power connections to ensure the sensor is receiving the correct voltage.
- Verify that the ground connection is secure.
Digital Output Always HIGH or LOW:
- Adjust the potentiometer to set an appropriate sound threshold.
- Ensure the sound level in the environment is within the sensor's detection range.
Analog Output is Unstable:
- Use a capacitor across the analog output pin and ground to filter noise.
- Ensure the sensor is not exposed to excessive vibrations or electrical interference.
Sensor Not Responding to Sound:
- Confirm that the microphone is not obstructed or damaged.
- Test the sensor in a quieter environment to rule out background noise interference.
FAQs
Q: Can the sound sensor detect specific frequencies?
A: No, the sound sensor is designed to detect overall sound levels and cannot differentiate between specific frequencies.
Q: How do I increase the detection range of the sensor?
A: You can increase the sensitivity by adjusting the potentiometer, but note that this may also make the sensor more prone to noise.
Q: Can I use the sound sensor outdoors?
A: While the sensor can operate in a wide temperature range, it is not waterproof. Use a protective enclosure if deploying it outdoors.
Q: What is the difference between the analog and digital outputs?
A: The analog output provides a continuous voltage proportional to the sound level, while the digital output provides a HIGH or LOW signal based on the set threshold.